latest
“Traditionalism: The Radical Project for Restoring Sacred Order”, by Mark Sedgwick (Book Review)
In 2014, speaking via Skype to a conference held at the Vatican, Donald Trump’s later advisor, Steve Bannon, casually mentioned Julius Evola (1898-1974), a thinker little known outside Italy, and who even within Italy was conventionally dismissed as a former Fascist whose writings still exerted a pernicious influence on the ’far right’. When that comment was unearthed by the US media in 2016, it sparked a furore amongst those desperate to discredit Trump as a danger to democracy. It also drew mainstream attention to a strange and possibly wide-reaching philosophy.
Evola’s Fascist sympathies went much deeper than anti-communist or nationalist sentiment, being rooted at least partly in a colourful and irrational worldview referred to by some authors (although not Evola) as ‘Traditionalism’. Through him, Bannon, and so by extension Trump, were potentially ‘linked’ to much broader intellectual currents, with connections across everything from the abstractest metaphysics to the earthiest ecologism.
There existed, obscure but important scholars had long argued, a mystical ‘perennial philosophy’ of transcendent religiosity and social stratification that was simultaneously as ancient as origin myths and applicable to modern discontents. Over the centuries, this concept has attracted intellectuals as diverse as the 15th century humanist Giovanni Pico della Mirandola, and Brave New World author Aldous Huxley. Other than Evola, its best-known and most systematic modern exponents were two metaphysicians, the Frenchman René Guénon (1886-1951), and the Swiss Frithjof Schuon (1907-1998), who issued writings and launched initiatives that channeled underlying cultural gloom, and still resonate powerfully. Like Evola, Guénon did not use the term Traditionalism, but his writings are regarded as key texts.
As well as Bannon, ‘Traditionalist’ sympathies of some kind were avowed by, or detectable in, influencers outside America – Hungarian politician Gábor Vona, the Russian ideologue Aleksandr Dugin (whom Bannon met in 2018, and who was supposedly an influence on Putin), and the Brazilian writer, Olavo de Carvalho, credited with helping Jair Bolsonaro win the presidency in 2019. Beyond politics, the connections were even more diffuse, with well-known academics, artists and even King Charles III (when Prince of Wales), articulating Traditionalist tropes to combat anomie and materialism, and promote organic agriculture, small-scale economics, traditional arts, and interfaith dialogue. But did all these different things have anything in common other than root-and-branch discontent with a drably dispiriting status quo? What possible relevance could Traditionalists’ distaste for democracy, and even politics, have for determinedly populist politicians?
This is a long-standing area of interest for Oxford-educated Arabist, Mark Sedgwick, now professor of Arab and Islamic Studies at Aarhus University. His 2003 book, Against the Modern World: Traditionalism and the Secret Intellectual History of the Twentieth Century, was the first to draw mainstream attention to Evola, Guénon, Schuon, and others dubbed or self-described as Traditionalists. He brings to this discussion special insight into Islamic influences on Traditionalism, from the inner ecstasies of Sufism to the academically distinguished elucubrations of the contemporary Iranian-American theologian, Seyyed Hossein Nasr. Along the way, he treats ably and interestingly of many subjects, from Hindu ideas about caste via 17th century theories of history to the trajectory of Western feminism, and analyses the influence of Jordan Peterson, whom he regards as a Traditionalist for the internet age.
Traditionalism is a catch-all sort of term, and its outcomes are so diverse it is difficult to discern much consistency at all. Had it not been for Bannon’s remark, it is hard to imagine many even noticing Traditionalism existed. Conceptual complexity could help account for Traditionalism’s apparent ascent; as the author notes, “That which is not easy to understand is not easy to deny”. Sedgwick also suggests that Guénon’s theories may be fundamentally flawed because based on early 20th century understandings of ‘the East’ which are now regarded as too colourful and generic, even condescendingly ‘Orientalist’. Evola’s more dynamic and Western-oriented variant is likewise a product of its time, suffused with Nietzschean contempt for Christianity, and the epochal pessimism of thinkers like Oswald Spengler (even though he criticized both). Sedgwick nevertheless treats it as a coherent corpus of thought, with much relevance for today.
The central element of all variants of Traditionalism is ‘perennialism’ – the notion that beneath all the exoteric differences of world religions there is a unifying ‘sacred order’ understood only by the deepest thinkers, although hazily intuitable by the masses, if only they can be detached from the trammels of modernity. This is not just a tradition, but the Tradition that unlocks all cosmologies, and renders the most impassioned theological and political disputes not just superficial, but almost risible. Traditionalist writings are predictably esoteric, aimed solely at a supposedly more spiritually attuned elite.
Traditionalists tend to be greatly interested in such things as hermetic philosophy, occultism, shamanism, and symbolism, and believe strongly in what the ethnomusicologist Benjamin R. Teitelbaum called “spiritual mobility” (see his 2020 book, War for Eternity). They regard 21st century preoccupations like equality, gender politics, individualism, material progress, and technology as mere aspects of modernity, harmful or simply inconsequential.
The second ingredient is a belief in cosmic circularity, as opposed to the ideas of inevitable linearity inherent in mainstream Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, and so throughout modern politics. The world, in this reading, goes through ‘ages’ of decline that can be followed by renewal. An original golden age of unity and quality is ineluctably succeeded by silver, bronze and ultimately dark ages of increasingly mechanistic reductionism – what Guénon memorably called the “age of quantity” – after which the cosmic wheel turns back to the start.
‘Golden Age’ thinking is common to many civilizations, but there are especially close parallels with the four ages (Yugas) of Hinduism, with ‘Kali Yuga’ (the last, sin-filled age of conflict) a shorthand term for today among ‘Aryan’-interested Rightists. This process is almost irrespective of politics, although some theorists see an expeditious role for ‘disruptors’. Evola saw Fascism as a means of reconstituting the Roman Empire, and Bannon saw (and perhaps still sees) Trump as a kind of creative destroyer of consensus, but politics has been a lower priority for other Traditionalists, who concentrated instead on transformation through self-realization.
It may easily be imagined that Traditionalists are prone to eccentricity; for instance, Evola believed that ‘Aryans’ were descended from an ethereal Arctic race which had decayed as they came south. In the 1980s, a writer calling herself “Alice Lucy Trent” officiated in County Donegal over a small community called the Silver Sisterhood, which worshipped a female deity, sported Victorian clothing, and refused to use electricity. Trent later changed her name to “Miss Martindale”, and moved to Oxford, to found a movement called Aristasia in a modest terraced house, where ambiguous persons wearing dresses and veils would hold ultra-reactionary court in a candle-lit, gramophone-sounding interior, and be seen driving around town majestically in a 1950s car. It was part-pantomime, part-serious critique, at once amusing and interesting.
Sedgwick rues some Rightists’ co-option of some parts of Traditionalism. Indeed, perennialism can be hard to square with ideas about a “clash of civilizations”, or immigration, or belief in physical racial differences (which even Evola downplayed). He nevertheless examines their thinking with commendable fairness. He differentiates between genuinely traditional teachings about religion and society, which really can be millennia old, and 1920s-to-present-day attempts to turn some of these teachings into realities. For Sedgwick, whatever about the youthful Evola, by his late period he had become a “non-traditional Traditionalist”, and the Evolan phraseology deployed by some on today’s radical Right is therefore mostly “post-Traditionalism”.
But logical consistency matters little in politics, even metapolitics. Traditionalism may persist as a presence on the Right, if sometimes more symbolically than as substance. Traditionalists’ emphasis on arcane knowledge is intrinsically appealing to some who aspire to be elite leaders. There are also similarities in outlooks and temperaments between Traditionalists and some Rightists – shared perspectives on the manifold problems of modernity, shared detestation of bleak materialism, and shared love of grand and sweeping narratives. As the once world-bestriding West shivers in winnowing new winds, and mainstream conservatism flounders, the epic appeal of a mythical past (and implied enchanted future) seems likely to grow. Sedgwick’s second book on this too long neglected theme makes another significant contribution to what may be an expanding as well as evolving field.
Book Details: Mark Sedgwick, London: Pelican, 2023, hb., 410pps., £25
My thanks to John Morgan for invaluable input on this article.
Barbie, Oppenheimer and Blue Sky Research
Barbie or Oppenheimer? Two words you would have never considered putting together in a sentence. For the biggest summer blockbuster showdown in decades, the memes write themselves.
In recent months (and years!), we’ve seen flop after flop, such as the new Indiana Jones and Flash films, with endless CGI superheroes and the merciless rehashing of recognised brands. The inability for film studies to recognise and attempt anything new has only led to the continued damage of established and respected franchises.
This in part is due a decline in film studios being willing to take risks over new pieces of intellectual property (something the Studio A24 has excelled in), and a retreat into a ‘culturally bureaucratic’ system that neither rewards art nor generates anything vaguely new, preferring to reward conscientious proceduralism.
Given this, there has been widespread speculation that films like Oppenheimer will ‘save’ cinema, with Christopher Nolan’s biographical adventure, based on the book ‘American Prometheus’ (would highly recommend), being highly awaited and regarded.
Although, I suspect cinema is too far gone from saving in its current format. I do believe that Oppenheimer will have long term cultural effects, which should be recognised and welcomed by everyone.
