latest
Ride (read) or Die: 2023 Book Report (Part III)
Following on from last years experiment of attempting to read at least 10 pages of a book a day to increase my reading, I found it thoroughly enjoyable and wished to continue my reading journey in 2023. About halfway through last year, a friend of mine suggested to me that the 10 pages target could be detrimental to my overall reading, as it would encourage me to simply put the book down after just 10 pages (something I later realised it was doing). This year, I chose to do away with the 10 pages target and have decided to just make a pledge to read every day. In the first week of the year, I have already read considerably faster than last year, so I think perhaps my friend was on to something.
I also realised, reading back on last years review scores, that I was a very generous reviewer. I think this was because I did not have enough experience to know what made a book good or bad. I hope that my reviews can be more reflective of the overall reading experience this year.
Book 11: The 48 Laws of Power by Robert Greene
Read from: 28/10/2023 to 28/11/2023
Rating: 3/5
I had seen this book pushed quite heavily online before by certain influencers and I was always curious to see what it was about. Robert Greene appears to have written a considerable number of these types of books, so I was very intrigued to know what the fuss was. I thought the book was fine but definitely lacking in some areas.
The book is essentially a series of lessons regarding how to better navigate life in a more Machiavellian way to attain power. Some of the ideas put forward are genuinely very interesting, and it was nice to have certain topics explained a certain way. Other areas seemed a bit obvious and repetitive which was annoying whilst trying to get through the book.
A lot of Greene’s rules essentially boil down to ‘don’t tell other people what you are up to’, which I suppose is a pretty good rule to follow if you are hunting power. But there are only so many times you can hear that ‘rule’ phrased differently before you start getting bored.
Greene backs up his claims with a plethora of anecdotes which I mostly enjoyed. He fell into the same trap as before, however, in that a lot of the anecdotes start to blend into one after a while – especially after using the same anecdote repeatedly. If I never hear the name ‘Charles Talleyrand’ again it will still be too soon! I only become disillusioned with Greene’s anecdotes after he started discussing the English civil war – an area of his anecdotes I was much more versed in than revolutionary France or Renaissance Italy. He made some obvious oversimplifications which annoyed me and made me question the legitimacy of some of his other tales to back up his ideas. I don’t think that this invalidates what he was saying, I just wish he had left less up to speculation regarding whether or not he actually knew the history.
Overall, a good book which I would still recommend. His insight is useful, and this would be a pretty good primer for Machiavellian style thinking. I would say, however, that you should stick to the audiobook over the actual paperback – it will make it easier to digest.
Book 12: One Day in the Life of Ivan Denisovich by Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn
Read from: 06/11/2023 to 09/11/2023
Rating: 5/5
I was strolling through Belfast on a trip there recently, when I picked up this book at a Waterstones for my flight home. Something short to keep me occupied and also increase my book tally on Goodreads before the end of the year. Sure enough, on my (very short) flight back to Newcastle the same day, I ploughed through about a third of it. I found it very difficult to put down and ignore, as I have my other books recently.
As the title suggests, the book tells the story of one day in the life of Ivan Denisovich – a prisoner at a Soviet Gulag in the early 1950s. It takes you through his agonising routine right from the moment he wakes up to when he finally goes to sleep again. It details the way in which he navigates the trials and tribulations of life in the Siberian gulag he is currently imprisoned in, and the many interactions he has with the other prisoners. The book is too short to summarise without spoiling the whole thing, so I won’t do that. I would highly recommend that you take the time to just read it instead.
There was something extremely biting about the way that this was written. The author, Solzhenitsyn, was a prisoner in a gulag for eight years, so he had a considerable amount of his own experience to draw from when writing this book. His main character, Ivan, is incredibly relatable and felt very human. Not necessarily a good or a bad person, just someone trying to survive and make the best out of a bad situation. Going so far as to describe his day as ‘a good one’ simply because he was able to get slightly more food after doing some favours for other inmates; routinely breaking minor rules to make his life easier, working cordially with his inmates, and doing everything possible to do as little work as possible for as much reward as he could.
Every aspect of the story felt very believable and not exaggerated; I never felt as though I was having the wool pulled over my eyes by what is, essentially, a piece of anti-communist propaganda. He describes the guards as harsh but lazy, the other inmates are not depicted as saints, but as a wide array of people with different motives and agendas – a very real and convincing story.
The book is very well written and was a genuinely fascinating insight into gulag life, an area which I have always been interested in but never researched much. It is a genuine ‘must-read’ for anyone interested in that aspect of Stalinist Russia and the early-cold-war Soviet system of punishment. It is also a delightfully short book and reads very easily. As I said before, I would thoroughly recommend reading this.
Book 13: Star by Yukio Mishima
Read from: 21/11/2023 to 22/11/2023
Rating: 5/5
I read two books by Yukio Mishima last year, and he is fast becoming one of my favourite authors. I was enticed to buy this book from the moment I saw it; a short story by Mishima is often a treat and I was not at all disappointed by this one.
The story revolves around the main character Rikio, a young Japanese actor in the prime of his career, and his ugly assistant and lover Kayo. The story revolves around his struggle with fame and the fleeting nature of his career; it also spends a fair amount of time touching on the absurdity of the film industry in Japan in the 1960s and 70’s (something which Mishima was personally accustomed to) and how Rikio navigates it as best as he can.
Due to the relatively short nature of the book, writing too long of a review would spoil it. However, I will say that I was absolutely entranced by Mishima’s style of writing and his amazing ability to describe some of the more vulgar elements of life (masturbation, sex, drug abuse, etc) in such a poetic and charming way. His powerful use of metaphor continues to amaze me with every book of his that I read. His characters feel painfully real, and his skill at describing scenes and people in such brevity are fantastic.
I would recommend this book to anyone interested in getting into Mishima and Japanese fiction. I thoroughly enjoyed it.
Book 14: The Call of Cthulhu by H.P. Lovecraft
Read from: 23/11/2023 to 27/11/2023
Rating: 5/5
Much like many other ‘American Classics’, the Call of Cthulhu is one of those books which seems to have considerable prominence in online circles solely due to the fact that large amounts of American teenagers are forced to read it at High School. As I am not (and never have been) an American teenager, I have had very little exposure to Lovecraft’s short stories besides the occasional reference on television or through conversations with American’s online. I must say, however, I was thoroughly impressed by this book and Lovecraft’s writing style.
The book is written from the perspective of a young man going through the notes of his dead relative, a university professor who seems to have stumbled on some kind of conspiracy regarding an ancient god-like figure, Cthulu, who drives people to madness. The story details, from the authors point of view, how he came to discover his uncle’s notes and the journey he went on to validate their authenticity. At the start of the book, he is quite the cynical sceptic; by the end of his journey, he is a terrified believer who wishes that his works are never found and is constantly paranoid that he will be murdered for what he has uncovered – that Cthulu is indeed real and that his very brief appearance made many ‘sensitive young men’ (artists, architects etc) all around the world go mad.
I am not a fan of horror films; I find them quite unpleasant. However, I have thoroughly enjoyed reading horror. The writer has no opportunity to shoehorn in cheap ‘jump scares’ and low budget special effects. Horror fiction has to be well written and, instead of a brief thrill, creates a genuine sense of dread. I could feel my own arm hairs pricking up with goosebumps whilst reading it.
I genuinely really enjoyed this book, and will be reading more of HP Lovecraft’s works in the future. A good read and a good introduction to his style of writing and short stories.
Book 15: The Shadow Over Innsmouth by H.P. Lovecraft
Read from: 27/11/2023 to 29/12/2023
Rating: 5/5
This was my final book of 2023 and was purchased alongside ‘The Call of Cthulhu’. I would have finished it much quicker if it weren’t for the many various Christmas festivities that fall at this time of year which has significantly impeded my reading progress.
The book follows the story of a young student who is touring the old towns and villages of the New England coast during a gap year in his studies. During his travels, he comes across the town of Innsmouth whilst making his way to Arkham. The town is shunned by the locals of the surrounding villages and is falling into a very ruinous state. During his visit, he meets an old drunkard who explains to him that the town is infested with fish-people who worship ancient eldritch gods and sacrifice people to the sea.
Due to its short length, to say any more about the plot would spoil it. However, I found the story very gripping and exceedingly exciting. I felt genuinely frightened during much of the latter half of the book and thoroughly enjoyed the way the town and its people were portrayed. Lovecraft does an excellent job at thrilling the reader and the book is worthy of the praise it receives.
I would recommend this book to anyone interested in classic American fiction or someone interested in the works of Lovecraft specially. However, I would say that it would probably be better to read ‘The Call of Cthulhu’ first, as this book is referenced quite heavily near the middle and end of Shadow over Innsmouth.
Ride (read) or Die: 2023 Book Report (Part II)
Following on from last years experiment of attempting to read at least 10 pages of a book a day to increase my reading, I found it thoroughly enjoyable and wished to continue my reading journey in 2023. About halfway through last year, a friend of mine suggested to me that the 10 pages target could be detrimental to my overall reading, as it would encourage me to simply put the book down after just 10 pages (something I later realised it was doing). This year, I chose to do away with the 10 pages target and have decided to just make a pledge to read every day. In the first week of the year, I have already read considerably faster than last year, so I think perhaps my friend was on to something.
I also realised, reading back on last years review scores, that I was a very generous reviewer. I think this was because I did not have enough experience to know what made a book good or bad. I hope that my reviews can be more reflective of the overall reading experience this year.
Book 6: Memoirs of a Kamikaze by Kazuo Odachi
Read from: 20/02/2023 to 23/04/2023
Rating: 5/5
I only came upon this book by accident whilst watching a video essay about Kamikaze pilots during the second world war. It was used as source material for the video, and was referenced frequently throughout. The gripping title alone was enough to get me interested in the story, and at the time I was in a bit of a frenzy of purchasing Japanese authored books (this can be seen in the chunk of Japanese books I reviews last year). Certain to say, I was amazed at the quality of this book, and the incredibly interesting story that it told.
The book was written by Kazuo Odachi, a now 96-year-old former Japanese fighter pilot who, after almost 70 years of silence on the matter, decided to tell his story in becoming a Kamikaze. The book details his childhood, and how growing up in a rural area of Japan meant that his main amusement was laying in tall grasses watching pilots train at the local aerodrome. At this age he would also discover the Japanese martial art of Keno, something which he talks about at great length in the latter half of the book, and clearly has had a huge impact of him. When the war began, he was still only a boy, and so he was only able to join up quite close to the end of the war. A very gifted young man, he was selected to become a fighter pilot, and would spend considerably time in the pacific engaged in various fighting missions.
Kazuo explains how, as the war began to turn against Japan, he – along with many of his friends – were forced to volunteer to become kamikaze pilots. He explains in painful detail the events which unfolded around them, and how they were powerless to decline the request to engage in suicide missions. Much mystery surrounds the motivations of Kamnikaze pilots, but Kazuo repeatedly states that no one actually wanted to be made to do it, but felt that it was the right course of action to preserve Japan and keep the country safe. He reflects on this a lot in the later half of this book, and states repeatedly that he lives his life to the fullest in honour of the men who gave their lives before him. Flying 8 unsuccessful Kamikaze missions (more common then you would think), Kazuo also goes over how lucky he feels to be alive and how easily it could have been him dead instead.
The second half of the book covers his life post-war, his time as a policeman and dealing with Tokyo’s criminal gangs. He also talks in great depth of his love of Kendo, and how he still continues to practice the martial art, even in his advanced old age.
I really enjoyed this book, it gave a very insightful view into a point in history which is cloaked in misinformation and ignorance of understanding. Kazuo eloquently and expertly paints a vivid picture of his experiences, and does not shy away from his more controversial opinions on the events that unfolded in his time before, during, and after the war.
I would thoroughly recommend this book to anyone interested in the history of Japan, the second world war, and especially anyone who wishes to know more about the motivations and feelings of the young boys sent off to die in Kamikaze missions. I would posit that it is also helpful in understanding the mindset of those people who commit contemporary suicide attacks today. An excellent read!
Book 7: Macbeth by William Shakespeare
Read from: 23/04/2023 to 04/05/2023
Rating: 4/5
I found this book at the bottom of my brother’s old school bag whilst we were cleaning out the attic, safe to say it had been left there for quite a long time, probably around 5 years at this point. I am remarkably pleased that I came upon this old schoolroom copy because it came with a handy study/reading guide alongside it which added more historical and literary context to what was being said. I am glad for this because, as I am sure you can understand, a lot of what Shakespeare writes is not always easy to decipher given the differences between contemporary modern English and Tudor English – lots of ‘thys’, ‘thous’, and ‘thees’ can get a bit tedious after a while. If you’re going to try and read this, and you aren’t fluent in Tudor English, I would recommend finding a copy that comes with a study guide.
A thrilling tale with many twists and turns, Macbeth showcases Shakespeare’s ability to subvert the expectations of the reader (or viewer, as this is supposed to be a theatrical performance, not really a novel). The tale of Macbeth is based in medieval Scotland, and follows the titular Macbeth and his wife, as he navigates his options after being promised that he, but not his children, would become King of Scotland by three witches. Driven mad by their prediction, Macbeth’s attempts to secure Kingship and then ensure that his hypothetical children do proceed to be monarchs themselves, have tragic results. In a futile attempt to both secure and then change his own destiny, he betrays himself and everyone around him.
I wont spoil any major details of the story, at the very least because you were probably taught them at school at one point or another. I would instead like to talk briefly about the importance of this book for the English literary tradition and culture which it represents. Indeed, we often take for granted just how much of our contemporary understanding of ‘what makes a good plotline’ comes from Shakespeare and his influences at the time. The mans work stands high above contemporary work of its time, and it would be easy to forget just how ahead of his time he really was. His work stands as a testament to his genius, and to this day still casts a large shadow over what we consider a good or bad story. This is remarkably impressive for a man who lived a half a millennia ago.
Reading Macbeth, much like reading any of Shakespeare is a lot like learning Latin. You might not enjoy it; it’s very confusing; and a lot of the time you are left wondering what in the world anyone is talking about; but at the very least, it can give you a good and grounded understanding of the history of your own language, where certain tropes come from, and how you could use them yourself more often in your own speech.
Overall, I would recommend this book. I am disappointed that I never got to study it at school, and I am glad that I have been able to read it now instead.
Book 8: The History of the Spurn Point Lighthouses by G de Boer
Read from: 04/05/2023 to 18/05/2023
Rating: 4/5
I appreciate just how incredibly niche and uninteresting this book must seem to the average reader. I would argue that it is even less relevant than the ‘Trans-Siberian Rail Guide’ book which I read and reviewed last year (which was written to give directions to western travellers boarding the now obsolete Soviet railway system). However, as someone who actually lives very close to Spurn Point with a keen interest in lighthouses (yes, I am that boring) I found it quite an interesting read.
The book, as the title suggests, details the history of the various lighthouse projects which took place on the Spurn Point (for those who don’t know, this is a large sand bank at the mouth of the Humber estuary) from the early 1600’s to the 1960’s (when the book was written).
I completely understand why this seems uninteresting at first glance; but the book, almost accidentally, ends up discussing more about the complex social and legal situations in place in Britain in the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries than it does about the lighthouses themselves.
The book details the true stories of the various warring factions in British maritime trade politics: the three Trinity House guilds (London, Hull, and Newcastle); sea captains; wealthy merchants; land developers; fleets of solicitors; ambitious venture capitalists; the fading aristocracy; parliamentary meddlers; and even the King of England (not to forget Cromwell of course). It provides a genuinely interesting insight into all of these interest groups and their constant struggle for control over the land and waterways of England, framed nicely around the construction of a highly controversial lighthouse in a rather uncontroversial part of Britain.
Perhaps you aren’t particularly interested in the history of lighthouses on Spurn Point, but if you would like to learn a little bit more about the seemingly ridiculous and overcomplicated nature of competing factions in Britain from the 1600s onwards, I would sincerely recommend this book. It’s short, it refuses to ramble on endlessly, and it has some genuinely amusing moments tucked away inside.
Book 9: Dune (Dune #1) by Frank Herbert
Read from: 18/05/2023 to 22/06/2023
Rating: 5/5
A couple of years ago my dad mentioned that he was really excited to see the new Dune film that was coming out… I was amazed by this statement – my father has never expressed any interest in any film made after 1990, and I was absolutely shocked to see him genuinely excited about a new film. After a bit of prodding, I discovered that the Dune series were his favourite books, and that he still had all his original copies stuffed away in the loft somewhere. Intrigued by this revelation, I watched the Dune film when it came out, and also thoroughly enjoyed it.
A few months later, after seeing how much I had enjoyed the film, I was bought a copy by a friend, and it had been sitting on the shelf at home ever since. I have an immediate disgust reaction to long books, they remind me too much of the musty yellow paged old tomes on my grandmas book case which I was forced to read as a child to ‘practice my grammar’. Perpetually worried that, once I started reading it, it would take me months to complete, I was overjoyed when I found myself unable to put the book down. It was a thoroughly brilliant read, and I cannot recommend it enough.
The book is set in the very distant future, where man has conquered much of the known universe, and a neo-feudal system has been established to govern it. Computers which mimic humans (referred to as ‘thinking machines’) have been completely abolished, and humanity relies heavily on a drug-like substance known as ‘spice melange’ to achieve a heightened state of clairvoyance to navigate the stars. Three main power structures exist in the setting: The Emperor (an all powerful ruler), The Lansraad (a group of all the noble houses), and The Spacing Guild (an organisation of space navigators). They control shares in the ‘CHOAM Company’ which is the main source of the ‘spice’ which can only be found on the desert planet Arrakis.
Duke Leto Atreides is forced by the emperor to govern Arrakis and take it out of the control of his bitter rival, Baron Harkonen. After arriving, it becomes clear that he has been put into a trap, and the forces of the Harkonens are very much still in place on the planet. Leto’s son, Paul, must work with the planet’s natives, the Fremen, to defeat the Harkonens and secure the future of his noble house.
I could write pages and pages more about this story, but I have no intention of spoiling the plot for you. This book is fantastic and had me totally gripped by it for the month I was reading it. It lives up to the hype and is absolutely fantastic, definitely one worth reading.
Book 10: How to be a Conservative by Sir Roger Scruton
Read from: 23/06/2023 to 31/12/2023
Rating: 3/5
If you truly enjoy political theory and are interested in learning about small-c conservatism, I would recommend the book. Scruton clearly and (somewhat) briefly lays out the case for it here. He uses it to discuss the truths in Socialism, Capitalism, and conservatism – which he seems to perceive as a middle ground between the two.
This book took me almost 6 months to read because large sections of it are painfully boring. I was devastated by how much of a slog fest this piece has been to get through. After finding myself unable to pick this book up, I let myself slide and just started reading the other books in my collection at the same time instead – something I have never done before.
I had the same reaction reading Marx and other political theory books last year and in the past. I just couldn’t bring myself to carry on. I find the subject extremely boring. I think my personal issue lies in the fact that these types of work are by no means fictitious but are also not truly non-fiction. Theory seems to lie in a cursed middle ground of quasi-non-fiction which I just don’t care for.
Some aspects of the book are genuinely very interesting – Scruton discusses his time in Communist Czechoslovakia before the collapse of the USSR dodging the StB secret police and giving lecturers to disenfranchised ‘pro-democracy’ students in attics; which was an insightful moment. He talks a lot about the importance of good aesthetics and beauty in public life, which was a refreshing chapter to read through. Unfortunately, the rest of the book comes across as a bit of a snooze-fest. He himself admits that it is difficult to make conservatism sexy, and this book is certainly a confirmation of that.
As stated at the beginning, I would recommend the book if you are genuinely passionate about political theory. Otherwise, it might be best to give it a miss. A friend of mine joked with my whilst I was reading it that “It’s a great book to quote from, not one to actually read”, and I think he is more or less correct about this.
This is the second installment in a three-part series. Follow The Mallard for part three!
Ride (read) or Die: 2023 Book Report (Part I)
Following on from last year’s experiment of attempting to read at least 10 pages of a book a day to increase my reading, I found it thoroughly enjoyable and wished to continue my reading journey in 2023. About halfway through last year, a friend of mine suggested to me that the 10 pages target could be detrimental to my overall reading, as it would encourage me to simply put the book down after just 10 pages (something I later realised it was doing). This year, I chose to do away with the 10 pages target and have decided to just make a pledge to read every day. In the first week of the year, I have already read considerably faster than last year, so I think perhaps my friend was on to something.
I also realised, reading back on last years review scores, that I was a very generous reviewer. I think this was because I did not have enough experience to know what made a book good or bad. I hope that my reviews can be more reflective of the overall reading experience this year.
Book 1: Brave New World by Aldous Huxley
Read from: 01/01/2023 to 08/01/2023
Rating: 4/5
When I was about 12 years old, I read 1984. Perhaps a bit too young to fully grasp the meaning of the book, I was still obsessed by it. I fell in love the ‘alternative history’ genre, which is why I am so surprised that I did not read this book sooner. Aldous Huxley’s ‘Brave New World’ gave me a great deal of nostalgia for my younger reading days. It brought back that same feeling of intrigue and dread which I had felt whilst reading Orwell’s work.
The book is set in the distant future, about 600 years after Henry Ford developed the assembly line and mass production. Ford is revered as a sort of semi-deity amongst the population, who regularly use his name instead of ‘God’. A society which praises stability and predictability above all else, no one knows of passion or love, no one is born naturally (instead being birthed through artificial methods), and a rigorous caste system is enforced by making some people stupid, and some people clever during the artificial birth process – alphas sit at the top, and epsilons at the very bottom. Children are ‘conditioned’ to be extremely comfortable with the roles they have been given in life, and to actively avoid intermingling and seeking activities the controllers of the world deem wrong. Sex is easily acquired, and children are encouraged to engage in ‘erotic activities’ with each other from a very early age. People live shorter but considerably happier lives with little to no unpleasant experiences, and regularly take ‘soma’, a near perfect drug with no hangover or negative side effects.
One of the main characters of the book, Bernard Marx, is a misfit. A designated Alpha, he is considerably shorter than his peers, and has been marked out because of this (as shortness is linked to being a member of a lower caste). He doesn’t understand why he is unhappy with the system around him, but he feels uneasy about it. For example, he has a strong attraction to another alpha, Lenina Crowne, but doesn’t understand why. He is skirting along the fringes of ideas like monogamy and chastity but can’t quite explain why he would want this.
Bernard takes Lenina to a ‘Savage Reserve’ (an area designated as not worth developing), and accidentally meets with a man called John who, through no fault of his own, has been stuck on this savage reservation, with the actual savages, since birth. Bernard takes the savage back to civilisation to attempt to learn more from him and his strange ideas about love, modesty, romance, and passion.
I really enjoyed the literary devices employed by Huxley in the book. His writing style is straight forward and relatively easy to follow. Sometimes it felt a bit too straight forward, however, with only one predictable twist and an ending which felt a bit flat and unexciting. Still, however, it was a pleasant read which conveyed the stories message (that a world free from want and sacrifice is not necessarily a good one) in a way that was subtle and very interesting. Overall, a book that I would thoroughly recommend.
Book 2: Storm of Steel by Ernst Junger
Read from: 08/01/2023 to 14/02/2023
Rating: 5/5
This book was given to me by a very good friend. He had, by some miracle, found this 1941 copy in a second-hand bookshop. Knowing that I was desperate to get my hands on an original translation copy of Storm of Steel before I had sullied myself by reading a more contemporary translation, he bought it for me to read.
What a superb book. What a fascinating read. Ernst Junger takes us on an incredible journey through his experiences in the first world war as a young officer in the German army with immense attention to detail and a spectacular writing ability. Alongside his more general accounts of the fighting, Ernst interweaves his own thoughts on the state of warfare, the reasoning behind conflict, and the virtue in soldiering. Ernst does not shy away from declaring that taking part in the first world war was one of the most foundational and important experiences of his life. He seems to have genuinely enjoyed his time as a soldier and was sincerely disappointed at Germany’s surrender. His rationale behind these beliefs are interesting, and he goes in to great detail to explain his personal philosophy around conflict, and why he believes that soldiering is inherently a good thing.
Not only does Ernst make haste to convince you of the benefits of being a soldier, but he also goes into detail to describe what makes a good person, or more specifically, a good man. Ernst talks a lot of honour, courage, and honesty in his writing. He speaks of his enemies, the English and French, in high esteem, and tells the reader that he tried to keep his own men in good standards. He discusses the importance of valour and of dying with courage (he himself never surrendered and was wounded multiple times). His philosophy on this is very interesting and has been a very jarring counter to the mainstream ‘war is bad’ angle that is taken by other accounts of World War One.
The general structure of the book is good. Ernst tries to remain as consistent as possible with his timing and pacing. However, due to the nature of a book about a war, it is not always possible to keep pacing at a consistent rate. This is understandable and does not detract from the book. Just be aware that there are moments when nothing is happening which are suddenly punctuated by moments in which everything seems to be happening.
I would thoroughly recommend this book to anyone interested in the first world war. It has been an exciting and amazing read which has proven to be a favourite of the year so far. Thank you again to my friend Andrew for buying it for me, I appreciate it very much.
Book 3: The Metamorphosis by Franz Kafka
Read from: 14/02/2023 to 19/02/2023
Rating: 3/5
I only know about this book from various niche references and jokes on twitter. I assume this is one of those books that is compulsory for American High School students to read (as they seem to be the type most frequently discussing it online and in the review sections). The concept of the story interested me – a man becoming a bug, how absurd? But I really had no bias going into this book. I normally understand at least a little bit about the books I am reading before I read them, but I had absolutely no clue what I was getting into when I read this.
Kafka is known for his absurdist and transformative pieces of work, and I can understand why this short story has become his most famous. The book focusses on the story of Gregor Samsa, a travelling salesman who wakes up one morning to discover he has transformed into a giant bug. You would assume at this point that more context would be given, but no. Kafka doesn’t supply us with anything else – only the knowledge that Gregor is now a bug and must live as a bug. Being the sole breadwinner for his parents and sister, his metamorphosis causes immediate problems for all of them, and forces his relatives to actually go out and find work in order to support themselves for a change. All while this is happening, Gregor is stuck at home and simply crawls around, as a bug would. Gregor becomes completely dehumanised whilst his family struggle and cope with their new situation, eventually not even being referred to as ‘Gregor’ but simply as a monster.
The book’s theme is heavily centred on the idea of dehumanisation and alienation. Gregor is beloved and revered by his parents and sister because he earns a very good salary and keeps them well. As soon as he is no longer able to do that (Kafka using the transformation into a bug as a metaphor for ‘becoming useless’) his family still care for him but grow to despise him as they are forced to take up all of the work that he once did to support them. His family, however, do become stronger without him. Suddenly forced into the ‘real world’ again matures them all. His father takes up a respectable job and literally becomes stronger and healthier. His sister matures and develops into a ‘full woman’, and his mother is able to cope with the grief and stress of life at home again in a less pathetic way. Overall, the experience is not entirely bad for the family. Kafka is using this to reflect how dependence can make a person weak, and having the rug finally pulled from under them can improve their lot.
The book is extremely short and can be read in a few hours if you were really desperate to finish it. Kafka is know for his novellas and short stories, and this is no exception. Overall I liked the book but I felt no great connection to it. It was ‘fine’. I often found myself bored by it and couldn’t be bothered to continue reading. Kafka’s writing style is not my favourite in this piece of work. Overall I would recommend it (especially if you want to get the kudos for reading a classic novella in a short amount of time), but I would say that you shouldn’t expect something breath-taking, its an alright book. I hope the next few short stories I read of his are a bit more engaging.
Book 4: In the Penal Colony by Franz Kafka
Read from: 19/02/2023 to 19/02/2023
Rating: 4/5
I only own this book because my copy of ‘The Metamorphosis’ came with it as well (along with ‘The Judgement). Kafka’s stories are very short, so it makes sense that they would bundle them all together like this, and I am glad that I can get a few different stories all together in one book.
This story is a very narrow one. A nameless visitor to a nameless penal colony is being shown around a piece of equipment by a nameless officer whilst a nameless soldier and a nameless condemned man watch on. The officer goes on to explain that this piece of equipment is a torture and execution device which was created by the penal colony’s previous commandant who is now dead. The officer laments the condition of the machine and says that executions have become very unpopular after the commandant’s death, and he is the sole advocate for it now (with promises that a silent majority still agrees with him).