In the past, there have been many films that, when made and consumed, have directly changed how we view topics and issues. Jaws gave generations of people a newfound fear of sharks, while the Shawshank Redemption provided many with the Platonic form of hope and salvation. I hope that Oppenheimer can and will become a film like this, because of what Robert Oppenheimer’s life (and by extension the Manhattan Project itself) represented.
As such, two things should come out of this film and re-enter the cultural sphere, filtering back down into our collective fears and dreams. Firstly, is it that of existential fear from nuclear war (very pressing considering the Russo-Ukrainian War) and what this means for us as species.
Secondly, is that of Blue-Sky Research (BSR) and the power of problem solving. Although the Manhattan project was not a ‘true’ example of BSR, it helped set the benchmark for science going forward.
Both factors should return to our collective consciousness, in our professional and private lives; they can only benefit us going forward.
I would encourage everyone to go out tonight and look at the night sky and say to yourself while looking at the stars: “this goes on for forever”. In the same breath, look to the horizon and think to yourself: “This can end at any moment. We have the power to do all of this”.
Before watching Oppenheimer, I would highly encourage you to watch the ‘Charlie Dean Archives’ and the footage of atomic bombs from 1959. Not only is the footage astounding, multiple generations have lived in fear of the invention; the idea and the consequences of the bomb have disturbed humans as long as it has existed.
Films like Threads in Britain played a similar role, which entered the unconscious, and films like Barefoot Gen for Japan (this film is quite notorious and controversial, but a must watch) did the same, presenting the real-world effects of nuclear war through the eyes of young children and the fear it invokes.
In recent years, we have seemingly lost this fear. Indeed, we continue to overlook the fact this could all be over so quickly. We have forgotten or chosen to ignore the simple fact that we are closer than ever before to the end of the world.
The pro-war lobby within the West have continually played fast and loose with this fact, to the point we find ourselves playing Russian roulette with an ever-decreasing number of chambers in our guns.
In the past, we have narrowly avoided nuclear conflict several times, and it has been mostly a question of luck as to whether we avoid the apocalypse. The downside of all this is that any usage of the word ‘nuclear’ is now filled with images of death and destruction, which is a shame because nuclear energy could be our salvation in so many ways.
Additionally, we need to remember what fear is as a civilisation; fear in its most existential form. We have become too indebted to the belief that civilisation is permanent. We assume that this world and our society will always be here, when the reality is that all of it could be wiped out within a generation.
As dark as this sounds, we need bad things to happen, so that we can understand and appreciate the good that we do have, and so that good things might occur in the future. Car crashes need to happen, so we can learn to appreciate why we have seatbelts. We need people to remember why we fear things to ensure we do everything in our power to avoid such things from ever happening again.
Oppenheimer knew and understood this. Contrary to the memes, he knew what he had created and it haunted him till the end of his days. Oppenheimer mirrors Alfred Nobel and his invention of dynamite, albeit burdened with a far greater sense of dread.
I hope that with the release of Oppenheimer, we can truly begin to go back to understanding what nuclear weapons (and nuclear war) mean for us as a species. The fear that everything that has ever been built and conceived could be annihilated in one act.
We have become the gods of old; we can cause the earth to quake and great floods to occur and we must accept the responsibility that comes with this power now. We need to fear this power once more, especially our pathetic excuse for leadership.
In addition to fear, Oppenheimer will (hopefully) reintroduce BSR into our cultural zeitgeist – the noble quest of discovery and research. BSR can be defined as research without a clearly defined goal or immediately apparent real-world applications.
As I mentioned earlier, whilst the Manhattan project was not a pure example of BSR, it gave scientists more freedom to pursue long-term “high risk, high reward” research, leading to a very significant breakthrough.
We need to understand the power of BSR. Moving forward, we must utilise its benefits to craft solutions to our major problems.
I would encourage everyone to read two pieces by Vannevar Bush. One is ‘Science the Endless Frontier’, a government report, and ‘As we may think’, an essay.
In both pieces, he makes a good argument for re-examining how we understand scientific development and research and calls for governmental support in such research. Ultimately, Bush’s work led to the creation of the National Science Foundation.
For research and development, government support played a vital role in managing to successfully create nuclear weapons before either the Germans or Japanese and their respective programs.
I believe it was Eric Weinstein who stated that the Manhattan project was not really a physics but rather an engineering achievement. Without taking away from the work of the theorists who worked on the project. I would argue that Weinstein is largely correct. However, I argue that it was a governmental (or ‘human’ achievement), alongside the phenomenal work of various government-supported experimentalists.
The success of the Manhattan Project was built on several core conditions. Firstly, there was a major drive by a small group of highly intelligent and functional people that launched the project (a start-up mentality). Secondly, full government support, to achieve a particular goal. Thirdly, the near-unlimited resources afforded to the project by the government. Fourthly, complete concentration of the best minds onto a singular project.
These conditions mirror a lot of the tenets of BSR: placing great emphasis on government support, unlimited resources and manpower and complete concentration on achieving a specific target. Under these conditions, we can see what great science looks like and how we can possibly go back to achieving it.
Christopher Nolan has slightly over three hours to see if he can continue to make his mark on cinema and leave more than a respectable filmography in its wake. If he does, let’s hope it redirects our culture away from merely good science, and back towards the pursuit of great civilisational achievements – something always involved, as a man with a blog once said: “weirdos and misfits with odd skills”.
A Scotsman with a Grievance?
Nigel Farage was, somewhat predictably, booed when he was named News Presenter of the Year at the 2023 TRIC Awards in London. The manipulability of online polls in the age of loyally mischievous Twitter followings notwithstanding, the two GB News victories (its breakfast show scooped one too) arguably represent another milestone in the plucky challenger’s march to credibility and, its viewers will hope for its commercial success.
When GB News launched in July 2021, I was living in the US and working on my second or third startup, depending on whether you only count the successful ones. I watched the go-live and for me the highlight of those initial hours of sometimes painful broadcasting (notable by the curiously low lighting) was veteran newsman Andrew Neil, whose presence lent the nascent broadcaster some grown-up editorial clout.
Personally, I like Neil, and in common with many others was optimistic when in 2020 he was lured from the stagnant BBC to become GB News’ founding chairman. As such, I was sad when, a few months later, he appeared to have flounced off – particularly as it gave the station’s detractors something to gloat about (many of whom seemed to have made up their minds before a single second of TV was broadcast, not least The Guardian’s perennial sideline sniper Owen Jones).
Yet my main regret about Neil’s departure was its manner: specifically, that he didn’t do it with dignity and discretion. Founders split all the time and there are always sensible reasons why. During the early stage of any venture there’s a vast amount of work to do, and it’s in this mad scramble that working relationships are tested. Not all will survive.
Sometimes it’s nothing to do with the individuals, but more the chemistry of a group under pressure. Yet the thing to avoid, in almost any situation, is to make a fuss upon leaving. However great the temptation may be to ‘set the record straight’, it almost always comes across as whiney.
I’ve yet to meet anyone who, years later, will say: “absolutely the right thing was to share a bunch of private stuff in public and stick the knife into my former colleagues”. Candidly, I imagine that Neil now regrets how he handled the split.
Imagine the counterfactual: Neil still left, but instead of throwing his toys out of the pram he settled on a cheerier statement along the lines of: “What a ride! Successfully launching a news station has felt like my biggest achievement to-date. Now we’ve gone live, I’m hankering for a break and will be scaling back my commitments starting immediately. I’d like to thank the team for the immense amount of valiant work to-date, particularly in the hard months leading up to launch, and I’m confident that the Board and management team will successfully steer the station to greatness going forward! I wish everyone the best of luck and will be with you, in spirit, every step of the way. I look forward to reporting on the channel’s success!”
Had he done so, perhaps he’d now be fondly (and rightly) remembered as a co-founder of a bold enterprise – rather than simply a disgruntled former employee who left on bad terms and did a media round to share his grievances, including an opportunistic appearance on his former employer’s programme, Question Time.
Water passes quickly under any bridge, and I’m surprised that Neil, with all his experience, either didn’t know this or ignored his better judgement. The momentary satisfaction one gains from a bout of bridge-burning is almost always outweighed – many times over – by the future ability to gather with former colleagues, on good terms, and share in the celebration of success while laughing about the often funny (and, in hindsight, trivial) disagreements that occurred along the way.
I suspect the wise warhorse Neil’s advice to anyone else might be similar to my own: always keep the bridge intact, however tempting the alternative may be in the short run. I’ve no idea whether he has sent any of the GB News executives a congratulatory message over the last couple of years, but for his sake I hope he has.
To quote PG Wodehouse, “It is never difficult to distinguish between a Scotsman with a grievance and a ray of sunshine” – and endearingly curmudgeonly Neil appears to be no exception.
A rapprochement with his former startup would surely earn him renewed respect in the eyes of his many admirers. Perhaps he could appear as a guest on News Presenter of the Year Farage’s show? A display of convivial bonhomie on, say, Talking Pints would surely put to rest any accusations that a certain esteemed Scot is harboring a grievance.