The officer is desperately excited to explain how the machine works in excruciating detail. He is extremely persistent in explaining to the visitor why it is so important and why it is an effective method of punishment.
The overall meaning of this book is difficult to grasp specifically, but can be read in different ways. It can be potentially read as a critique of totalitarianism, with the officer taking the law into his own hands and becoming a tyrant. The book can also be read as an analogy to the Old and New Testament (the old commandant being an analogy for God in the Old Testament and the new commandant being an analogy for God in the New Testament). Another common reading of the book is that it is a critique of carrying out acts which no longer have meaning or relevance to the bitter end – few people like the machine, so why does the officer continue to use it?
This book is very short and can be comfortably read in a day. I preferred this book to The Metamorphosis. I am not sure why, I just felt more inclined to want to read it. The flow of the story is more readable, and I found the characters and their plots more engaging, hence the 4 out of 5 star rating instead of a 3. If you’re looking for a short classic, I would recommend it.
Book 5: The Judgement: A Story for F. by Franz Kafka
Read from: 19/02/2023 to 20/02/2023
Rating: 4/5
Much like the previous book, I only read this because it was at the back of my copy of ‘The Metamorphosis’. This is a very short story, the shortest of the three that I have read so far. Owing to that, please don’t expect a long review as there is not a great deal to talk about.
The book is very narrow and focusses on only two main characters, a son and his father. The son is in the process of inviting his friend, who lives in Russia, to attend his wedding. His father, who is clearly senile and afraid of being forgotten by his son, has a very strange reaction to this – initially claiming he doesn’t know the Russian friend, before finally admitting that he does know him and then claiming that he, in fact, is a far better friend to the Russian than his son is.
It is difficult for me to explain this book more fully without giving too much away, as it is such a short story. But I do find it very odd. Kafka’s style of writing and his general themes continue to boggle and confuse me, but I am glad for this – it is quite refreshing to read things which are so absurd and strange.
The more I read his work, the more I become interested in Kafka. When I first started reading him, I was quite put off. I found his style very rough and difficult to ease in to. But, after getting more acquainted with his work, I’m actually starting to enjoy the lunacy. I have a much better grasp on what ‘Kafkaesque’ means now, and I would be more than happy to read more of his work in the future.
Overall, a good book which can be read in less than an hour. If you were interested in getting into Kafka, this is a good one to start with given its shortness. After doing some research, I also discovered that Kafka himself thought that this was one of his best pieces of work – yet another reason to read this if you wanted to ‘get into’ Kafka.
This is the first installment in a three-part series. Follow The Mallard for part two!
The Importance of National Storytelling
I’m warming myself by the fire where pork shish-kebabs crackle, as I gulp down sweet homemade wine with cured belly fat and black village-bread. We are at a friend’s dacha about 150 miles southeast of Moscow. As we drink the talk gets more political. Eventually a bearded armchair expert starts explaining a theory involving different ethnic groups having innate biological proclivities. He explained Englishmen were ‘sailors’, they live on an island, and they sailed around the world and settled new lands. Jews were ‘traders’ and therefore became widespread but remained on the outside. Russians were the ‘forest men’, who conquered the Eurasian steppes, uniting Slav with Turk in a forest-steppe continuum – or something like that. I didn’t realise until much later that this was a bastardised layman’s understanding of a genuine, developed school of thought now popular in Russia and beyond.
The once-obscure theories of Lev Gumilyov, the Gulag-surviving Soviet social scientist and son of influential poets, are now deeply embedded in the Russian mainstream. Gumilyov conflated nationality and ethnicity into ‘ethnos’ – a universal element of history that makes its foundation. He believed that each ethnos acquired ‘behaviour stereotypes’ in its early stages of development or ‘ethnogenesis’ (presumably what my drunk acquaintance was referring to), connected to geography but also to another concept – passionarity. Passionarity can loosely be defined as an intrinsic motivation towards purposeful activity. Putin has described it as ‘the will of a nation’; its ‘inner energy’. This became the ontological framework for Eurasianism which, part-philosophy part-ideology, is newest part of the story that Russia tells itself. In practice, Eurasianists believe that the post-Soviet states of the ‘near abroad’ are Russia’s natural allies, and not the Slavs or others to their West. They believe Russia and the states that surround it make up a unique, ‘Eurasian’ civilisation united by a ‘Tatar-Mongolic’ heritage, making up the heartland, destined to be in constant battle with the outer rimland.
This might sound like (and likely is) wishful ahistorical nonsense, but there are worse examples. Hungary is an observer state of the Turkic Council, and every year hosts the ‘Great Kurultay’ event, where participants from across the Turkic states and Turkic regions of Russia gather to ride horses and dress like Genghis Khan. The debates over Hungarian pre-history are as confusing and they are endless but basically, they also involve a lot of Eastern-European Turkophilia and dubious historiography. The Turks themselves are split between being a reincarnation of an ancient nomadic people in the body of a Kemalist republic or the rebirth of Islamic power rising from the Ottoman ashes. We might find all this story telling strange, but what stories do we tell ourselves today? What is the level of our ‘inner energy’?
One of the stories we tell ourselves is that ‘the West’ exists as a civilisational bloc due to a shared European and Christian culture, but how true is this now? Our leaders almost never define us in this way. We are instead liberal, democratic nations united by ‘shared values’. The power of ‘the West’ is invoked only when we are being convinced of virtues of the latest war. In this values-based understanding, Taiwan is just as much a part of the West as Israel and Japan are. When that loose definition can’t be convincingly stretched enough (thinking for example of our good friends Saudi Arabia), then we simply become ‘the international community’. All of this is collapsing in front of us, as forgotten civilisations re-emerge with powerful narratives. The West’s old stories do not even convince any more, let alone inspire.
If we look under the hood of this artificial construct of the modern West, we see that it’s held together by little other than the political, economic, and military ties of the globalist regime. I shouldn’t have to say that this does not diminish the magnitude of the West’s contribution to art and science, but a culture must be lived to exist. When it ceases to be, it becomes mere history. We must look at the reality of what today’s West is and not just where it came from. We can divide the modern West into roughly three parts (if we exclude for now the strange parallel Western world that is South America) and they are the Anglo-Saxon countries, the ex-communist states, and the rest of continental Europe. Let’s look at them one by one.
The nations that spent decades under communism are undergoing what can only be described as a cultural renaissance. Hungary and Poland are notable examples, but the pattern is at play across the former Warsaw Pact countries. Being frozen off from the rest of the West for all those decades has unexpectedly left these societies uninfected by the viruses of cultural guilt, atheism, mass immigration, degenerate pop culture and third wave feminism, just to name a few. In fact, the repression of national cultures, religion and traditional family life has led people to embrace and guard those aspects of their identity and lifestyle with a militant zeal. I am aware that most of these countries suffer chronic demographic issues of some kind, but unfortunately most of the world are now victims to a similar fate, so let’s park that for now.
These countries suffered occupation and oppression from many empires across the past centuries, all engaging in national struggles, only to engage in new ones as the red yoke fell. They are therefore not short of stories to tell themselves. The revival of Christianity in these lands only adds to the spiritual rebirth that is evidently sweeping this part of the world. Gone are its Orwellian regimes and rigid state ideologies, very obviously authoritarian, offensively so to our Western sensibilities. Yet the Brave New World-style totalitarian society that we now live in is less obvious, most of us refusing to see it despite it being all around us. It may well be the case that the future will see a new Iron Curtain, where EUSSR citizens try to escape to the sunlit uplands of Eastern Europe. This is what the direction of travel indicates.
Next up is the rest of continental Europe. For all its faults and afflictions, countries like France, Italy, Germany, the Netherlands and even Sweden, are in better positions to get out of the mess they find themselves in than, say, the UK (which finds itself in a near-identical mess). It turns out that the European system of proportional representation and regionalism is a far better bulwark against globalist top-down policies than the much revered Westminster system of government, as the success of Meloni, Wilders and other patriotic populists shows. Here, the inferior status of the English-language along with inherent protectionist tendencies have acted as shields from the extremes of financialised progressivism. Not having the world’s lingua franca as your native tongue adds a filter between national cultures and the globalist monoculture.
Despite most European capitals being marked with giant conquering rainbow flags, thousands of non-metropolitan regions maintain the standards and traditions of their forebears. Culture is preserved on the local level, with much disdain and distrust directed towards the centre. An understanding that traditional way of life relies on a healthy nation, rather than on liberal democratic values, is pervasive and comes naturally. Folk music, national dress, culinary customs, community events, religious occasions and even superstitious traditions are more prevalent and taken more seriously on the continent. These countries are locked in a tug-of-war between the chauvinist East and the emasculated West. Preserving these rich cultures by reclaiming the nation-state seems like a motivating purposeful activity and compelling story.
So, what do you do when you are a country made up of four nations? What if your language is not a delicate national treasure but the universalist tongue of billions? What if your country was set up by people from one part of the world, but is now populated by people from a different part? These are just some of the identity crisis challenges that face the Anglo-Saxon world today. What stories can these countries tell themselves about their place in history and their destiny as a people, outside of materialist comparisons? GDP rankings aren’t the stuff that give you goosebumps. Christian heritage holds these societies together, but actual belief in Christianity is largely missing. Other non-religious ‘values’, like ‘tolerance’ and ‘belief in the rule of law’ are as perverted as they are meaningless. Even Ireland with its unique story was until recently one of the most cohesive, vibrant, and successful of the English-speaking countries, but has now followed its cousin-countries down a road of ruinous self-flagellation.
The United States likes to tell itself that its constitutional system is so perfect that it has been able to melt the peoples of the world into a nation based on life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. It’s the official narrative. Like many official narratives, not only are they instantly challenged by people’s reality, but they are fundamentally untrue. The country was founded by settlers from a very small triangle of the world roughly covering England and Holland. Its system has worked only insofar as the White Anglo-Saxon Protestant culture has dominated. As we are realising to our horror today, our social order is not based on what laws we have, but on how ordinary people behave. Yes, it is illegal to commit rape and murder, but that fact is not the only thing stopping me from doing those things. Somehow, I also don’t want to.
America seriously struggled with integrating first German then Irish and Italian immigrants, due to what were then considered as huge differences in culture. In time, the shared aspects of European culture proved to be enough of a basis to integrate these masses of people into a new nation. Yet it was the efforts of a handful of Ashkenazi Jews in the early 20th century that would cement the homogenous American identity and bring it to life. Through the studio system, the barons of Hollywood’s golden era created folklore for a virgin country, projecting an Anglo good life and WASP values across the land and world. The American dream was not about getting rich but raising strong God-fearing families behind a white picket fence.
This America has long been lost and its 21st century replacement is on a trajectory to become part of Latin America. Like Brazil now, it’s set to become a country where the south is populated largely by White European evangelical Christians while its coastal cities are made up of wealthy gated communities and skyscrapers, separating the liberal elites from the mixed favelas and shanty towns. Adopting Spanish as a national language also adds to this analogy. Part of this region’s problem is that, with Europeans, Africans and natives mixed throughout the arbitrary post-colonial borders, it lacks convincing stories to tell itself. This is probably behind the Latin American habit of entering abusive relationships with radical ideologies.
This leaves us with the rest of the English-speaking countries, the British Isles, and their offspring. The British identity formed with the union of kingdoms and came into its own with the growth of empire. The Scots, Irish, English, and Welsh spread out from their small corner of the globe and settled its far-flung frontiers, producing developed and orderly societies. Far from diminishing the British identity, the loss of empire should have been an opportunity, a released burden, from having to govern large masses of alien people. The British world, with its shared state structures, language, and history, should have been a proudly embraced inheritance, ensuring the culture of these small islands lives on across the world. Instead, America took our place as the mother country, and along with the other realms we have all become part of the American world. Yet the American dream is now clearly a nightmare.
Interest in increasing ties between these extremely similar countries was revived during the Brexit campaign, with the idea of CANZUK, a proposed political alliance between Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and the UK being one of the more promising projects. Its proponents argue that it makes sense for countries with similar economic, political, and legal systems to increase cooperation. Yet these systems have brought the same ills to all these countries. All these countries have had decades of mass immigration and state multiculturalism. All these countries engaged in inexcusable tyranny and criminal negligence during the covid years. All these countries are fully signed on to serving the military-industrial complex and the agenda behind the climate scam. All these countries are losing their identities far quicker than anywhere in Europe or even than America. Is there a common cause of this? It seems more likely than not that a once shared-cultural space left us victim to the same cultural decline, and the extreme liberalism of today’s CANZUK nations (even in comparison to ‘progressive’ European countries) suggests there’s something running through all that ties us together and has sent us all down the same wrong paths. It therefore seems unlikely that further integrating these countries in their present states would make anything better. There’s been such a demographic shift, an erosion of national sentiment and a detachment from the traditional culture of the British Isles, that the populations of these countries would reject this.
Another trait shared by these countries is the seeming inability to think outside of modern ideologies; leftism, capitalism, socialism, liberalism, secularism, nationalism, etc. These all take different objects of study, be it class, the individual, the nation, and increasingly in our post-modern world, race, sexual identities, and other perceived oppressed characteristics. What lies outside all these largely Western constructs is traditionalism. Traditionalism isn’t an ideology but rather a school of thought. It’s of course entangled with right wing politics, but it is a separate prospect. Time to the traditionalist is not linear but cyclical. We’re not going somewhere in the future but instead always coming back to a past. It’s seeing the immaterial in the material. The inherent virtue of tradition and moral good of beauty. It is possible to embrace this mindset without believing in God, but it’s easier when you do. Either way, it requires a breaking out of our utilitarian conditioning. Shun the bugman world!