The Exhibition (Review)
Much of the British right occupies itself with complaining about the dismal state of things. This does not lack all merit, but everyone with a functioning mind should understand by now that highlighting the ‘hypocrisy’ of political opponents or bleating about the latest manifestations of madness will change nothing. Then there are those of a more enterprising sort, predominantly North Americans, who turn political frustrations into a business opportunity by selling products solely on the basis that they are not from whichever socially liberal company riled them up. This also achieves very little in the grand scheme of things and portrays a right that is incapable of articulating an independent vision of the world.
Now we have an alternative in The Exhibition, an opening salvo from a group of artists who desire a culture which energises and inspires once again. Here was no place for coordinated agitprop, self-loathing or any of the other trends which make contemporary art so entropic and tiresome. Instead, the walls and pedestals of the Fitzrovia Gallery were adorned with a tangible yet heretofore seemingly unobtainable motivation towards creation.
Am I overplaying its significance? That is partially a question for posterity, yet even for laymen the momentum and excitement these artists are generating is undeniable. The art on display was eclectic in styles, themes and mediums across several dozen pieces. More importantly, however, it was fundamentally good art made by individuals who clearly have a passion for their craft. The nature of this act is political in its affront to progressive sensibilities, but the artists’ avoidance of explicitly political works served their aim of aesthetic appeal. The Exhibition was not a petty episode of ‘culture warring’, but something beyond it with a burgeoning artistic language reemphasising power, virtue and beauty within the human condition. In this sense, modernist inspirations could cooperate with more traditional styles without too much friction, and perhaps the breadth of traditions available to artists in the present can allow synthesis without imitation. I know too little about art to determine the originality of what was on display compared to historical forms, but it was nonetheless impressive to see.
Beyond my emphatic recommendation, I shall mention a few features of The Exhibition which stood out during my visit for those unable to attend; accompanying images can be found fairly easily on the artists’ Twitter feeds. It would be amiss to not mention our very own Sam Wild’s contributions. Amongst his works were a couple of our magazine covers, which are vivid watercolours in actuality. Three textiles by Ferro were a surprising but worthwhile inclusion, according to the website in the Arts and Crafts tradition yet with uniquely mystical patterns. The larger paintings, belonging to Alexander Adams, Matthew Fall McKenzie and Harald Markram, provided yet another advantage to holding this exhibition in that viewing art online seldom gives a sense for each piece’s scale. The epic scenes depicted on several larger canvasses by McKenzie and Markram were simply fantastic. Indeed, all the art on show had more impact from being proudly arranged in a gallery than could be obtained in front of a screen.
I hope this will be the first act in a more active reaction from these artists against cultural stagnation and decline. From my conversations with the artists present during my visit, they are certainly willing to continue fighting for culture. It shall be up to readers and fellow writers to continue supporting this (and other worthy endeavours) in the absence of friendly institutions or the wealthy patrons of times past. At least it has now been proven that our aspirations for the future of culture have the ability to become reality.
Enjoying The Mallard? Consider subscribing to our monthly magazine.
Economic Bondage Against the Family (Magazine Excerpt)
In his 1936 Essay on the Restoration of Property, the author Hilaire Belloc recalls an image he had read two decades before and reproduces to the best of his memory. I’ll adapt it: imagine a single machine that produces everything society could possibly need. If this machine is owned by the collective, through a caste of bureaucrats, we have socialism. Everyone who tends the machine are regularly doled-out what they allegedly need by this bureaucratic caste. If the machine is owned not by many but by just one man, we have monopolistic capitalism, of the type resulting from complete laissez-faire. Most people work the machine and get a wage in return so they can buy its produce. Some others are employed in entertaining the owner, and all the rest are unemployed.
Belloc doesn’t say it, but we could imagine that working the machine involves just pushing a button repetitively. If technology did advance to the point that all which humans need could be provided by one machine, surely it could be worked by merely pushing one button repeatedly.
I rehearse this second-hand image because through it Belloc makes a point: these are capitalism and socialism as “ideally perfect” to themselves. If such a machine existed, this is what each system would look like.
Both monopoly capitalism and socialism share an agnosticism about the role of property and work in human life. Neither ideology views work nor property as ends in themselves but only means to further ends. For the socialist this end is consumption. Material needs are more important than freedom. To borrow again an image from Belloc, socialists view society as like a group stranded on a raft. The single overwhelming concern is not starving, so food is rationed and handed out according to a central plan. Perhaps a man finds fishing fulfilling and would lead a happy life honing the fishing craft. Maybe he would benefit from selling fish for a profit so he can support his craft. But the circumstances are extreme, so the group take collective ownership of his fishing rod and collective charge of distributing the fish. It’s for this reason that socialism is so appealing to ideologies that see existence as struggle.
For the monopolist this end is profit. Money-making is the only purpose of economic activity, separate from any human need or fulfilment from work. Property is good only if it generates money; not because it has any fixed purpose within human life. Work also is good only if it generates money, and if profits can be increased while reducing the amount of work needed, this is preferable. This is the reasoning Adam Smith uses to create the production line. The goods produced, further, also have no value apart from the profit they create.
Neither system recognises that humans are rational animals who flourish by both having and using private property as an extension of their intelligence. Thus, if a machine existed which could produce everything needed for life by repeatedly pushing a button, both systems would adopt it and consider themselves having achieved perfection. Everybody (or almost everybody) could be employed doing the same repetitive activity, differing only on the matter of whether their employer is private enterprise or the collective.
The worker pushing a button is akin to one working on a conveyor belt in a factory, or in bureaucratic pen-pushing. His livelihood consists in a single repetitive and mindless task which requires little intelligence to perform. A craftsman, on the other hand, creates something from start to finish by himself or as part of a team effort with other craftsmen. Intelligence runs all through the activity. Making a teapot, fixing a car engine, building a house, or ploughing a field, each requires applying a design with one’s hands, that has already been worked-out by one’s mind.
Another effect of this agnosticism involves the consumer. The sort of consumption monopolists think about is a limitless glut happening in a social vacuum. It is want unrelated to need, because the only way we can truly specify need is by defining a fixed purpose for human life. Human needs, on an ancient view, relate to the kind of life humans must live to be truly happy and flourishing. So, we need food, water, shelter, and other commodities. But we also need to exercise our uniquely human faculties, like creativity, aesthetic appreciation, imagination and understanding. We also need to know how much of a good or activity to have. After all, eating until we pass out isn’t good for us, and to sit around imagining all day may run into idleness.
As a result, neither system has much room for organic human community at the local level. Such communities depend on need which goes beyond the mere satisfaction of material wants. Work, for example, is more than just a way to get what we need to live. It’s a vocation, which taps into our rational human nature, and gives us joy through creating and shaping our surroundings.

This is an excerpt from “Nuclear”.
To continue reading, visit The Mallard’s Shopify.
Kino
The Whitewash – A Review of ‘War on the West’ by Douglas Murray
To begin, it’s worth saying I owe something of a debt to Douglas Murray. He brought me to many of the positions I hold today, and while my overall impression of ‘War on the West’ was disinterest, it is only upon looking back at my own political journey I’m beginning to understand why I felt that way.
‘War on the West’ follows ‘The Madness of Crowds’ and the ‘Strange Death of Europe’ as Murray’s third book discussing the state of political affairs in the Western world. Murray’s thesis is best laid out by Murray himself:
“People began to talk of “equality”, but they did not seem to care about equal rights. They talked of “anti-racism”, but they appeared deeply racist. They spoke of “justice” but they seemed to mean revenge.”
Herein lies the problem with ‘War on the West’, and why I moved away from Murray in my own life: there is no examination of what equality is to mean, what anti-racism is to look like, or what kind of justice is to be enacted, if any. The primary objection Murray has to the armies waging a war on the West is that their vision is not a classically liberal one. Explicitly antagonising white people with terms like ‘white fragility’, ‘white tears’, or ‘white privilege’ is bad because it racialises things Murray believes to have been deracialised by the Civil Rights Movement and other changes that occurred between the 1950’s to early 2000s. In his previous work, Murray uses an analogy of a train of equality pulling into the station, only to careen off down the tracks at a greater speed than ever before without allowing its passengers to get off. Throughout Murray’s work is an unexamined liberalism, that at best, is only ever criticised for being too pure. Liberalism, by its nature, criticises social orders for creating barriers for individuals. The many freedoms the West has provided have always come at the expense of the social orders liberalism eroded. Freedom for women came with the erosion of a patriarchal social order, and took with it the benefits such a system provided – such as the ability to raise a family on one income, a high degree of social trust, and a defined relationship between the sexes. It was inevitable that liberalism would eventually critique itself, and many of the authors Murray cites, from Kendi to DiAngelo, often build on those drawing on Herbert Marcuse and Theodore Adorno. The former was given money by the Rockefeller Foundation, and even worked for what would become the CIA. In many ways, it was Western liberalism with its free flow of capital and revolving door between the academy and influential roles of state that enabled these theories to promulgate.
In his interview with the Telegraph promoting the book, Murray states:
“As long as people are armed with the right facts and the right arguments, I just don’t see how the cultural revolutionaries can win. I don’t know about you, but I’m not spending the rest of my life cringing and being told I’m guilty of things I never did. Not doing it, not guilty.”
This really begs the question of how exactly we got to this position to begin with. What’s most striking about ‘War on the West’ is that it does read almost like a recap of a war. Battlefields are specified, different players and their decisions are named, and Lord knows there are a huge number of casualties in the culture wars Murray describes. But, were the people who permitted things to reach this stage simply incapable of posing arguments against it? In one chapter, Murray notes that claims that America is founded upon stolen land are self-refuting because the many tribes of America stole the land from one another. Are we to believe Americans are so ignorant of their own history that this argument has never been made? Murray himself notes in the conclusion that outlets such as MSNBC and the New York Times will deny that Critical Race Theory is taught in schools, but acknowledge that it exists when forced. There are no arguments that can be used against such a thing.
Left out of ‘War on the West’ is any truly systemic analysis of the problem. The aforementioned New York Times moved to a paywall model in 2011, and from that point forward, the focus on things like ‘racism’, ‘sexism’, ‘homophobia’, and ‘transphobia’ increased many times over. Around this time, legacy media was dying slowly. So newspapers moved from selling papers to many people to selling stories to a niche audience. The niche audience of the New York Times is the kind of cosmopolitan liberal who is very interested in niche identitarian trends, and in pitching themselves as radical while at the heart of the very system they claim to dislike. Despite this being a veritable War on the West, according to Murray, the emergency powers of war are never called upon. There are no calls to take decisive action to halt or prevent these systemic changes that led to this point. And in the conclusion, he defends the same economic system of capitalism that gave the New York Times its power, and forced it to change its business model to appeal to a niche audience of people hostile to Western people.
This attachment to a liberal historiography, in which individuals are given The Arguments and Make The Case, with spontaneous and emergent bottom-up change coming about as a consequence blinds Murray to the economic and legal realities that influence and shape this War on the West. Multiple universities are stated as battlegrounds for this war, but there is not a single mention of the fact universities are public authorities under the Equality Act (2010). That they have an ‘equalities duty’ to publish routine equalities reports, and must legally keep permanent members of staff dedicated to pushing this anti-Western message.
The only law Murray appears to mention in this vein is the Civil Right Act, which he defends as an example of the kind of good equality that he desires. Yet it was the Civil Rights Act which created the Civil Rights Commission, which in 1973 wrote to the Civil Service Commission and had them drop the standards for algebra in order to allow them to hire more non-white civil servants. Similar acts can be found in the UK. The Race Relations Act of 1973 (which performed the same anti-discrimination function as the Civil Rights Act he praises) created the Commission for Racial Equality. Today, the Race Relations Act has been assimilated into the aforementioned Equalities Act, and the Commission for Racial Equality has become the Equality and Human Rights Commission, which forces compliance with the Equalities Duty. There is a clear through-line from the civil rights legislation both in the USA and the UK, to the situation we are in now. The back of ‘War on the West’ reads as follows:
“The anti-Western revisionists have been out in force in recent years. It is high time we revise them in turn…”
Fundamentally however, there isn’t much of a revision of dominant left-wing narratives within ‘War on the West’ at all. Instead, it seeks to remind leftists that their own heroes, from Marx, to Foucault are also not spotless figures. This can only go one of two ways: either they ignore this, and nothing changes, or they recognise this, and move away from those figures, and as a consequence have doubled down on their principles of removing any and all unsavoury figures from public life. Regardless, none of this is at all revisionary, nor does it fundamentally challenge the values and beliefs of the cultural revolutionaries. A truly revisionist view of things would challenge the dominant understanding of things like the Civil Rights Movement, which was not (as Murray describes) people ‘making the case’ for rights, that the American public was so blown away by that they accepted and endorsed. Academic studies like that done on Rosedale show the side of desegregation that was forced upon people, and came at the cost of schools, neighbourhoods, communities and lives. Rosedale was a segregated community, but desegregation and the tensions that came with it made it difficult for authorities to maintain peace. The result was that many of the former residents who didn’t move out of their homes, found themselves the victims of racial violence by those who moved into the area, and had no regard for the police, who stopped policing the area out of fear of creating tensions. When Brown v. The Board of Education ended the desegregation of schools in America, and people protested, the national guard was sent in to disperse the crowd at gunpoint.
All of these changes were not the natural unfolding of human progress. They came today as they did in the civil rights movement, through force. Eisenhower and the national guard did not make the case for desegregation in light of Brown, they imposed it down the barrel of a gun. Whether that was right or wrong is irrelevant, that fact alone disproves the notion Murray insists upon in his recent public life – that the train of equality was chugging along gently, and only recently got out of hand. Equality is not a train chugging along set tracks, it is an amorphous blob that seeks to desacralise everything and dissolve all boundaries between all things. It does not progress in one direction alone, like a train, but expands in all directions and infects all things, including our supposedly right wing public figures.
In light of this, I still see some utility in Douglas Murray. Challenging double standards and hypocrisy is a cheap tactic which ultimately will not defeat those Murray opposes. Yet it is often the first chink in the armour for many people. I know I first came to move away from liberal beliefs because I found them to be contradictory, it was only in time I rooted out my own inherently liberal views, and ultimately moved to the political views and positions I hold now. In this respect, Murray is useful – he can confirm people’s suspicions about the modern left, and give them comfort that there is a public figure who opposes these things. It’s incumbent upon people with more bravery and introspection to take that one step further, and marry it with a systemic analysis of the situation, and propose and action a plan to undo these things and institute something new in its place.
Humber Bridge 2
When the Humber Bridge was completed in 1981, it was the longest single span suspension bridge in the world. 41 years later, it has been reduced to a mere 11th place. The current longest single span suspension bridge in the world, the Akashi Kaikyo bridge in Japan, stands a mere 500 metres longer. This is an unfathomable disgrace for the people of Great Britain and is, quite frankly, a national tragedy and embarrassment. To add to this disgrace, another bridge, the ‘Çanakkale 1915 Bridge’ will soon be completed in Turkey. It will kick the Akashi Kaikyo bridge from its number one spot, and move the Humber Bridge to a measly 12th place.
Therefore, for my submission to The Mallard’s project 22, I would like to make a simple but resoundingly important proposal: build a second Humber Bridge (Humber Bridge 2 some would say) and make it precisely one metre longer than the Çanakkale 1915 Bridge, therefore reclaiming Britain’s rightful place in the world as the country with the world’s longest single span suspension bridge.
This proposal is likely to ruffle some feathers internationally, and I imagine our friends in the East would be quick to try and build another, even longer single span suspension bridge somewhere else. The solution to this possible outrage is, of course, simple: Build a third Humber Bridge.
These proposed projects have a myriad of benefits that I am sure are obvious. I will however go over them in an attempt to convert the non-believers. Not only will these projects drastically increase the infrastructure of the East Riding of Yorkshire and Northern L*ncolnshire, they will also bring desperately needed construction work and employment to an otherwise overlooked region. The construction of perhaps five or six Humber Bridges over the next 50 years would create literally thousands of jobs for engineers, technicians, builders, and labourers.
Coming in with an estimated price tag at just over £2 billion each, I am sure you can see that these bridges would be an absolute steal for the price!
I know what you’re thinking ‘He can’t be serious! This is a joke right?’. No, I am being very serious. As the nation which invented the bridge, I think it is perfectly reasonable that Great Britain goes to great lengths to have the longest one in the world, the lack of one is wounding to our pride. If you do not support the construction of perhaps eight or nine more Humber Bridges in our lifetime, not only are you a coward, but I can only assume that you are also working in favour of foreign governments, which makes you a traitor, and I’ll be damned if I’m going to sit here and be lectured by some fifth columnist.
The Tragedy of the Praying Indians
A generation after the first Thanksgiving, colonial Massachusetts experienced the single deadliest per capita war in North American recorded history. Though the famed declaration of friendship between White settlers and Native tribes was within living memory for many of the fighters in this war, it did not in any way soften the animosity nor stay the violent hands of either side. This was King Philip’s War, a turning point for American history, the war that set the precedent for Anglo/Native relations for centuries to come, and yet one that is woefully unknown and underdiscussed even West of the Atlantic. It left all parties involved scarred, traumatised, and for one group even less understood than this forgotten war, a betrayal never to be overcome.
It is 1675, and the titular King Philip, Christian name of the Sachem (chief) of the Wampanoag, Metacomet, has lead a raid on the New England colony town of Swansea in retaliation for the English executing three of his countrymen for the murder of one John Sassamon. Despite his European name, Sassamon was a Harvard-educated Praying Indian, the name given by the Puritan colonists to the groups of Native Americans that had adopted the faith and customs of their new neighbours. He was a respected member of Metacomet’s court and a cultural mediator who had recently informed the Plymouth governor of the Sachem’s intention to gather tribes for war. His murder was seen as revenge for this betrayal by the English, but this perceived overreach of the colonial authorities, in killing his kinfolk without consultation, was the pretext Metacomet was waiting for to being this war he had been so wanting.
The raid on Swansea was a horrible affair. The Wampanoag laid siege to the town before overcoming the militiamen defenders and laid a terrible waist upon the hapless civilians. Many women and children were butchered neath the tomahawk that day, and the other colonies were quick to respond to the massacre. The Praying Indian warriors were keen to come to the assistance of their European allies to meet this aggression, and expected naturally to be accepted as a welcome aid by their dear friends. They were in this, and in much else, utterly and tragically mistaken. Though the Praying folk saw the English as firm allies, this was a decidedly one-sided relationship. That these natives had taken as their own European clothes and custom, and English tongue and English Bibles, mattered little, for to the Europeans the Praying Indian inescapably remained, above all, an Indian. An outsider worthy always of suspicion over trust.