There is a clear difference between the health and overall robustness of modern British and Turkish cultures, to give an example. This can be demonstrated in how cultures collide. In Turkey, the native culture reigns supreme, forcing all forms of art and entertainment to conform to local tastes or bend itself in some way. Netflix and Disney plus can’t just dish out subtitled versions of their usual fare, they must create locally produced, Turkish-oriented content or they won’t survive. Likewise, foreign music is a rarity on the airwaves, with outside genres being morphed and orientalised out of recognition before taking final form. International fast-food chains perform well but will never outcompete the legion of local takeaways with their motorcycle delivery armies. Even then, country-specific modifications are common. The point is, this is a robust culture that absorbs and bounces away outside elements. Modernity is only accepted once it has been infused with tradition, or domesticised.
Unfortunately, modern British culture does not absorb and shape incoming elements but rather accepts and is taken over by them. Such is the dogmatic nature of the near-official state ideology of Diversity, Equality, and Inclusion, that the concept of a supreme, native culture is a thoughtcrime. If you told a Turk that Britain’s national dish was something called ‘Chicken Tikka Masala’ he would look at you with a mix of bemusement and disdain. Multiculturalism does not have to mean accepting foreign cultures as they are and putting them on a pedestal, but in the absence of a muscular home-culture this becomes a fait accompli. Britain, a country that just a few decades ago was a net cultural exporter, has undeniably lost its mojo. The reasons for this are likely to do with our modern economic system and the various cultural and sexual revolutions visited upon it in this period. Adding many millions of immigrants from the most incompatible parts of the world to the population in a short timeframe has undoubtedly contributed to the decline in shared identity, but it is not the root cause. Few offer a compelling way forward. Traditionalism offers a way to relook and renew.
There is something universalist in this perspective that deserves appreciation. Traditionalism has a ‘to each their own’ attitude that is especially attractive those of us who are sympathetic to non-interventionism and realism in international relations. At present, we ‘the West’, have not given up our position of the constant moral lecturer of the world. This position becomes ever more absurd as the reality of our corruption and social decay is further exposed. We lament the imprisonment of Alexei Navalny and other political dissidents in Russia yet have nothing to say about the imprisonment of Julian Assange or the death of David Kelly. We condemn the primitive corruption of local officials in the third world yet have nothing to say about the institutionalised corruption of our military and pharmaceutical industries and their revolving door self-regulating agencies. We scare ourselves with stories of China’s ‘social credit system’ while living in a comparable digital dystopia ourselves. We invade countries on false pretences, only to bait-and-switch into a Darwinian superiority battle of civilisations.
Our reaction to spending trillions of dollars, two decades and thousands of lives to replace the Taliban with the Taliban, is to Twitter shame Afghanistan for being culturally backward. It is therefore no surprise that Israel has done its own bait-and-switch, abandoning its anti-Hamas line in favour of posting pictures of gay IDF soldiers kissing, therefore demonstrating its cultural superiority compared to the backward homophobic Arabs. All this hypocritical and psychopathic nonsense is thrown out when you view the world through the traditionalist lens. It accepts the world as it should be; differing realms with their own ways of life. The world will not end if we simply let the Arabs be Arab and let China be China. The important thing is that we let Britain be Britain. We should own the right to be ourselves and drop the self-imposed burden of trying to change others. Live and let live – at the moment we do neither.
As far as cultural inheritances go, these islands are luckier than most. The rich tapestry of clans, tongues and kingdoms are genuinely ‘diverse’, and when you drive out of the big cities their beauty is on full display. This is a great lot to work with. As modern urban life becomes increasingly unbearable, it will be to the countryside and villages where people will escape and try to reconnect with the eternal. In the last few years especially, people of individual, independent, conservative, and alternative persuasions have (ironically) used the power of the internet to become part of a revival of traditional ways of eating and living. These people are entitled to (and do) make their own meanings and tell their own stories, but a nation is like an organism and relies on all its constituent parts to function properly. For this, we need grand narratives not of a brighter material future, but of a deep, spiritual, and eternal connection to the land and the people we share it with. It doesn’t particularly matter what stories we tell, but we need to think of some new ones because the old ones don’t work anymore. It will not make me popular to observe that the Second World War, for whatever reason, is no longer the unifying national myth that it once was (at least for Britain). Even countries like Russia, which treats the Second World War as a sort of national religion, needs other tales and stories to tell itself in addition to that. We need big narratives about who we are, where we’ve come from and where we’re going. Celebrating St George’s Day and Margaret Thatcher isn’t going to cut it. We are faced with a fundamentally different country at a critical time in its history.
Britain is a nation with extraordinary prospects that are being wasted because there is no vision. It has, to use Gumilyov’s terminology, low passionarity. Many British people to do not feel that group-specific inner biocosmic force inside of them, and that is a failure of culture over anything. My few childhood years spent in an Irish primary school imbued me with more of an appreciation and affection for that island and its culture than I ever got from a lifetime of secondary and higher education in the UK. The stories of my parents and grandparents, who as immigrants are more inclined to engage in cultural propaganda, instilled in me a visceral feeling of belonging and connection with my ancestors, and their cultures and histories. Yet I only truly connected with the traditionalist mindset after a long process of consciously deprogramming myself from the globohomo monoculture. I now experience a complete synthesis of my various identities, without succumbing to shallow partisanship. I see the beauty in and take strength from them all. The stories and traditions sustain me every day. These bedrocks of any culture need serious replenishing in our country. Our future depends on it. It won’t be an easy task and there are no overnight fixes. The many decades and multiple generations it took for the long march through the institutions to bring us to our current state can only be counteracted through an equally long period of renewal. As the cultural Marxists attacked the family and hijacked education, watching the consequences ripple through to the rest of society, so too must we rebuild the family and reclaim education over a long period of time. If this is viewed as a political project with goal posts, we will be doomed to fail. Instead, this should be viewed as an unending, cyclic process of passing on and telling stories to inspire meaning and bravery. So, reject modernity, embrace tradition!
It’s Not Just Any Christmas, It’s a Little Shop of Horrors Christmas
What is Christmasy about setting fire to Christmas cards? What is festive about a giant Venus flytrap almost eating a small dog? Nothing, but apparently those are the kinds of Christmases two of the largest high-end retailers are trying to sell us, and we aren’t buying.
The release of Christmas ads in November launches the holiday season, and there are few greater British traditions than gathering around the kettle in the work kitchen to talk about the new John Lewis advert the day after it’s aired.
But the first major retailer to release its ad did not get the reaction it had hoped for. Marks & Spencer faced a backlash over its ‘Love Thismas, Not Thatmas’ ad, which sent the message that traditional Christmas needs to be burnt down, shredded, smashed, and go swimming with the fishes.
In one scene of the retailer’s clothing and home campaign, Sophie Ellis-Bextor turns her attention from browning marshmallows on a gingerbread house with a kitchen blowtorch to setting a stack of Christmas cards on fire. In another, paper hats get mulched into confetti, an elf gets launched off the roof of a house with a baseball bat – you get the idea.
Sound the klaxon, our clothing and home Christmas ad for 2023 is here! #LoveThismasNotThatmas pic.twitter.com/uI0tKNnIGc
— M&S (@marksandspencer) November 1, 2023
It ends with the voiceover saying: ‘This Christmas, do anything you love.’
‘Do anything you love.’ Eschew the spirit of charity. Destroy Christmas and make it all about you. Not about family. Not about children. Reject tradition.
The John Lewis ad was worse. If the Little Shop of Horrors did Christmas ads, it would look like this.
John Lewis Christmas advert 2023 – Watch ad that follows boy’s quest for perfect tree with key tearjerker moment pic.twitter.com/JrHrOacjGy
— The Sun (@TheSun) November 9, 2023
In short, a boy’s Christmas tree seed grows into a giant voracious Venus flytrap with multiple sharp-toothed mouths, that at one point appears to snap after the family’s Pomeranian. Fearful of the carnivorous plant, the boy’s mother, grandmother, and sister take it outside.
But the narrative that you shouldn’t judge a predatory plant based on its natural inclination triumphs when the family joins the flytrap in the garden with their presents. And as if taking inspiration from the feverish delusions of a sick toddler, the ad ends with the plant snatching the wrapped gifts, gobbling at them, and spitting them back at the family, unwrapped.
John Lewis’s message is spelt out and very much the same as M&S: reject tradition. Or as the major retailer phrased it, the ad “celebrates the joy in the UK’s changing Christmas traditions.”
At one time, John Lewis set the standard for Christmas ads. Memorable favourites like Monty the Penguin (2014), the 2010 montage ad accompanied to Ellie Goulding’s rendition of ‘Your Song’, or the adventurous snowman ad of 2012, were warm, festive, and at times tear-jerking. They celebrated dreaming and childlike innocence. They felt like they were produced with true love for the season. While not all were cookie-cutter traditionally Christmasy in appearance, they conveyed those timeless values of family, sharing, hope, and gratitude. They were crafted with the skill of Don Draper.
The 2023 John Lewis ad is ugly nightmare fodder.
The affordable food retailers, however, embraced and celebrated the traditional messages of Christmas.
Asda leans enthusiastically into the festive season with its joyful, light-hearted ‘Make This Christmas Incredibublé’ ad, featuring Michael Bublé as a store quality officer.
No-one loves Xmas as much as us 🤩🎄💚
— Asda (@asda) November 4, 2023
Okay, there might be one person – our NEW Chief Quality Officer Michael Bublé 🎤
Watch to see how he's been helping us make this Xmas one to remember @michaelbuble #AsdaXmasBublé #AsdaIncrediBubléChristmas https://t.co/f4lYJJn7w7 pic.twitter.com/Kr2HE3PXyP
Showing off turkey, mince pies, panettone, and enough cheeses to put a lactose intolerant into a coma, Bublé is funny and ostentatious. The sets are tastefully but festively decorated, and the ad is finished with the singer joining a choir of staff in an energetic rendition of ‘Walking in a Winter Wonderland’.
Asda struck the right chord and knew its audience. It knows they’re suffering under the cost-of-living crisis and says without saying: you can still afford to have a nice Christmas dinner this year.
See what happens when Kevin and his vegetable friends visit William Conker’s Christmas Factory in our 2023 Christmas Ad 🎄 #AldiAmazingChristmas #KevinTheCarrot pic.twitter.com/oqDqJbBOQq
— Aldi Stores UK (@AldiUK) November 6, 2023
The Aldi advert sees a return of Kevin the Carrot, this time in his adventures in a Christmas food-themed Willy Wonka’s factory. Narrated by British actor Jim Broadbent, lines of poetry convey deep-rooted values such as: ‘Only Kevin the carrot clearly understood the true meaning of Christmas and the importance of being good.’
And: ‘The season of goodwill was truly in the air, for Christmas is a time that’s sweeter when you share.’
But it was fellow German food retailer Lidl that stole the paper Christmas crown. A racoon who loves Christmas goes on a little hero’s journey to make sure a toy monkey gets delivered to the boy who he’s been watching through the window. While never discovered to be the creature that placed the toy under the tree, the raccoon is rewarded when the family dog takes a portion of Christmas dinner outside to share with him.
It was old John Lewis: full of innocence, adventure, mild peril, and generosity. It was moving and warm. It shared an important message: little gestures of kindness matter.
We're ready for A Magical Christmas here at Lidl, are you? 🎄✨#LidlChristmas #AMagicalChristmas pic.twitter.com/ucC69AFw14
— Lidl Ireland (@lidl_ireland) November 2, 2023
And the latter two retailers put their money where their mouth is: both Aldi and Lidl are part of the Neighbourly charity network to distribute unsold surplus food to local communities. Lidl is also hosting toy banks for donations in their stores and has said that it will be producing the monkey and raccoon toys for sale, with the proceeds going to Neighbourly.
These aren’t just empty words, but action. The desire to help comes through these ads and touches people. These are authentic expressions of the season of good will towards all men.
What I and people who took issue with in the M&S and John Lewis ads is not that some individuals reject traditional Christmas. People are free to have whatever unconventional Christmases they want and not be judged for it.
No, this is about people tired of being nudged by forces that shape our society and craft our media that our world must change. That even though we are in the majority, we must have our expression of our culture and tradition come second – or not at all – to unconventionality, modernity, and progression.
‘Don’t touch or break our Christmases,’ we’re saying.
These messages from John Lewis and Marks & Spencer were intentional, crafted by professional agencies that have been captured and work to serve the woke agenda and their ‘purpose-driven’ campaigns – sometimes at the expense of profit. While unconventional unChristmas ads are not woke in themselves, they originate from the same spiteful anti-tradition place.
But the fickle monster you feed eventually comes back to bite you over any perceived form of ‘hate’, slight, or microaggression. Case in point: Marks & Spencer had shared a still outtake from their ad to social media, showing paper hats burning in a fireplace, before quickly deleting it and apologising for any offence caused.
Marks & Spencer is facing backlash after it unveiled its Christmas advert for 2023 showing burning paper hats having the colors of #Palestine flag. pic.twitter.com/por1Xuq1fu
— Quds News Network (@QudsNen) November 1, 2023
Not apologising to those Christmas-lovers who might have thought it mean spirited, but to pro-Palestinian activists. Yes, Marks & Spencer took seriously complaints that burning red and green paper hats was insensitive and stoking tensions because Palestinian flags also happen to feature red and green.
Let no good pandering go unpunished.
This is Anglofuturism
Britain is in doldrums, the days of Cool Britannia are a distant memory, the Empire is now our greatest shame, and pride in our nation has been replaced with an ever-expanding circle of chaos. Whether it’s the Tories’ latest political implosion, Labour backbench rebellions, the cost-of-living perma-crisis, Brexit bickering, or simply ‘decolonising’ anything and everything involving a dead white male. We’re in a mess, the vibe is gone, it’s so over, as they say.
But wait, what is this? Is that a green shoot of optimism I see before me?
Yes, last year a bold new philosophy for Britain was articulated by Aris Roussinos, he called it Anglofuturism, and after being published online it promptly disappeared into the dark corners of the internet where old e-articles go to make out with forgotten cat memes.
That is until it was rediscovered by a Twitter anon who armed appropriately enough with futuristic AI technology created the infamous ‘Anglofuturism Aesthetics’ thread, propelling the concept from online academic-journal obscurity to the heady heights of niche micro-influencer obscurity!