The early stages of King Philip’s war were not good for the English. Despite the common contemporary view of the various North American colonial conflicts as being between technologically advanced musket-wielding Europeans versus bow and hatchet-armed Natives, there were a lot of shared weaponry and tactics between them. This makes sense when considering that by the late 17th Century Natives and colonials had known of and been trading with one other for decades, and many groups had enthusiastically adopted firearms to fight their tribal rivals in wars over fur-trapping land. These years using European technology served the Wampanoag well in the first engagements of the war, and using them they beat the English militias in a number of battles up and down Massachusetts Bay. An opportunity of spiritual warfare was also presented; when a near total eclipse of the moon one night allowed the tribal warband to slip out of the colonial noose tightening on their swampland capital and make for the wilds. Such a freak lunar event at such a crucial time was seen as a divine blessing by the Wampanoag, and an ominous sign of heretical magic by the English, who were thoroughly demoralised by the affair.
Native successes in the war made the situation for the Praying Indians deteriorate rapidly. The English feared uprisings amongst the settled natives, and in a grim turn, dissolved the praying towns that had until then served as a shield for the colonies, and moved thousands of Indian civilians into internment camps, with over 1,000 being crammed into just one at Deer Island. Conditions in the camp were dreadful, and the families kept there doubled as hostages to ensure the loyalty of the Indian scouts fighting with the English. Many hundreds would die over the cruel winter of 1675-6. Puritan minister John Elliot would fight hard against this policy, but by this time it was dangerous to say anything to the defence of Native Americans, no matter the tribe or custom, and he was powerless to stop it.
As for the success of the Wampanoag and their allies, it would not be the English that finally overcame them, but their own kin. Upon hearing that the Mohawk tribe to the West were moving in force towards Massachusetts Bay, Metacomet and his men eagerly turned to await these new allies in their fight against the White man. He was, however, gravely mistaken. In a single action the Mohawk warriors fell upon the Wampanoag, upon the Narragansett, upon all the troublesome Algonquin Confederation and massacred them almost to a man. Metacomet’s power was in a single night broken, and broken by his own kind. He fled to the wilderness, shattered and alone, and would be later slain by the musket shot of one of those who had been, despite everything, loyal to the end; a Praying Indian called John Alderman. The war continued for a further two years in scattered skirmishes, but hope for victory died with Metacomet, King Philip himself, in the Massachusetts swamplands.
King Philip’s War devastated all involved. It resulted in the deaths of 2,000 Natives and 2,800 colonists, the near total annihilation of the Wampanoag and their allies, and of the English settlements nearly half were attacked with hundreds of civilian deaths. The Praying Indians suffered perhaps more than any; hundreds of their already small population had died, and the discrimination and suspicion they had suffered from the English before the war had metamorphosed into open hostility and hatred. They had considered the Europeans their brothers, in culture and Christ. They had adopted their ways and their God, severing themselves from their Algonquin brothers of Old in favour of the civilised and energetic New.
It did not save them.
The newcomers did not see brothers, they saw Indians. They did not see Christians, they saw Indians. They did not see allies, they saw Indians.
When it came down to it, ingratiating themselves to their new neighbours did not save the Praying Indians. For their efforts and their loyalty, they received only tragedy and betrayal, they died like the rest.
Perhaps there is a lesson to be learned here.
Featured
To be Anti-Refugee is Un-British
I
Compassion for asylum seekers is a traditional British value – a real British value, not a Quango-invented value like ‘tolerance’ that wouldn’t be out of place in any Western European country.
Britain’s reputation as a friendly haven for the oppressed is wholly based in historical fact – and I don’t mean “we found the skeleton of a 15th century black man in Cornwall, and that’s why unfettered channel boat crossings are a good thing”.
Now to be clear: a refugee is not a migrant. Most channel crossers are economic migrants looking for wealth, which I am not here to defend nor discourage. When this article says “refugee”, I am referring to those fleeing war or persecution, such as Ukrainian civilians, Iranian political opposition, or Uyghur Muslims from China. And while I do not advocate handing out visas to all 21 million stateless refugees in the world today, it is my opinion that we should take in many more than we currently do – regardless of any policy towards other forms of migration – and make the United Kingdom the best and most welcoming place in the world to be a refugee. Not just for altruistic reasons either – we can greatly benefit from this arrangement.
From 1828 to 1905, at the height of her imperial power, the number of immigration restrictions the British Isles had was zero. The borders were completely flung open, allowing anyone who was downtrodden, oppressed, or impoverished the chance to live a life of freedom and security behind the protection of the Royal Navy.
This was a point of pride to the Victorians – the Times newspaper wrote in 1858;
“Every civilised people on the face of the earth must be fully aware that this country is the asylum of nations. We are a nation of refugees. There is nothing on which we are prouder and more resolute.
All Europe knows and respects the asylum of these isles.”
The first wave of refugees from the continent – since the Huguenots – were the French clergy and nobility fleeing the Reign of Terror. Around 4,000 arrived in 1792, settling mostly in Soho and other affluent areas of London. They were forced to undertake manual labour for the first time in their lives, working as tailors or publishers. Due to a lack of Catholic churches in London at the time, Anglican churches such as Saint Pancras welcomed their brothers in Christ and offered church facilities for Catholic masses and burials. No fewer than eight former French bishops are interred at the church.
The Duchess of Gontaut wrote of her arrival to England;
“Arriving at Harwich…made my heart beat faster in the hope of a better future. It was a happy premonition because from that moment we experienced the good and loyal hospitality of the English.”
Successful integration of refugees is surprisingly easy – give them the chance to work, and access to resources. Economic deprivation is the number one predictor for whether or not an ethnically diverse neighbourhood is socially coherent, but current policies make this nearly impossible; Refugees in Britain must wait 12 months after arrival before they have the right to employment.
Labour is the world’s most valuable commodity—yet for 12 months, a refugee is forced to relax in a four-star hotel and eat free chef-prepared meals, all paid for by taxpayers. The faster a refugee can obtain a job, the faster they can be turfed out of hotels and become productive members of society.
II
The Victorians were so committed to the policy of free asylum that they were even willing to create diplomatic scuffles to uphold it.
In the mid-century came the socialists. Marx, Engels, Kropotkin and co. all escaped harassment from tyrannical European governments by making the free and prosperous shores of Britain as their home.
In 1858, a collection of these continental anarchists based in a London lodging house plotted a failed assassination of Napoleon III. One man who stood trial for this conspiracy was French exile Simon François Bernard. The French government demanded he be punished – but the British press were steadfast in their opposition to a conviction. Partly because it would undermine the policy of open borders (some things never change), but also because anything that frustrated our eternal rivals was surely a good thing.
While I don’t suggest we invite any Islamic terrorist groups to set up an embassy in Fitzrovia, we can learn from this example to forge our modern-day policy on political refugees.
I and many readers of The Mallard yearn for a restoration of Britain’s prestige on the world stage, a way for our now Empireless nation to regain that global reach. So what could be more of a leverage over our enemies than aiding those who are consistently a thorn in their side?
Several Hong Kong dissidents such as Nathan Law have already fled here and continue to campaign for a free Hong Kong from the safety of the UK. We could extend this to other Chinese, Iranian, or Russian political dissidents, and be the first port of call for Governments-In-Exile. Provided that they do not actively harm British or Western interests, we can only gain geopolitically by being the prime destination for exiled activists the world over.
III
The open borders policy came to an end at the start of the 20th century. The last wave of refugees were impoverished Poles and Jews escaping persecution from the Russian Empire. One such refugee named Israel Lipski was hanged in 1887 for the murder of a woman in Whitechapel, and the story gave rise to the notion of “pauper aliens” committing crimes, stealing jobs, and pushing up rents.
The Conservative government of the day proposed the first restrictions on immigration in 1902. But they weren’t completely without opposition – it was none other than Winston Churchill who said these new rules were;
“a loathsome system of police interference and arbitrary power that would harass the simple immigrant, the political refugee, the helpless and the poor…This country has so greatly gained from the old, tolerant, and generous practice of free entry and asylum. This law is expected to appeal to insular prejudice against foreigners and racial prejudice against Jews.”
And Churchill was right. Even today (despite eye-catching headlines) the effect refugees have on the crime rate is low. During the 2015 European migrant crisis, Germany took in over 1.4 million refugees – yet by 2019, their crime levels had fallen to the lowest in thirty years.
And if a refugee does commit a crime, surely the only person who should be punished is the guilty refugee – not the thousands of other innocent, law-abiding evacuees with whom they arrived alongside.
Nonetheless, the Aliens Act introduced the first restrictions in 1906; immigrants were required to prove they could support themselves financially, not be “liable to become a charge upon the public rates” (i.e. disabled), and have a clean criminal record.
IV
But this was not the end for Britain’s role as an international safe haven for the oppressed. During the Great War, almost 250,000 Belgian refugees were given shelter on these isles, all housed and fed for the duration of the war despite the hardships and food shortages suffered by the nation. The generosity displayed by the British is illustrated in the 1916 Fredo Franzoni painting “Landing of the Belgium Refugees”, showing dozens of boats carrying huddled masses landing in Kent. They are being welcomed by a large crowd led by the mayor of Folkestone. To the side, a nurse stands ready to tend to the sick, while two children bear welcoming gifts. A British ensign flies prominently from one of the ships.
Many of the Belgians were housed by individuals volunteering a spare room. Others were housed in purpose-built villages ran by the Belgian government-in-exile, where inhabitants used Belgian currency and spoke Flemish. Despite some local objections to these ethnic enclaves, within a year of the war being over, 90% of refugees had returned to Belgium. Their only lasting impact being a few memorial plaques, and Agatha Christie’s Hercule Poirot – who was based on a Belgian that Christie had housed during the war.
If we could do it in 1914 during total war, we can certainly do it today.
Granted, the cultural differences between a Brit and Belgian are smaller than a Brit and a Syrian, or an Iranian, or a Venezuelan. But those of you who are worried about the social and ethnic composition of Britain needn’t worry about refugees – like the Belgians, the average refugee spends less than ten years in exile before returning to their native country, and only the most protracted conflicts such as in Afghanistan or Vietnam produce refugees who stay longer than 20 years. Those who choose to stay permanently are clearly integrated Anglophiles who prefer British society over the land most of their compatriots have since returned to.
Overall, while you and I may disagree on general high or low skill migration into Britain, it’s quite clear that compassion for asylum seekers is a long-forgotten tradition that we should reclaim. We can learn from the 19th century to build an asylum system that is both economically and geopolitically a benefit to us – as well as, of course, being the moral thing to do.
Notes From the Bleak Midwinter (Magazine Excerpt)
The weather has been rather dreary in what little of this year has transpired, so it is almost logical that my first article of the year for this publication might be similarly pessimistic. I was invited specifically to write about my expectations for 2023, so I invite readers to prepare to be depressed over the next couple of pages.
In short, 2023 will probably be a continuation of 2022 in many ways. For example, the war between Ukraine and Russia will remain an orgy of bloodshed and hysterical moralising with no end in sight. Ergo, Western political actors will continue to exploit the war for global brownie points, weakening their militaries and frittering away their citizens’ taxes to keep the useful distraction to the burden of responsible governance the war has provided since last February. That said, the overwhelming worldwide focus on that war should stop some (but not all) flashpoints elsewhere from becoming all-out conflicts, notably in Taiwan, Kosovo and the Aegean Sea. Not all proxy sponsors are in the right places to give a space where armed conflict could occur, but it might end up a different story for the possibility of Turkish intervention into northern Syria and of Azerbaijan into Armenia.
Speaking of domestic politics, the picture is not much rosier. Yes, Rishi Sunak might fulfil his “promise” of falling inflation through simple laws of economics at the bottom of a cycle, but his inevitable attempt to take credit will undoubtedly ring hollow with the masses. One cannot read inflation like poll numbers, meaning the price rises are already embedded into economic reality alongside the below-inflation wage growth. Consequently, the strikes will rumble on for at least the first half of this year as the trade unions try to extract a victory from kicking a government when it is down. It has seemed to me that Mick Lynch and company want to re-enact the ‘Winter of Discontent’, but the reduced scale of unionised workers in proportion to the overall workforce will not make life as holistically dysfunctional from striking alone as it was during the mass strikes of the 1970s. I guess their ambitions, borne out by romanticised period role-playing, are at least typical of the present time. After all, similar fantasies which only the children of later Cold War politics are capable of conjuring drives the foreign policy situation I discussed earlier.

This is an excerpt from “Provenance”. To continue reading, visit The Mallard’s Shopify.
It’s Over/We’re Back or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Rollercoaster (Magazine Excerpt)
In short, the year started badly but was peppered with good moments. By mid-2022 it was going excellently, and I thought I was finally past the worst of what this year could throw at me. My hubris was rewarded with some of the worst few months of my life so far. I know that, in the grand scheme of things, I should be thankful for all that I have, and I certainly recognise that I have it much better than most people. It helps to remember that, but it doesn’t change how I felt and acted at the time.
I suppose that that is the nature of life and hindsight. At the time, these moments seemed to mean everything. They either crush your soul and spirit or bring you to the highest heights. I think that this sentiment is expressed quite well in the ‘it’s over/we’re back’ memes that have propagated themselves across my twitter timeline for the past few years. We outright refuse to recognise our own mundane victories and losses, and instead focus on the peaks and troughs – this is natural of course, we would go completely insane otherwise.
I don’t think it is bad to allow these experiences to hit you. Part of the human experience is to be hit by these ups and downs. It is the dwelling on these events that becomes a problem. Holding on to fading hurt and fleeting success instead of moving on in some sort of twisted nostalgia for our best and worst moments can lead us down a very dark and dangerous road. It makes us forget who we are and who we can be. Our lessons learnt, we should embrace the change and simply move on. It is in these moments that we grow and mature as people, and become a better version of ourselves.
For me personally, this year has been an absolute rollercoaster of highs and lows, and that has been very hard to deal with. Things seem to be better now, however, and I am filled with enthusiasm for what the new year can bring me. I think that 2023 will be an amazing time for personal growth and development. I still have a lot of weight to lose, but I am steadfast in my determination to see it through this year. Coming to terms with my situation and state of mind will not be easy, but life is not supposed to be easy. Nothing worth doing is easy.

This is an excerpt from “Provenance”. To continue reading, visit The Mallard’s Shopify.
Predictions for 2023 (Magazine Excerpt)
The 2022 midterms should have been a bloodbath. It should have been a huge sweep for the Republicans, relegating the Democrats to the depths of minority rule. Instead, the Republicans managed to win the House only respectably, whilst the Dems kept the house. It’s widely believed that better candidates could have kept the house.
Good candidates do exist. Ron DeSantis managed to make gains in Florida. Glenn Youngkin flipped Virginia. Brian Kemp safely won re-election in Georgia. Unfortunately, there were also many poor candidates. A competent Republican could have beaten John Fetterman in Pennsylvania. Somebody else could have beaten Katie Hobbs.
The same is true for Presidential elections. The Republicans have only won one election in the 21st century outright, with both the Electoral College and popular vote – George W. Bush in 2004. 2000 and 2016 both saw Electoral College wins but popular vote losses. Whilst external events came into play, it’s not a great look.
That being said, it almost seems that the Republicans like losing. They’re not making any real attempt at winning. Whilst they might choose decent candidates, there’s a high chance they won’t.

This is an excerpt from “Provenance”. To continue reading, visit The Mallard’s Shopify.
Avatar: The Way of Water Review (Magazine Excerpt)
It has been almost 12 years since the release of one of the highest grossing films of all time – that being 2009’s Avatar, James Cameron’s sci-fi epic.
There has been a running meme for the last couple years that despite the first Avatar film’s wild success in the box office, it isn’t a memorable film. The characters aren’t memorable, the storyline is a copy and paste of 1990’s Dances With Wolves, and that its success hinged on the technological breakthroughs in CGI and 3D film that were a staple feature of the film.
In retrospect, the running joke isn’t far from the truth. Avatar is a film that hasn’t held up for casual viewers on its own merits, but rather through nostalgia of a time that has long passed – a time before the insanity of the last 10 years in the social and political scene, where most people were more concerned about the film’s core messages; that being a deeply environmentalist film, a critique on colonialism, and the insatiable appetite of human discovery wreaking havoc on innocent and more noble creatures.
While there are aspects of the original film I enjoy, such as the detailed world-building that Cameron is known for, and the cutting edge visual effects, it still failed to resonate with me the way it has with many other viewers.
The preaching was exhausting when I watched it the first time in 2009, and it is still exhausting today. I get it. Humans are bad, save the trees, the military industrial complex is so evil, etc, etc.While the second installment Avatar: The Way of Water certainly delves a little deeper into the lore and ups the stakes for the protagonists, it still carries the same bare-bones environmentalist sermon that has become all too exhausting in this day and age, especially when we have Extinction Rebellion and Just Stop Oil cronies ruining fine art and causing general inconvenience to all those around them in our current reality.

This is an excerpt from “Provenance”. To continue reading, visit The Mallard’s Shopify.
Politics is About Winning
In the aftermath of the 2020 Presidential Election, Joe Biden proclaimed victory with a vomit-inducing call for unity. “They are not our enemies. They’re Americans. This is the time to heal in America”. Such pleas are suspect when you’ve spent the last four years treating the other camp as enemies; deplorable Neo-Nazi maggots that need removing from society, etc. “Coming together as Americans” would be easier to do if a common American identity still existed; a concept that politicians like Biden have always felt uncomfortable talking about. Trump’s allegations of election fraud have caused outrage, but why should they? Given that his opponents have convinced themselves he’s a tyrant comparable to Hitler or Mussolini, why wouldn’t they do everything they could to remove him from office? Democracy cannot sustain itself if it allows forces perceived to be anti-democratic to gain power via the democratic process. This is when the most self-righteous defenders of democracy, discover they are not, and cannot be, as “democratic” as they first thought. If the election was rigged, Biden becomes President, and he is seen as legitimate, then I must give him props. A masterclass in the art of winning.