ANGLOFUTURISM AESTHETICS THREAD – “A Better Future IS Possible!” 🧵 pic.twitter.com/J55xjn5lz4
— ɖʀʊӄքǟ ӄʊռʟɛʏ 🇧🇹🇹🇩 (@kunley_drukpa) October 4, 2023
And what followed was the birth of an idea; obscure YouTubers envisaged a steam-powered galactic empire, a heady mix of nostalgia and farsighted fantasy. It was, dare I say in our grim times, fun! This sense of frivolousness prompted me to seek out the original article ‘It’s time for Anglofuturism’ and what I found surprised me.
Anglofuturism was no glib joke, but contained the seeds of a whole new mental model for Britain and the Anglosphere itself. While these ideas were not fully formed and the lively debate in the comments section indicated there was not a consensus, it did get people talking. Most importantly it took aim at a positive vision for the future, in stark contrast to the managed decline offered by our managerial class. But what is Anglofuturism?
Firstly, it is an acknowledgment of where we are at, the economic tailspin we are in and the cultural collapse we are experiencing. This is the death of neo-liberalism and we have front-row seats. The once shiny new successor to Keynesian economics (which itself came to an inglorious end during the strikes and uncollected rubbish of the Seventies) has now also had its day. The ruinous effects of neo-liberalism’s gluttonous money printing, addiction to debt and slavish devotion to short-term profits are all becoming horribly clear. And the consequences of this will only intensify.
Further the people’s discontent with an intellectual elite wedded to bizarre continental philosophies that distort reality, destroy grand narratives, and reduce everything to a mere power struggle is growing too. It is becoming clear that postmodernism and Marxism in its various strains are also destined to join neo-liberalism on the scrapheap of out-of-date and out-of-touch ideas. They’ve had their moment and that moment is over. But the problem we face is the lack of a clear successor waiting in the wings.
And so, we must build it. And this is Anglofuturism, the blueprint for an exciting new intellectual direction. One that is deeply Anglo incorporating the key cultural attributes and identity that have been the source of Britian’s strength for centuries.
It begins with the nuclear family, recognising this is the engine that drives our society, and one we must embrace, cherish and support if we are to have a future. Then housing, the cliché that an Englishman’s home is his castle points to a deeper truth; our homes are our security and our sanctuary. But the recent trend to treat them like speculative financial products rather than where we live and raise the next generation of Britons is a massive social failure that must be rectified.
Next is crime; a low-crime society is a high-trust society, and a high trust society is a wealthy society. For centuries we ensured that crime was punished so communities could flourish and we must resurrect this ethos. Education is the bedrock of Anglo inventiveness and creativity, which gifted us the Industrial Revolution that we generously shared with the world. We must reinvigorate our devotion to learning to once again unlock new opportunities.
And finally, competency. The ‘best man for the job’ is a trope, but it is one that took centuries to establish. From breaking down clannish tendencies to banning cousin marriage and establishing trade guilds, the Anglo vision of a society is one built on competence. We must again enshrine this in our nation. This is the rich cultural heritage of the Anglosphere. Our current reticence to embrace it, and profit from it, is the result of the huge shifts in consciousness that have taken place since the cultural revolution of the Sixties, and the hangover from a century of brutal warfare that we are not yet recovered from. However in terms of the timespan of Anglo culture itself, this is a mere blip, we must look back over a thousand years of intellectual capital and remember the boldness of King Alfred the Great, who, alone with no more than 30 acres of swampy marshland in Wessex, had a vision to unite the warring Kingdoms of Britain into a single England. It’s because of his grand vision that we are the land we are today.
But Anglofuturism is more than looking back. It is also about creating a vision for Britain that is not focused on the next election cycle or TikTok politics of popularity. Instead, it is a commitment to a multi-generational project that truly looks to the future. A future that we as a nation create for our descendants, and the belief that we should leave to them a prosperous, resilient and united Britain, rather than a collapsing economic zone drowning in debt.
A belief that we should utilise our ingenuity, creativity, and technological acumen to power a bold vision for 21st-century Britain, fearlessly embracing radical new ways of doing things that can exponentially change our world. Think of the revolution that was the steam train then times it by a thousand; this is Anglofuturism.
Kino
Squandering a Revolution
Ignore the snarky joylessness of self-important losers and the performative perplexing of Very Serious Political Commentators, the past few days have been hilarious. Brought down by inadvertent kamikaze molester “Pincher by name, Pincher by nature” Chris Pincher, appointed to be (you couldn’t write this) a party whip, amounts to more than another Gay Tory Predator scandal. Instead, we are finally witnessing the end of Johnson’s inert and wasteful premiership.
Here I was thinking we’d be dealt an anti-climactic resignation over a piddly piss-up. All those times half-wit pundits, with their mundane alcoholism, lapsed anuses and hyperlinked relatives on Wikipedia, insisted that “it’s over” for Boris, only for such prospects to be dashed when a big fat *nothing happens*, effectively wore down the belief that Johnson could be removed at all.
However, just as a monkey could write Shakespeare if given enough attempts, journalists occasionally conjure the ability to publish something with a kernel of veracity, in this case – the government is imploding because Johnson feigned ignorance of Pincher’s pinching.
As funny as it is to see Boris’ top guys do a 180 in less than 24 hours, contrasted to the inexhaustible ride-or-die energy of Nadine Dorries, you came here for Insightful Political Commentary; a lucid outline of What is To Be Done, you came here for The Ideas. Very well, ladies and gentlemen. After all, chaos is a ladder.
Like most conservatives, I am torn between my hatred of Johnson and my hatred of full-time Johnson-haters. The former was handed an unconstrained sledgehammer to smash the Blairite machine. Criminally underutilised, it was primarily used for tasks completely incongruent with the telos of a sledgehammer – Building Back Better, Levelling Up, etc.
Adding insult to injury, the constructivist rhetoric was entirely devoid of actual construction. Housing prices continue to climb, the borders are wide open, the tax burden continues to punish the most productive, supply-side solutions to energy problems are practically non-existent, and all ‘attempts’ at resolving [REDACTED] have mounted to nothing more than superficial lip service to whip up momentary support from disaffected voters. For a man versed in the classics, Boris should know Heraclitus’ First Cause – Construction and Destruction were born joined at the hip, the fire which festers within a blacksmith’s forge and the fire which springs from a Molotov cocktail are the same force.
In the case of the latter, the full-timers sincerely believe that Boris has made extensive use of his loaned hardware, obliterating Those Ancient British Traditions: the NHS (1946), the HRA (1998), Supreme Court (2005), Britain’s membership of the EU (1992), etc. Ironically, had Johnson aspired (never mind achieved) more than a measly fraction of the aforementioned, he would be leading by double-digits.
The derangement of these full-timers makes one wish Johnson had made like Caesar and crossed the Rubicon. If not to pursue a revolutionary agenda, then to amplify the deserved misery of Britain’s worst inhabitants; the type of people that Tumblr-format tweets about having integrity in politics – “The Parties, The Lies, The Cheese and Wine, it’s DISGUSTING” – as they listen intently to the most recent episode of Alastair Campbell’s podcast.
It’s old news, but it’s worth remembering that Boris is not a conservative. He’s a liberal whose self-obsession disrupted what would have been his natural Brexit alignment. He’s managed to court support from people who would otherwise not have supported him, knowing full well they have little realistic alternative. A socially liberal chieftain of a socially conservative tribe, a Globalist commander of a nationalist army, Boris’ betrayal of both sides of Britain’s politico-cultural schism are finally converging, depriving him of what he values the most: popularity. Like Louis XVI awkwardly donning the revolutionary bonnet, Johnson found himself divided between his political inclinations, those of his new compatriots, and his desire to remain popular irrespective of circumstance.
A high-tax, high-immigration, high time-preference, low-wage, low-cohesion, low-growth Britain with a political life routinely interspersed by the misdeeds of a Prime Minister that backstabs his own supporters and elevates pillow-talk policy over national priorities. Brexit was always more than technical independence from the EU. Sovereignty was never the ultimate end. The Leave coalition was underpinned by the pursuit of sovereignty, but it was the prospect of exercising this sovereignty that brought about the electoral realignment. It was why the Nationalist-Brexiteer majority and the Globalist-Brexiteer minority could co-operate. Not a means to an end, but a means to greater means, and from these greater means a true ultimate end. A half-baked means (see: ECHR), but a necessary means, nonetheless. Even without Brexit, to waste such a supermajority, as a Conservative, should be grounds for life imprisonment.
In case you haven’t noticed, I am not outraged at “THE LIES”. Expecting politics to be free of lies, noble or otherwise, is like expecting the sea to be free of fish. It’s that a national revolution, literally decades in the making, has been squandered by a fat, self-absorbed, Etonian mutt that cares more about getting cummies from mid women and supporting The Current Thing like the insufferable libtard he is, rather than using a historic opportunity to liberate his country from institutionally inflicted self-harm; a stranglehold that will certainly be reinforced under a Labour government.
Speaking of Labour, how is the mortician doing? Has he recovered from his divorce yet? If the polls are to be believed, he’s doing better than a country with half-serious political system would allow. I do not believe mass reconversions to Labour will occur. The next election will be decided by the magnitude of [c]onservative disaffection.
And what of future Conservative leadership? Oh joy, a choice between Loony Liz and Total War Tom; an accidental hot war with Russia vs an intentional hot war with Russia. Decisions, decisions. Then again, what do you expect when given the option between an ex-Liberal Democrat and a dual-citizen neocon? It all screams “Look at me, I’m a rat that will jump wherever!”.
Rishi? The ‘Diversity Built Britain’ guy? Okay sure, he didn’t run cover for Pincher but he’s still a dull gremlin with a non-dom wife – not a good look! Besides, he’s still “implicated” by “Partygate” – an even worse look! Hunt deserves more contempt than can be articulated by the human tongue. Javid is an NHS fundamentalist. Not only does he worship the NHS, but he also unnecessarily attacks people on Twitter that dare to criticise it. Braverman is a Judas Goat – either she puts up or shuts up. Does anybody have an opinion of either Gove or Zahawi that isn’t associated with unnecessary underhandedness?
Mordaunt will be Theresa May 2.0 – the untainted candidate that slides in from the side-lines, garnering popularity from the prospect of some maternal reconciliation. Indeed, thoroughly disgusting prospect. This country can’t endure five seconds of political excitement without wailing like an infant. Speaking of Theresa May, she’s rumoured to be a potential “caretaker Prime Minister”. Does nobody remember her premiership? She embodies this country’s infuriating sentimentalism towards mediocre politicians. Furthermore, the timeline will be unbearable. Every sycophantic bint with a “Bloody Difficult Woman” tote bag from 2017 will re-emerge, squawking about the totally-not-astroturfed-and-definitely-politically-attractive notion of Compassionate Conservatism.
For all his faults, at least Boris had some charisma. One suspects people were banking on 2019 to make Parliament a little less boring, replenish it with at least a few interesting people. But no, we got potato sacks.
It is easy to imagine that Johnson will become a Girardian scapegoat for the coming Parliament – an environment defined by his ostracization and anything that can be construed to be representative of his presence (very easy for a man with the track record of an erratic ape). Onto him, all the ‘sins’ of the past 3 years will be unanimously piled; his resignation will represent an exorcism that alleviates whatever is political convenient for his ex-compatriots and the neurotic full-timers. An insulated circlejerk which will barely disguise an aggressive repositioning against the progressively minded – “if Johnson’s premiership was the result of Brexit, then nothing like Brexit can happen again”, and so on.
In the end, whatever maximises political randomness may best serve the betrayed. January 6th kino isn’t coming to Britain (we’re far too boring for something like that), but there’s certainly no reason to support the Conservatives at the next election. At this point, democratising the Conservative Party should be on the table. We cannot carry on with a system which consistently produces such terrible representatives – ones which can so easily abuse (literally and figuratively) the party’s support base and continuously get away with it.
Brace for the self-righteous gush that will begin to flow courtesy of Johnson’s neuron-cranking retardation. The BBC will find another reason to put Ian Hislop on the television and use “Should I Stay or Should I Go” in whatever slapdash documentary comes out of this. Unfunny comedians will tune into radio shows to compare Johnson to their ex-boyfriends. “The 2022 UK Government Crisis Shows the Enduring Problem of White Male Fragility. Discuss.” (40 marks).
Enoch Powell said that “all political careers end in failure”. On a technical level this is true, but few political careers end with the squandering of a revolution. The boy who wanted to be king was gifted the crown on a velvet cushion and, when placing the crown onto his head, dropped it into the gutter. Here’s hoping the crown can be retrieved by someone of kingly calibre and salvage the future that could have been.
Neoconservatism: Mugged by Reality (Part 1)
Well, they finally got Liz Cheney but she sure deserved what was coming to her. After being thwarted by the President Trump backed conservative lawyer Harriet Hageman from her once safe seat as the Republican candidate and Congresswoman for Wyoming’s sole congressional district, Cheney now finds herself in the wilderness amongst an array of anti-Trump Republican candidates who have been falling like flies in recent Republican primary races for Congress.
The overwhelming paleoconservative pro-Trump wing of the Republican party has taken no prisoners and given no apologies for enacting democratic vengeance on those who they perceive to be traitors to the America First agenda. Decrying many, including Cheney herself, as RINO war-hawks who are more interesting in pandering to Democrats and embezzling public funds into the pockets of the corrupt military-industrial complex than standing up for the American people.
The successes of the America First Republicans have been many, but dethroning Cheney from her seat is being lauded as the crowning jewel of their recent achievements. Not just because she was anti-Trump, but because she belonged to and was essentially the heiress to an ideological sect that these AF Republicans have declared as their public enemy No.1 – neoconservatism.
Neoconservatism is not exactly in vogue in political modernity nor do you hear many politicians and pundits wilfully adhering to the label as a badge of honour. If anything ‘neoconservative’ has become a derivative label to signify an ‘establishment’ Republican who is in bed with organisations and people who lie and work against the American people. However, neoconservatism was once the coolest ideological kid on the right-wing block and had a plethora of supporters who carried the mantle unashamedly. More than that, neoconservatives were a powerful force to be reckoned with at the turn of the 21st century, to such an extent that much of the establishment at that time were self-professed neoconservatives.
How can a group that was riding on such a high and essentially controlled everything worth controlling have floundered and failed to such a large degree? (their ideology now being as respectable as a Pagan nudist in a Catholic Mass). To answer this question, it is important to first understand what neoconservatism is.
What is Neoconservatism?
Neoconservatism found a home in the American and British right-wings during the early 20000s, although its origins largely date back to the 1960s. Those associated with the term often declared that neoconservatism could not be coherently defined, nor had a unified manifesto or creed. It is worth noting that this has led to neoconservatism becoming a largely misused term; often being reduced to an epithet in which to throw at anyone who supports an interventionist foreign policy. However, the idea that neoconservatism cannot be coherently defined is not entirely accurate. One only has to look at the plethora of books, articles and journals that illustrates the existence of a coherent intellectual underpinning of neoconservatism. And no intellectual is more important to neoconservatism than Irving Kristol.
The often titled ‘Godfather of neoconservatism’ aptly summed the political philosophy up as the position a liberal adopts after he is “mugged by reality”. What Kristol is illustrating by this turn of phrase, is that the origins of neoconservatism fundamentally come out of the liberal (by which I mean American progressive) side of the political spectrum.
During the 60s, some sections of American liberals increasingly saw that the promotion of liberal social values, weak foreign policy and the ‘Great Society’, as envisioned by President Lyndon B. Johnson, were proving ineffective and misguided. The New Left counterculture, hippie peaceniks and the policy platform of the 60s Democrat Party caused a group of American liberals to move away from this new ideological consensus amongst the left and encouraged them to form their own amongst the right – namely neoconservatism. But it is specifically the peaceniks that neoconservatives hate the most. In Neoconservatism: The Autobiography of an Idea, Kristol lays the blame at the feet of New Left intellectuals for creating much of the pacifistic feeling that existed during the 60s and 70s – sneering at them as ‘sermonising clerics’ who spend their time inflaming passions without having any real grasp on foreign policy. Neoconservatives saw themselves as the remedy to this epidemic of pacifism pushed forward by countercultural leftists, New Left intellectuals and pro-détente Democrats.
While the 60’s were important in formulating the movements ideological malaise, neoconservatism would not see a rise in interest in it until the end of the Cold War. With the USSR gone and the US reigning as the supreme victor of not just the war against Communism but the 20th century at large, many neoconservatives saw this as their opportunity to solidify the US as the dominant power for the next century. This solidification would come about via the development of a new view on US foreign policy which, by today’s standards, is quite radical.
The 1992 ‘Defence Planning Guidance’ document, which was written by the then Under Secretary for Defence for Policy Paul Wolfowitz, can be seen to be the quintessential source in order to properly grasp what neoconservative foreign policy is all about. The document states:
“Our first objective is to prevent the re-emergence of a new rival, either on the territory of the former Soviet Union or elsewhere, that poses a threat on the order of that posed formerly by the Soviet Union. This is a dominant consideration underlying the new regional defence strategy and requires that we endeavour to prevent any hostile power from dominating a region whose resources would, under consolidated control, be sufficient to generate global power.”
In its purest essence then, neoconservative foreign policy is about eliminating potential threats to American global hegemony. But more importantly, eliminating these threats to ensure that America has no rivals, allowing for it to solidifying itself as the superior and dominant power on the world stage. This desire to eradicate all potential threats to secure the safety and dominance of a nation and its ideology is reminiscent of Trotskyist positions concerning ‘permanent revolution’. A ‘permanent revolution’ is the belief that socialist revolutions need to occur on a worldwide basis to combat global capitalist hegemony and, more importantly, secure the futures of pre-existing socialist states. Mirroring Trotsky, Kristol explained that:
“American democracy is not likely to survive for long in a world that is overwhelmingly hostile to American values, if only because our transactions (economic and diplomatic) with other nations are bound eventually to have a profound impact on our own domestic economic and political system.”
This link between neoconservatism and Trotskyism is not an original formulation. Paleoconservatives such as Paul Gottfried and Pat Buchanan have spent their entire careers evidencing this link between neoconservatism and Trotskyism as well as stressing the fact that various neoconservatives were ex-Trotskyists, including Kristol himself. Due to what paleoconservatives consider to be the Trotskyist and thus revolutionary nature of neoconservatism, they consider neoconservatism to be one of the most dangerous ideological groups in existence, with Gottfried writing:
“What makes neocons most dangerous are not their isolated ghetto hang-ups, like hating Germans and Southern whites and calling everyone and his cousin an anti-Semite, but the leftist revolutionary fury they express.”
Alongside Trotsky, Leo Strauss’s influence on neoconservatism is equally as important and, some would say, equally as controversial. However, unlike the Trotsky association – which neoconservatives unequivocally deny – various neoconservatives state Strauss as being a primary influence on their thinking. Strauss’ belief that liberal civilisation was faltering came from a belief that the West had become increasingly nihilistic – Strauss being heavily influenced by the Nietzschean diagnosis of a post-‘God is Dead’ world. “The crisis of the West consists in the West’s having become uncertain of its purpose,” wrote Strauss, and it was this pessimism that led Strauss to the position that it was only the West’s immense military power that gave it any measure of confidence.
This pessimism bled nicely into neoconservatism and justified their views concerning the need to create a new global hegemony in which America was its lord and master. Furthermore, the obsession with military strength as a means to combat this pessimism is a direct inheritance from Strauss and – as elucidated by the Kristol quote earlier – is a core motivator behind neoconservative views on foreign policy. Neoconservatives are fundamentally pessimists, something that they do have in common with their paleo and more mainstream conservative counterparts.
So, if neoconservatism believes in foreign interventionism as a method in which to establish and maintain American global hegemony and quell the nihilism innate in modern America, the question remains: what does American global hegemony entail? Ultimately, it entails every country adopting the values of the United States i.e. liberal-democratic capitalism. For the early 20th-century historians reading, this may sound similar to President Woodrow Wilson’s position on US foreign policy – you would be correct. Neoconservatives see themselves as being the inheritors of the Wilsonian tradition regarding foreign policy and this fact becomes quite starkly clear when one looks at American involvement in the First World War.
The famous American First World War propaganda poster ‘Make the World Safe for Democracy’ is a great example of the ethos of Wilsonian foreign policy. Enter the war, win it and then use the aftermath to overturn European monarchies so that they can become democracies and thus fall under the sphere of American influence. The austrolibertarian political philosopher Hans Hermann Hoppe elucidates in his book Democracy: The God That Failed the significance of Wilson entering the United States into the First World War:
“World War I began as an old-fashioned territorial dispute. However, with the early involvement and the ultimate official entry into the war by the United States in April 1917, the war took on a new ideological dimension. The United States had been founded as a republic, and the democratic principle, inherent in the idea of a republic, had only recently been carried to victory as the result of the violent defeat and devastation of the secessionist Confederacy by the centralist Union government. At the time of World War I, this triumphant ideology of expansionist democratic republicanism had found its very personification in then U.S. President Wilson. Under Wilson’s administration, the European war became an ideological mission—to make the world safe for democracy and free of dynastic rulers.”
Replace ‘Wilson’ for ‘Bush’, ‘European’ for ‘Middle Eastern’ and ‘dynastic’ for ‘theocratic’ and you have the foreign policy platform of a modern neoconservative. Like Wilson at the end of the First World War, neoconservatives saw the end of the Cold War as an opportunity for a new ‘Pax Americana’. A time in which they could universalise the American system of liberal-democratic capitalism and thus eradicate the potential for any ideological opposition. This idea somewhat echoes Francis Fukuyama’s seminal work The End of History and the Last Man, in which he illustrates, via the use of a Hegelian historical framework, that liberal democracy has emerged as the final and universal form of human governance, with the United States as its custodial head. Neoconservatism (a label Fukuyama once associated himself with), via American military involvement abroad, simply wishes to bring about this new American-dominated epoch closer to the present.
Interventionism for the sake of strengthening and maintaining American global hegemony isn’t the only element of neoconservatism that makes it unique from regular American conservatism. In the words of Ben Wattenberg (a key neoconservative intellectual), neoconservatives also believe in a “muscular role for the state” at home. Hence, neoconservatives advocate for sizeable welfare states along with heavy regulation and taxation of the economy to ‘rig’ capitalism in the manner they wish it to operate. To use the language of James Burnham, one can describe neoconservatives as being the rightist torchbearers of the managerial state that began under FDR via their wish to maintain and even expand the post-Second World War welfare-warfare regulatory state. While a jaded right-libertarian like myself finds this abhorrent, neoconservatives do not share the libertarian fear of state power, as Kristol wrote:
“Neoconservatives are impatient with the Hayekian notion that we are on ‘the road to serfdom.’ We do not feel that kind of alarm or anxiety about the growth of the state in the past century, seeing it as natural, and indeed inevitable.”
Authoritarianism, welfarism, managerialism and, most importantly, a pessimistic belief in military intervention as the tool in which to promote and enforce American ideals abroad and secure American dominance internationally are all core elements of what defines a ‘neoconservative’. But while these ideas were being developed in the 60s and thereafter, it wasn’t until the dawn of the 21st century that neoconservatism would find its hands tightly wrapped around the levers of power.The Ascendancy of Neoconservatism
When George Bush Jr took his oath of office in January 2001, it was not thought that he would become a president known for foreign wars and the growth of the American welfare-warfare state. Bush’s candidacy for president did not chest thump about the might of the American military, nor did it view military intervention as the sole way in which America should conduct itself on the international stage. Nor was Bush particularly authoritarian, at least in comparison to his contemporaries. As Stefan Halper’s book America Alone: The Neo-Conservatives and the Global Order highlights, Bush’s platform on foreign policy was originally in direct contradiction to neoconservatism. Many neoconservatives were so opposed to Bush that some ended up funding and supporting Bush’s primary opponents such as John McCain (a long-time icon of the neoconservative right) and stressed amongst neoconservative allied Republicans that “getting into bed with Bush is a mistake”. However, once it was clear Bush had won the candidacy, and later the presidency many neoconservatives flocked around him and were overjoyed. They now found themselves away from the think tanks and university campuses they resided in and finally within Washington’s halls of power; taking key positions in the Pentagon, the Vice President’s Office, and the National Security Council.
Vice, a film about the life and career of Vice President Dick Cheney, perfectly illustrates the extent to which neoconservatives were now in control. In one memorable scene, Cheney (played by Christian Bale) signals to his Chief of Staff Scooter Libby to explain the “lay of the land” of the Bush administration to his new team. Libby gleefully highlights how, thanks to the incompetency of Bush’s team, Cheney-allied neoconservatives now ruled the roost. Paul Wolfowitz, Donald Rumsfeld, John Bolton, David Addington and the Vice President’s Daughter Liz Cheney (remember her?) to name but a few, formed core parts of the new neoconservative regime. From the State Department to the Pentagon to the Oval Office itself, neoconservatives now had unobstructed access to the steering wheels of power that would allow them to drive the American state in the way they saw fit. The neoconservative state had finally arrived.
However, one crucial part of the puzzle was missing – an excuse. The neoconservatives couldn’t swing the American state in the manner they saw fit without a viable reason. After all, their policies and ideas would prove immeasurably unpopular with the general public and indeed other members of the political class. Especially considering the administration was already perceived to be on a knife-edge after only winning the election by 537 votes. So, they simply bided their time until an opportunity presented itself.
Luckily for the neoconservatives now riddled throughout the Bush administration, they did not have to wait for long.
Liberalism and Planned Obsolescence
Virtually everyone at some point has complained about how their supposedly state-of-the-art phone, tablet, laptop, or computer doesn’t seem quite so cutting-edge when it either refuses to work properly or ceases to function entirely after a disappointingly brief period of time. This is not merely the grumblings of aggravated customers, but a consequence of “planned obsolescence.” The term dates back to the Great Depression, coined by Bernard London in his 1932 paper Ending the Depression Through Planned Obsolescence, but a practically concise definition comes courtesy of Jeremy Bulow as “the production of goods with uneconomically short useful lives so that customers will have to make repeat purchases.” Despite being an acknowledged (and in some cases encouraged) practice, it is still condemned; both Apple and Samsung have faced legal action on multiple occasions for introducing software updates which actively hinder the performance of older devices. In the face of all this, planned obsolescence isn’t going anywhere so long as there is technology, nor does anyone expect it to. It is, as death and taxes are, one of the few certainties of life.
As the title of this essay suggests, I do not intend to delve any further into the technological or economic ethics of planned obsolescence. Interesting as they may be, I want to focus on how the concept appears in a political context; more specifically, in liberalism.
One of the core tenets of liberalism is a belief in the “Whig interpretation of history.” In his critique of the approach, aptly titled The Whig Interpretation of History, Herbert Butterfield outlined the Whig disposition as being liable to “praise revolutions provided they have been successful, to emphasize certain principles of progress in the past and to produce a story which is the ratification if not the glorification of the present.” To boil it down, it is the belief that history is a continuous march of progress, with each successive step freer and more enlightened than the last. A Whiggish liberal is dangerously optimistic in their opinion that history has led to the present being the greatest social, economic, and political circumstances one could hitherto be born into. More dangerous still is their restlessness, for as good as the present may be, it cannot rest on its laurels and must make haste in progressing even further such that the future will be even better. The pinnacle of human development lasts as long as a microwave cooking a spoon, receiving for its valiant effort little other than sparks, fire, and irreparable damage resulting in its subsequent replacement.
The unrepentant Whiggery of the modern world has prompted scholars of the Traditionalist School of philosophy to label it an aberration amongst all other societies, as the first which does not assign any inherent value to, or more accurately, openly detests, perennial wisdom (timeless knowledge passed down through generations) and abstract metaphysical truths. In the words of René Guénon, “the most conspicuous feature of the modern period [is its] need for ceaseless agitation, for unending change, and for ever-increasing speed.” Quite literally, nothing is sacred. One of the primary causes of this is that modernity, defined by its liberalism, is materialist, and believes that anything and everything can and should be explained rationally and scientifically within the physical world. The immaterial and the spiritual are disregarded as irrational, outmoded and unjustifiable; it is, as Max Weber says, “disenchanted.”