Nevertheless, anyone with even a slither of intelligence can see this farce; rhetoric espousing the need for unity is not only disingenuous, little more than an implicit demand that your opponents should start agreeing with you, but also contrary to the notion of democracy. Democratic politics is irremovably state of conflict. At first, this seems a rather peculiar claim to make. Democracy can be divisive perhaps, but not a state of conflict. Conflict is a word we associate with war and terrorism; it is what democracy theoretically seeks to avoid, making it hard to imagine how these words can be synonymous. Nevertheless, it is reasonable to conclude that, as Carl Schmitt said: “the specific political distinction which political actions and motives can be reduced is that between friend and enemy”. The formulation of political motives cannot be removed from the formulation of political friends and enemies. Politics is about power, and if power is the ability to actualize one’s desires, then politics is the ability to triumph over the enemy in the pursuit of an end; politics is about winning.
Democratic politics is not an alternative to conflict, rather it is an obfuscation of it. If “war is the continuation of politics by other means”, then surely politics is the continuation of war by other means, or as Mao Zedong put it: “politics is war without bloodshed while war is politics without bloodshed”. Nevertheless, whilst we may concede that democratic politics is innately adversarial, defining it as a “state of conflict” sounds hyperbolic. Democratic politics is closer to contest than conflict. Both are fundamentally adversarial, but the former is chaotic and brutish, whilst the latter implies a sense of fair play, established rules, and marks of mutual respect. So be it, politics is a contest, even if contests are about winning.
Political contestation appears in many forms. Voting, joining a party, leafleting, petitioning, protests, debate, discussion, rhetoric, making your opponent look cringe, careerism, parallel institutions, etc. are all methods of contestation. We would separate these from methods of conflict: terrorism, revolution, civil war, etc. Unsurprisingly, bribery, blackmail, and deception fall in the ambiguous twilight zone. Nevertheless, whilst methods of contestation and methods of conflict are different, they both imply adversity and the attainment of victory. If one’s goal is victory, it shouldn’t come as a shock to suggest that some methods of contestation are more effective than others. After all, victory is achieved through assertion that is skilful and effective, rather than reckless or impotent. The idea that we must choose between meaningless debate and senseless violence is a delusion.
Darren J. Beattie was correct in his analysis as to why conventional conservative rhetoric has been so weak. Mainstream conservatism (see classic liberalism injected with a bit of transmogrified Trotskyism) rhetoric falls flat is because it is inherently pacifistic; it immediately puts conservatives on the defensive. Ascendant left-wing slogans by contrast does not have this problem. Their ideas are not posed for your consideration, they are commands by which you must abide. They are not policies, they are instructions. They are not posed as potential solutions; they are prescribed as the solutions. Sir Scruton also identified this problem, whilst the Left tells us we must march forward into the future, conservatives can only advise us to hesitate. Conventional wisdom has been taking a battering in recent times, but it appears that attack is still the best defence. Power is a vacuum to occupied, not something to be left in awe at. Fill it or your enemies will.
The idea that politics being downstream from Parliament is a disease. In the context of politics, the words “winning”, and “power” will be connotated with becoming an MP and forming governments. As such, it makes this doctrine common-sense to the partisan shill and problematic to the enlightened moralist. This is one of the reasons debating has become so futile; nobody agrees on what anything means. You will find that everyone nods their head at the word “equality” but ask them to clarify what “equality” means and you will find their hands at each other’s throats. Herein lies the fundamental rule: the metapolitical defines the political. As omnipresent as they are, bickering politicians and the parties they comprise are little more than pawns in a game of cosmic chess. What shapes them? Hegemony. Our politicians are shaped by the forces, attitudes, and ideologies that are ascendant. Not popular, but ascendant. Ways of thinking that everyone is expected to subscribe to. The subjects of the Prince can argue amongst themselves as much as they please, so long as they do not anger the Prince. For the Prince is the being around which they orient themselves; the Prince is hegemonic. As Machiavelli notes, it is important that the Prince’s priority that he be feared, rather than loved.
The Centre-Ground is a concept often banded around in politics. In divided times it is portrayed as a place to which we ought to return, an alternative to clustering at the polarising extremes. What is the centre-ground specifically? We are told it is the realm of reason as opposed to the dunes of dogmatism which lie beyond its borders. Much like the holy land, it is something in need of conquering, something to be held on to, and immediately recaptured when lost. Of course, this is all rubbish. It’s the kind of fanciful rhetoric that centrists insist they don’t indulge in. Centrism is a dead meme at best and cringe LARP at worst. Nevertheless, the Centre-Ground is an important concept because dissecting it can help us understand hegemony. Look to any self-identifying centrist individual, and you will find a cosmopolitan corporate-friendly establishment wet-wipe who flaunts their “high-status” opinions like the latest expensive consumer item.
However, it must be noted that hegemony is not static. As Macron has shown in France, secular hegemony cannot sustain itself by being a vacancy of something (in this case: state religion). Rather, it must define itself as something, necessitating exclusion. A secular republic cannot tolerate pockets of Islamism if it wants to remain a secular republic. As such we now find Macron, the establishment liberal technocrat, espousing rhetoric expected of Marine Le Pen. The rules are clear: hegemony is not only necessary, it needs to be asserted or it will be lost. Hegemony, even if cannot become a totality, is obligated to move in the direction of becoming one. The irony of secularism is that, despite its portrayal as a liberating nothingness, it is no different than religions in a theocracy; it must do more than exist, it must reign like Jupiter.
Hegemony is an organic manifestation. It is subject to ascent, apotheosis, and decline. It is not immune to contest, corruption, and death. As with hegemony on the international stage, when it is decline it becomes assertive and militant to sustain itself when it is challenged by a potential alternative. This is perhaps why the rise of right-wing populism across the West has coincided with more combatant and coercive forms of egalitarianism. Politics is a contest for power, and like all contests requires a winner and a loser. Contests end in the following ways: victory, stalemate, or defeat. Defeat and stalemate, obvious differences aside, do not depose hegemony. Only by winning can the groundwork for a new order commence. The Thucydidean Trap is escaped only though victory.
Moldbug quipped: “if you can explain to me how democracy can be a good thing and politics a bad thing then… you must know something I don’t”. The effect of a politicised populous has on the social fabric is entropic. Given the array of frontiers that a liberal democracy opens for contestation, it eventually finds it necessary level of cohesion there are subjects and values which become incontestable. When everything is up for contestation, there is chaos. To avoid chaos, somethings must be made incontestable; the things to we can say we all agree upon, that which we have in common. The paradox being that what should be considered incontestable is a highly contested matter; that the apolitical is not immune to politicisation.
Marcus Rashford’s campaign to extend and expand the serving of school meals is a good recent example of how the idea of humanity is made distinct from political matters. The government’s decision was not a political one, it was display of “a lack of humanity”. What is one man’s idea of humanity is another man’s political matter. Under such circumstances, how does one engage in rational discourse? Short answer is that they don’t. What appears in the place of rational discourse? Nothing pretty. Of course, the thought of people violently clashing on the streets of London like political street-gangs in Weimar Germany over whether to tweak a school-meal policy is absurd, although it does make for some bitter squabbles. Besides, such a concept may not be so absurd if the subject matter was substituted for something for fundamental. For instance, are we comfortable to put something as fundamental as the basic essence of our civilization to a vote? Is this really something we can afford to disagree about? Life is defined by degrees of difference; some differences are trivial whilst others more severe, some differences may not actually exist, whilst others are real and downright fundamental. It is when those trivial differences exhaust themselves, in the process of becoming fundamental, is an impasse reached and conflict burdens.
When hegemony is truly challenged, a political disagreement mutates into a Manichean struggle between lightness and darkness, between the “human” and the “inhumane”. This is perhaps why the term “Taking the Red Pill”, the breaking of an illusion as seen in The Matrix, has become so prominent in dissident right circles; it implies that the sanctity of the Cathedral has become contestable. The idea of neutrality is important as it implies a lack of contestation, and therefore it is fair to say neutrality is a product of hegemony. To “win” at politics is not to win an election or win a debate, it is to achieve hegemony; it is to turn something from contestable to something incontestable, it is making whatever opinion you may hold, benchmark of neutrality; neutrality defined in your own terms.
Is losing a contradiction of the idea politics is about winning? No, of course not. Losing implies the existence of winning, and to point out someone’s loss is to concede that it was their intent to win, because it was necessary. You may win the war, but if you aren’t flying your colours by the end of it then it has all been for nothing. Nobody goes into politics to lose; what matters is that people don’t want to. Politics is a realm of contestation. If you have political desires but do not actively contest on behalf of them, then you are destined for disappointment and failure. If you don’t have political desires to contest on behalf of, you shouldn’t be in politics. The former is unaware of the nature of politics, whilst the latter reduces it to a conduit from which to extract things that, albeit are useful for achieving political end goals, are themselves not political (e.g. money, wealth, prestige); politics turns from something to be a part of to something be in. It is better to lose fighting for your ideals, than winning on the behalf of someone else.