To understand this further, we must consider Plato’s conceptions of the two distinct natures of the spiritual and the material/physical world, “being” and “becoming” respectively. Being is constant and axiomatic, characterised by abstract ideas, timeless truths and stability. Becoming on the other hand, as the nature of the physical world, reflects the malleability of its inhabitants and exists in an endless state of flux. Consider your first car, it will alter with time, the bodywork might rust and you may need new parts for it, and indeed it may eventually be handed on to a new owner or even scrapped entirely. Regardless of what changes physically, its first car status can never be separated from it, not even when you no longer own it or it’s recycled into a fridge, for it will always hold a metaphysical character on a plane beyond the material.
Julius Evola, another Traditionalist scholar, succinctly defined a Traditional society as one where the “inferior realm” of becoming is subservient to the “superior realm” of being, such that the inherent instability of the former is tempered by orientation to a higher spiritual purpose through deference to the latter. A society of liberalism is unsurprisingly not Traditional, lacking any interest in the principles of being, and is instead an unconstrained force of pure becoming. Perhaps rather than disinterest, we can more accurately characterise the liberal disposition towards being as hostile. After all, it constitutes the “customs” which one of classical liberalism’s greatest philosophers, John Stuart Mill, regarded as “despotic” and a “hindrance to human development.” Anything which is perennial, traditional, or spiritual is deleterious to the march of progress unless it can either justify its existence within the narrow rubric of liberal rationalism, or abandon its traditional reference points and serve new masters. With this mindset, your first car doesn’t represent anything to do with the sense of both liberation and responsibility that comes with being able to transport yourself, it is simply a lump of metal to tide you over until you can get a more expensive lump of metal.
Of course, I do not advocate keeping a car until it falls to pieces, it is simply a metaphor for considering the abstract significance of things which may be obscured by their physical characteristics. In the real world, the stakes are much higher, where we aren’t just talking about old cars but long-standing cultural structures, community values and particularisms, and other such social authorities that fall victim to the ravenous hunger of liberal progressivism.
The consequence of this, as with all things telluric, material, or designed by human effort, is impermanence. Without reference to and deliberate denigration of being, ideas, concepts and structures formed within the liberal system have no permanent meaning; they are as fickle as the humans who constructed them. Roger Scruton eloquently surmised this conundrum when lambasting what he called the “religion of Rights”, whereby human rights, or indeed any concepts of becoming (without spiritual reference, or to being) are defined by subjective “moral opinions” and “legal precepts.” Indeed “if you ask what rights are human or fundamental you get a different answer depending whom you ask.” I would further add the proviso of when you ask, as a liberal of any given period appears to their successors as at best outdated or at worst reactionary. Plucking a liberal from 1961, 1981, 2001, and 2021, and sitting them around a table to discuss their beliefs would result in very little agreement. They may concur on non-descript notions of “freedom” and “equality”, but they would struggle to find congregate over a common understanding of them.
To surmise, any idea, concept or structure that exists within or is a product of liberalism is innately short-lived, as the ceaseless agitation of becoming necessitates its destruction in order to maintain the pace of the march of progress. But Actual people, regardless of how progressive or rational they claim to be, rarely keep up with this speed. They tend to follow Robert Conquest’s first law of politics: “everyone is conservative about what he knows best.” People are naturally defensive of the familiar; just as an aging iPhone slows down with time or when there’s a new update it can’t quite cope with, so too will liberals who fail to adapt to changing circumstances. Sadly for them, the progressive thirst of liberalism requires constant refreshment of eager foot-soldiers if its current flock cannot keep up, unafraid to put down any fallen comrades if they prove a liability, no matter how loyal or consequential they may have once been. Less, as Isaac Newton famously wrote, “standing on the shoulders of giants”, more “relentlessly slaying giants and standing on a pile of their fallen corpses”, which as far as I’m aware no one would ever outright admit to.
You don’t have to look particularly far to find recent examples of this. In the 1960s and 70s, John Cleese pioneered antinomian satire such as Monty Python and Fawlty Towers, specifically mocking religious and British sensibilities. Now, in response to his assertion that cultural and ethnic changes have rendered London “no longer English”, he is derided for being stuffy and racist. Indeed, Ken Livingstone, Boris Johnson, and Sadiq Khan, the three progressive men (in their own unique ways) who have served as Mayor of London since its establishment in 2000, lined up on separate occasions to attack Cleese, with Khan suggesting that the comments made him “sound like he’s in character as Basil Fawlty.” There is certainly a poetic irony in becoming the very thing you once satirised, or perhaps elegiac for the liberals who dug their own graves by tearing down the system, only to become the system and therefore a target of that same abuse at the hands of others.
Another example is George Galloway, a staunch socialist, pro-Palestinian, and unbending opponent of capitalism, war, and Tony Blair. Since 2016 however, he has come under fire from fellow leftists for supporting Brexit (notably, something that was their domain in the halcyon days of Tony Benn, Michael Foot, and Peter Shore) and for attacking woke liberal politics. Other fallen progressives include J. K. Rowling and Germaine Greer, feminists who went “full Karen” by virtue of being TERFs, and Richard Dawkins, one of New Atheism’s four horsemen, who was stripped of his Humanist of the Year award for similar anti-Trans sentiments. All of these people are progressives, either of the liberal or socialist variety, the difference matters little, but their fall from grace in the eyes of their fellow progressives demonstrates the inevitable obsolescence innate to their belief system. How long will it be until the fully updated progressives of 2021 are replaced by a newer model?
On a broader scale, we can think of it in terms of generational divides regarding social attitudes, where the boomers and Generation X are often characterised as the conservatives pitted against the liberal millennials and Generation Z. Yet during the childhood of the boomers, the United Nations was established and adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and when they hit adolescence and early adulthood the sexual revolution had begun, with birth control widespread and both homosexuality and abortion legalised. Generation X culture emerged when all this was fully formed, and rebelled against utopian boomer ideals and values in the shape of punk rock, the New Romantics, and mass consumerism. If the boomers were, and still are, ceaselessly optimistic, Generation X on the other hand are tiringly cynical. This trend predictably continued, millennials rebelled against Generation X and Generation Z rebelled against millennials. All of them had their progressive shibboleths, and all of them were made obsolete by their successors. To a liberal Gen Zer in 2021, it seems unthinkable that will one day be the crusty boomer, but Generation Alpha will no doubt disagree.
Since 2010, Apple’s revolutionary iPad has had 21 models, but the current could only look on in awe at the sheer number of different versions of progressive which have been churned out since the age of Enlightenment. As an object, the iPad has no choice in the matter. Tech moves fast, and its creators build it with the full knowledge it will be supplanted as the zenith of Apple’s capabilities within two years or less. The progressives on the other hand are inadvertently supportive of their inevitable obsolescence. Just as they were eager not to let the supremacy of their ancestors’ ideas linger for too long, lest the insatiable agitation of Whiggery be halted for a moment, their successors hold an identical opinion of them. Their imperfect human sluggishness will leave them consigned to the dustbin of history, piled in with both the traditionalism they so detested as well as the triumphs of liberalism that didn’t quite get with the times once they were accepted as given. Like Ozymandias, who stood tall over the domain of his glory, they too are consigned to a slow burial courtesy of the sands of time.
As much as planned obsolescence is a regrettable part of modern technology, so too is it an inescapable component of liberalism. Any idea, concept, or structure can only last for a given time period before it is torn down or has its nature drastically altered beyond recognition to stop it forming into a new despotic custom. Without reference to being, the world and its products are left purely in the hands of mankind. Defined by caprice, “freedom”, “equality”, or “democracy” can be given just as quickly as they can be taken, with little justification required other than the existing definition requiring amendment. Who decides the new meaning? And what happens to those who defend the existing one? Irrelevant, for one day both will be relics, and so too shall the ones that follow it. What happens when there is no more progress to be made? Impossible to say for certain, but if we are to take example from nature, a tornado once dissipated leaves behind only eerie silence and a trail of destruction, from which the only answer is to rebuild.
Featured
Britain Is No Longer a Land of Opportunity
A recent viral tweet showed two doctors leaving a hospital. They’ve surrendered their licenses to practice medicine in Britain and are instead heading off to work in Australia. It’s not unusual- the majority of foreign doctors in Australia are Brits. The problem lies in the fact that young, educated doctors do not see themselves thriving in Britain. Our pay and conditions are not good enough for them.
Are you annoyed at them for being educated through taxpayer funding before going abroad? Many are. Are you understanding as to why? So are others.
Whilst this particular tale does come down to problems with the NHS, it’s also an example of what is wrong with Britain at the moment. People, especially younger ones, haven’t got the opportunities that they should have. There is no aspiration. There is a lot to reach for and not a lot to grab.
What has happened?
Wages and Salaries and Income, Oh My!
A recent investigation by a think tank has revealed that 15 years of economic stagnation has seen Brits losing £11K a year in wages. Let’s put this into perspective. Poland and Eastern Europe are seeing a rise in GDP- Poland is projected to be richer than us in 12 years should our economic growth remain the same. The lowest earners in Britain have a 20% weaker standard of living than Slovenians in the same situation.
That’s a lot of numbers to say that wages and salaries aren’t that great.
By historical standards, the tax burden in the U.K. is very high. COVID saw the government pumping money into furlough schemes and healthcare. As the population ages, there is a further need for health and social care support. This results in taxes eating into a larger amount of our income. In fact, more adults than ever are paying 40% or above in taxation. It’s a significant number. One might argue that this does generally only apply to the rich and thus 40% is not a high amount for them, but is that a fair number?
With inflation increasing costs and house prices rising (more on that later), a decent standard of living is beyond the reach of many. This is certainly true for young people. With wages and salaries falling in real time, we do not have the same opportunities as our parents and grandparents. Families used to be able to live comfortably on one wage, something that is near impossible. Our taxes are going on healthcare for an aging population.
Do we want old people to die? Of course not. We just do not have the benefits that they did. Our income is going towards their comfort. Pensioners have higher incomes than working age people.
Compared to the United States, Brits have lower wages. One can argue that it is down to several things- more paid holidays and taxpayer funded healthcare. That is true, and many Brits will proudly compare the NHS to the American healthcare system. That is fine, but when the NHS is in constant crisis, we don’t seem to be getting our money’s worth. The average American salary is 12K higher than the average Brit’s. The typical US household is 64% richer. Whilst places like New York and San Francisco have extortionate house prices, it’s generally cheaper across the US.
Which brings us onto housing.
A House is Not a Home
Houses are expensive- they are at about 8.8% higher than the average income. This is compared to 4% in the 1990s. That itself is an immediate roadblock to many. Considering how salaries have stagnated, as discussed in the previous section, it’s only obvious that homeowning is a dream as opposed to reality.
Rent is not exactly affordable either. In London, the average renter spends more than half of their income on rent. Stories of people queuing for days and landlords taking much higher offers are commonplace.
House building itself is not cheap- the price of bricks have absolutely rocketed over recent years. Factors include a shortage of housing stock and increased utilities. House building itself is also not easy.
NIMBYs have an aneurysm at the thought of an abandoned bingo hall being turned into housing. MPs in leafy suburbs push against any new developments, lest their wealthy parishioners vote for somebody else. Theresa Villiers, whose constituency sees homes average twice the U.K. mean price, led Tory MPs in an attempt to prevent house building targets.
We get the older folks telling us that we just need to work harder. It’s easy for them to say, considering a higher proportion of our income is needed to just get a damn deposit. If we’re paying more and more of our income on rent, how can we save?
Playing Mummy and Daddy
The ambition to become a parent is something many hold, but it is again an ambition that is unattainable. Well, the actual having the child part is easy, but it’s what comes after that makes it tough.
Firstly, we cannot get our own homes. Few want to raise their children in one bed flats with no gardens. To plan for a child is to likely plan a move.
Secondly, childcare is very expensive. Years and years ago, men went to work and women stayed home with the children as a rule. Of course, that did not apply to the working class, but it was a workable system. Nowadays, you both have to work. Few can survive on a single income from either parent. Grandparents are often working themselves or simply don’t/can’t provide babysitting duties. This leaves only one choice- professional childcare. The average cost of childcare during the summer holidays is £943. Some parents pay more than half of their wages on childcare.
Thirdly, as has been said, everything is more expensive these days. One only has to look at something basic like school uniforms- some spend over £300 per child. It’s not cheap to look after adults, let alone children.
The Golden Years
The focus of this piece is generally on young and working age people, but the cost of social care is pretty bad. With the costs of home and residential health care increasing constantly, it means that many will lose their hard earned savings. Houses must be sold and pensions given up. It is unfair that we must work all of our lives but then leave nothing for our children if we wish. Whilst residential homes are alien concepts to many in cultures where they look after the elderly, many factors in the U.K. mean that it is more common.
On balance, pensioners are better off than the young, but what about those who need care? It may be bad now, but what about when we ourselves are old? We will likely still be working at 70 and having to pay more for our care.
The Party of Aspiration and 13 Years of Power
The Conservatives have always called themselves the party of aspiration. They’ve been in power for 13 years, eight of which were without a coalition party. The Tories won a stunning majority in 2019 under Boris Johnson. They’ve had the opportunity to do something about this but haven’t. It’s amazing that they wonder why young people don’t vote for them anymore.
Let’s not pretend Labour and the Lib Dems are any better either. The Lib Dems won the historical Tory seat of Chesham and Amersham partially by appealing to those worried about new housing. Labour’s plans aren’t particularly inspiring.
We cannot dream in Britain anymore. The land of hard work and fair reward is no more. We must simply sit by as our wages stagnate, houses get too expensive and the opportunity for family passes us by. Our doctors head to Australia for better pay and better conditions. Countries that would see immigrants come to us for a better life are seeing their own economies grow.
People shouldn’t be living with roommates in their 30s when what they want is a family. We deserve to work hard to secure a good future. We don’t deserve for our income to go on poor services and for our savings to go on residential care.
The Tories have had thirteen years to sort it out. Labour and the Lib Dems have had chances to put their plans across. Our politicians care more about talking points and pretty photo ops than improving our lives.
Let us have ambition. Let us seek opportunities. Let Britain be a land of opportunity once again.
Technology Is Synonymous With Civilisation
I am declaring a fatwa on anti-tech and anti-civilisational attitudes. In truth, there is no real distinction between the two positions: technology is synonymous with civilisation.