The contradictory nature of politics is that it is both viewed as a private matter, something personal, and yet it is something which inherently concerns matters beyond just the self. The word politics comes from politiká: “the affairs of the cities”. The foundation of the City of Rome is encapsulated in story Romulus’ murder of his brother Remus, a story that summarises the ruthless nature of politics. However, as Machiavelli wrote of Romulus’ actions in The Discourses: “the end is good, it will always excuse the means; since it is he who does violence with intent to injure, not he who does it with the design to secure tranquillity, who merits blame. Such a person ought however to be so prudent and moderate as to avoid transmitting the absolute authority he acquires, as an inheritance to another; for as men are, by nature, more prone to evil than to good, a successor may turn to ambitious ends the power which his predecessor has used to promote worthy ends”.
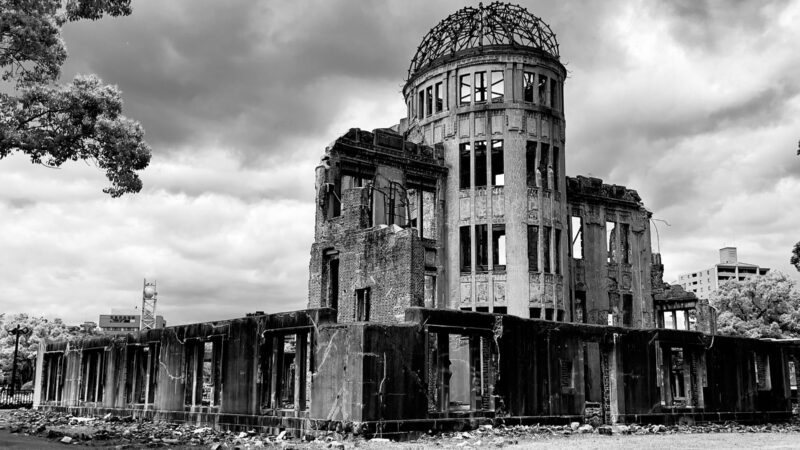
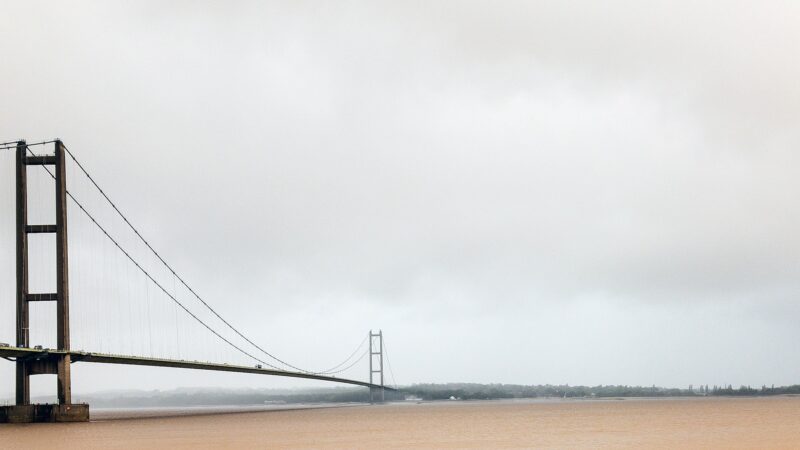















In Conversation with Curtis Yarvin (The Return of Don Quixote and Anglo-Meiji Restoration)
Curtis Yarvin, known by his pen name ‘Mencius Moldbug’, is one of the most prominent social critics and reactionary writers of the contemporary era. Yarvin’s blogs, ‘Gray Mirror’ and ‘Imperial Melodies’, can be found on Substack.
Yarvin’s words are in light.
There’s a little-known Chesterton work called The Return of Don Quixote. Don’t know it at all?
I don’t. I mean, I’m familiar with the original Don Quixote by Cervantes.
Yeah, yeah, yeah, The Return of Don Quixote, and it’s about the victory of a joyous reactionary movement, written as an Edwardian novel, set in the future. It’s very interesting and it sort of catches the sort of joyousness right, which is an absolutely essential part of, like, any kind of restoration of this type.
And yet, you know, kind of Russian Hide And Seek, which is of course a much later work, is more…black-pilled, you might say, and perhaps a little more convincing. And I would say, sort of read them both. You’ll get kind of some of both of these ideas, but just breaking out of this incredible, I mean, it’s like, when you look in the rear-view mirror at Brexit. It’s like 0.1% of a British Meiji, right? And it’s a completely failed venture, and a completely failed thing, you know, I was reading Richard North’s blog EU Referendum, back in the earlier ‘00s, you know, I think he was associated to some extent with, like, early UKIP, and, um you know, the idea of having a referendum on Britain leaving the EU in 2005, let alone that referendum winning, it seemed like such, what we call here, a stretch goal.
It seemed so unimaginable and it happens. This incredible revolution happens and of course it happens and it doesn’t amount to shit. It just has no momentum. As soon as it wins it begins to lose. And, actually, the main effect of Brexit was to destroy the Brexit movement.
Pretty much.
You can’t help but feel that when you do something and people put that much effort and that much hope into something, and in retrospect you can look at it and just say “Well duh, obviously that was gonna…there was no way that could have worked in any way, shape, or form and done anything useful or relevant, or whatever,” and, the, you know…the definition of insanity is making the same mistake twice, and, right, and here, is just the form of government that has been how England rose to greatness and has been governed for pretty much all of the last two millennia, you know, before the invitation to William, right? You know, I guess, you know, William, it’s hard to know to what extent William of Orange was really interested in British domestic affairs. I don’t know how great it was.
Queen Anne was certainly pretty feeble and um, you did know that the um, the king has the right to veto legislation in parliament, right?
Yes.
And do you know who the last person, the last king, who actually used that power was?
It’s not going to be James I is it? Someone distant. Charles I?
Here’s a hint. It wasn’t a king at all.
Really? OK, so was it Queen Anne then? Was it in fact Queen Anne?
It was in fact Queen Anne. Uh, she did it once, and I forget over what. Probably some completely symbolic bullshit.
I see. They went “No, no, this is no good, we’ll get this Dutch fellow”.
Yeah, yeah, it was sort of their ‘lordships die in the dark’ moment. I think, like you know, the People’s Budget of 1911 or whatever. Yeah, Queen Anne was like the legitimate daughter of James II, right? And there was some hope that – and she was basically a Jacobite heir – it’s sort of like this woman Georgia Meloni who gets elected in Italy spouting all this rhetoric and then she’s like “We must fight for the Ukraine, the cause of Ukraine is the cause of all of us”, right?
You know, when I was in Portugal, I was in a small town in this summer and, you know, all of the…you would swear the whole population of Setúbal, Portugal, had come out and, like, popular enthusiasm for the cause of the Ukraine was everywhere, spontaneous graffiti, right, you know, and it’s like, these expressions of popular enthusiasm, like ‘workers of the world, unite’ in Czechoslovakia in 1976. You know, the greengrocer does not really care about workers of the world and I’m pretty sure that if you’re a bus driver in Setúbal, Portugal, your interest in the Dnieper isn’t really – excuse me, Dnipro – is fairly limited, and the uh, just, I mean, it’s increasingly comical, and so, the idea of just like, this whole structure collapsing in one boom is so much more realistic than the idea of Brexit. It’s so much more realistic. People think it’s unrealistic, no, it may be unrealistic, but it is vastly more realistic than Brexit.
I read your piece about a Meiji Restoration. I was sat in the middle of a bunch of naval officers and I was thinking “You know what? Rishi Sunak’s not very popular, neither is Keir Starmer, nobody likes parliament, what would actually happen right now if King Charles did in fact just go ‘guys’…”
Martial law.
Yeah exactly. What would actually happen? And you know, there’s been this sort of endless slew of headline after headline after headline of “Oh, this thing isn’t working, we’ll get the army in to drive trucks” and “Oh, this isn’t working, we’ll get the navy in to sort out this hospital”, and you just sort of look at this thing and think “Why is it that the last sort of functional bit of our government is essentially military?” And “Why is it that…” what would actually happen if…would anyone stop it? Would anyone in the military?
Yeah, yeah, yeah.
I was in Dartmouth. I was at BRNC when the Queen died.
Oh wow.
It’s full of these young, early twenties cadets, who are going through…you know, I was there the day…so I think I was one of the last people to officially join the Queen’s navy and one of the first to join the King’s, and you know, everybody, the whole, the whole college just stopped. I went out onto the Parade Ground at about 5pm in the early evening and every church bell in Dartmouth was ringing across the valley. And yes, there’s a huge amount of symbolic nothingness to it –
But that symbolism can be converted back into reality.
Right!
And everyone would be stunned at how easy it was, and how obvious it was.
I don’t think anyone would say no.
Well, would Sir Arthur Scargill bring the unions into the street? Would like, you know, would the SpADs like set up barricades outside of Nelson’s Column? What?
Right, right. I don’t see it.
I don’t see it. And so you can have your New Jerusalem in England’s green and pleasant land. You just have to realise that the chains that are bonding you are made of paper.
But that’s the question. The new Prince of Wales hands out copies of the Big Issue –
[*Laughs*]
And I just don’t see the king going along with this, so what do we do? Do we have some kind of new Cromwellian parliamentary lie where oh no, no, the king is held captive by these malignants and bad ideas, what is it? What on Earth are we doing?
Yeah, yeah, well, you know, um, maybe we, you know, uh, I don’t know, if Prince William did enough acid, maybe?
Photo Credit.