What made the Romans an empire and the Gauls a disorganised mass of tribals, united only by their reactionary fear of the march of civilisation at their doorstep, was technology. Where the Romans had minted currency, aqueducts, and concrete so effective we marvel on how to recreate it, the Gauls fought amongst one another about land they never developed beyond basic tribal living. They stayed small, separated, and never innovated, even with a whole world of innovation at their doorstep to copy.
There is always a temptation to look towards smaller-scale living, see its virtues, and argue that we can recreate the smaller-scale living within the larger scale societies we inhabit. This is as naïve as believing that one could retain all the heartfelt personalisation of a hand-written letter, and have it delivered as fast as a text message. The scale is the advantage. The speed is the advantage. The efficiency of new modes of organisation is the advantage.
Smaller scale living in the era of technology necessarily must go the way of the hand-written letter in the era of text messaging: something reserved for special occasions, and made all the more meaningful for it.
However, no-one would take seriously someone who tries to argue that written correspondence is a valid alternative to digital communication. Equally, there is no reason to take seriously someone who considers smaller-scale settlements a viable alternative to big cities.
Inevitably, there will be those who mistake this as going along with the modern trend of GDP maximalism, but the situation in modern Britain could not be closer to the opposite. There is only one place generating wealth currently: the South-East. Everywhere else in the country is a net negative to Britain’s economic prosperity. Devolution, levelling up, and ‘empowering local communities’ has been akin to Rome handing power over to the tribals to decide how to run the Republic: it has empowered tribal thinking over civilisational thinking.
The consequence of this has not been to return to smaller-scale ways of life, but instead to rest on the laurels of Britain’s last civilisational thinkers: the Victorians.
Go and visit Hammersmith, and see the bridge built by Joseph Bazalgette. It has been boarded up for four years, and the local council spends its time bickering with the central government over whose responsibility it is to fix the bridge for cars to cross it. This is, of course, not a pressing issue in London’s affairs, as the Vercingetorix of the tribals, Sadiq Khan, is hard at work making sure cars can’t go anywhere in London, let alone across a bridge.
Bazalgette, in contrast to Khan, is one of the few people keeping London running today. Alongside Hammersmith Bridge, Bazalgette designed the sewage system of London. Much of the brickward is marked with his initials, and he produced thousands of papers going over each junction, and pipe.
Bazalgette reportedly doubled the pipes diameters remarking “we are only going to do this once, and there is always the possibility of the unforeseen”. This decision prevented the sewers from overflowing in 1960.
Bazalgette’s genius saved countless lives from cholera, disease, and the general third-world condition of living among open excrement. There is no hope today of a Bazalgette. His plans to change the very structure of the Thames would be Illegal and Unworkable to those with power, and the headlines proposing such a feat (that ancient civilisations achieved) would be met with one million image macros declaring it a “manmade horror beyond their comprehension.”
This fundamentally is the issue: growth, positive development, and a future worth living in is simply outside the scope of their narrow comprehension.
This train of thought, having gone unopposed for too long, has even found its way into the minds of people who typically have thorough, coherent, and well-thought-out views. In speaking to one friend, they referred to the current ruling classes of this country as “tech-obsessed”.
Where is the tech-obsession in this country? Is it found in the current government buying 3000 GPUs for AI, which is less than some hedge funds have to calculate their potential stocks? Or is it found in the opposition, who believe we don’t need people learning to code because “AI will do it”?
The whole political establishment is anti-tech, whether crushing independent forums and communities via the Online Harms Bill, to our supposed commitment to be a ‘world leader in AI regulation’ – effectively declaring ourselves to be the worlds schoolmarm, nagging away as the US, China, and the rest of the world get to play with the good toys.
Cummings relays multiple horror stories about the tech in No. 10. Listening to COVID figures down the phone, getting more figures on scraps of paper, using the calculator on his iPhone and writing them on a Whiteboard. Fretting over provincial procurement rules over a paltry 500k to get real-time data on a developing pandemic. He may well have been the only person in recent years serious about technology.
The Brexit campaign was won by bringing in scientists, physicists, and mathematicians, and leveraging their numeracy (listen to this to get an idea of what went on) with the latest technology to campaign to people in a way that had not been done before. Technology, science, and innovation gave us Brexit because it allowed people to be organised on a scale and in ways they never were before. It was only through a novel use of statistics, mathematical models, and Facebook advertising that the campaign reached so many people. The establishment lost on Brexit because they did not embrace new modes of thinking and new technologies. They settled for basic polling of 1-10 thousand people and rudimentary mathematics.
Meanwhile the Brexit campaign reached thousands upon thousands, and applied complex Bayesian statistics to get accurate insights into the electorate. It is those who innovate, evolve, and grow that shape the future. There is no going back to small-scale living. Scale is the advantage. Speed is the advantage. And once it exists, it devours the smaller modes of organisation around it, even smaller modes of organisation have the whole political establishment behind it.
When Cummings got what he wanted injected into the political establishment – a data science team in No. 10 – they were excised like a virus from the body the moment a new PM was installed. Tech has no friends in the political establishment, the speed, scale, and efficiency of the thing is anathema to a system which relies on slow-moving processes to keep a narrow group of incompetents in power for as long as possible. The fierce competition inherent to technology is the complete opposite of the ‘Rolls-Royce civil service’ which simply recycles bad staff around so they don’t bother too many people for too long.
By contrast, in tech, second best is close to last. When you run the most popular service, you get the data from running that service. This allows you to make a better service, outcompete others, which gets you more users, which gets you more data, and it all snowballs from there. Google holds 93.12% of the search engine market share. Amazon owns 48% of eCommerce sales. The iPhone is the most popular email client, at 47.13%. Twitch makes up 66% of all hours of video content watched. Google Chrome makes up 70% of web traffic. There next nearest competitor, Firefox (a measly 8.42%,) is only alive because Google gave them 0.5b to stick around. Each one of these companies is 2-40 times bigger than its next nearest competitor. Just as with civilisation, there is no half-arseing technology. It is build or die.
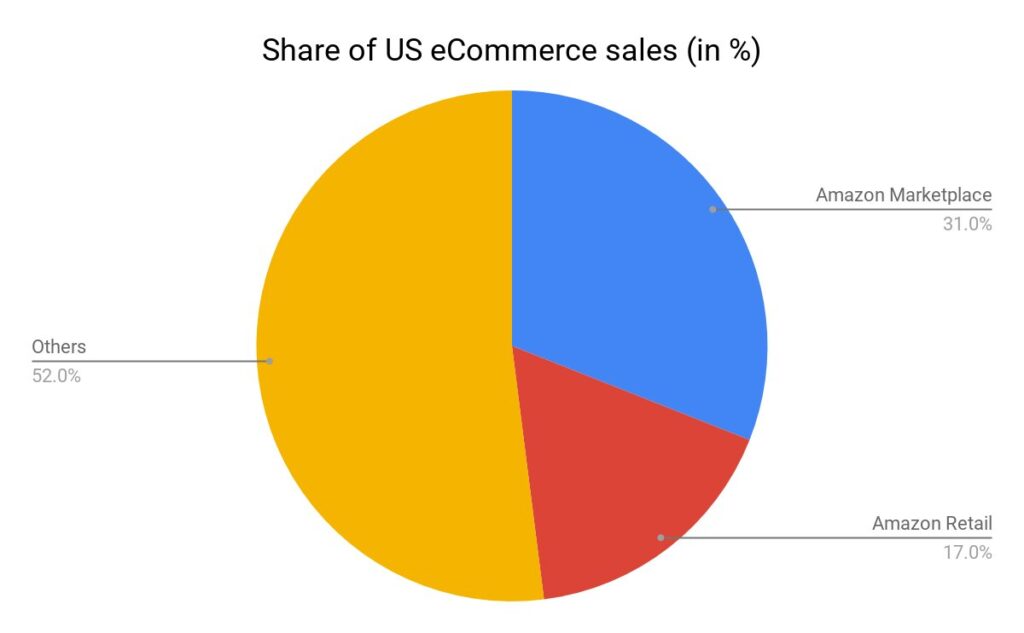
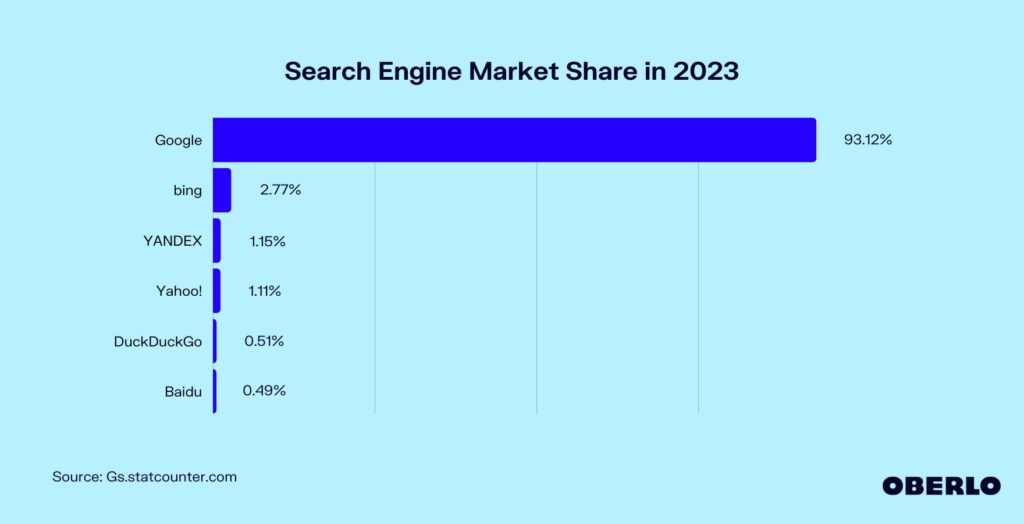
Nevertheless, there have been many attempts to half-ass technology and civilisation. When cities began to develop, and it became clear they were going to be the future powerhouses of modern economies, theorists attempted to create a ‘city of towns’ model.
Attempting to retain the virtues of small town and community living in a mass-scale settlement, they argued for a model of cities that could be made up of a collection of small towns. Inevitably, this failed.
The simple reason is that the utility of cities is scale. It is the access to the large labour pools that attracts businesses. If cities were to become collections of towns, there would be no functional difference in setting up a business in a city or a town, except perhaps the increased ground rent. The scale is the advantage.
This has been borne out mathematically. When things reach a certain scale, when they become networks of networks (the very thing you’re using, the internet, is one such example) they tend towards a winner-takes-all distribution.
Bowing out of the technological race to engage in some Luddite conquest of modernity, or to exact some grudge against the Enlightenment, is signalling to the world we have no interest in carving out our stake in the future. Any nation serious about competing in the modern world needs to understand the unique problems and advantages of scale, and address them.
Nowhere is this more strongly seen than in Amazon, arguably a company that deals with scale like no other. The sheer scale of co-ordination at a company like Amazon requires novel solutions which make Amazon competitive in a way other companies are not.
For example, Amazon currently owns the market on cloud services (one of the few places where a competitor is near the top, Amazon: 32%, Azure: 23%). Amazon provides data storage services in the cloud with its S3 service. Typically, data storage services have to handle peak times, when the majority of the users are online, or when a particularly onerous service dumps its data. However, Amazon services so many people – its peak demand is broadly flat. This allows Amazon to design its service around balancing a reasonably consistent load, and not handling peaks/troughs. The scale is the advantage.
Amazon warehouses do not have designated storage space, nor do they even have designated boxes for items. Everything is delivered and everything is distributed into boxes broadly at random, and tagged by machines so the machines know where to find it.
One would think this is a terrible way to organise a warehouse. You only know where things are when you go to look for them, how could this possibly be advantageous? The advantage is in the scale, size, and randomness of the whole affair. If things are stored on designated shelves, when those shelves are empty the space is wasted. If someone wants something from one designated shelf on one side of the warehouse, and something from another side of the factory, you waste time going from one side to the other. With randomness, you are more likely to have a desired item close by, as long as you know where that is, and with technology you do. Again, the scale is the advantage.
The chaos and incoherence of modern life, is not a bug but a feature. Just as the death of feudalism called humans to think beyond their glebe, Lord, and locality, the death of legacy media and old forms of communication call humans to think beyond the 9-5, elected representative, and favourite Marvel movie.
In 1999, one year after Amazon began selling music and videos, and two years after going public – Barron’s, a reputable financial magazine created by Dow Jones & Company posted the following cover:

Remember, Barron’s is published by Dow Jones, the same people who run stock indices. If anyone is open to new markets, it’s them. Even they were outmanoeuvred by new technologies because they failed to understand what technophobes always do: scale is the advantage. People will not want to buy from 5 different retailers because they want to buy everything all at once.
Whereas Barron’s could be forgiven for not understanding a new, emerging market such as eCommerce, there should be no sympathy for those who spend most of their lives online decrying growth. Especially as they occupy a place on the largest public square to ever occur in human existence.
Despite claiming they want a small-scale existence, their revealed preference is the same as ours: scale, growth, and the convenience it provides. When faced with a choice between civilisation in the form of technology, and leaving Twitter a lifestyle closer to that of the past, even technology’s biggest enemies choose civilisation.
Consorts (Part 3)
Eleanor of Castile
- Life: 1241-28th November 1290
- Reigned: 20th November 1272-28th November 1290
- Spouse: Edward I (m. 1254)
- Children: Sixteen, including Edward II
- Parents: Ferdinand III of Castile and Joan, Countess of Ponthieu
- Origin: Spain
Early Life: Eleanor of Castile was born sometime in 1241 in Burgos, Castile (later Spain). Her parents were Ferdinand III of Castile and Joan, Countess of Ponthieu. Ferdinand was one of Castile’s most successful rulers, as he greatly expanded its territory and joined it with León. Joan was Ferdinand’s second wife- Elisabeth of Swabia had died in 1235. Their eldest son, Alfonso, would succeed to the throne after his father’s death.
Eleanor was her mother’s successor as Countess of Ponthieu. She had five brothers, seven half-brothers and three half-sisters, though most did not live past early childhood. Eleanor was extremely well-educated, even for the time, and enjoyed the arts and literature. This extended to Alfonso and the Castile court itself.
Marriage and Children: The only living daughter of Ferdinand III and half-sister of Alfonso X, Eleanor was a desirable candidate in the marriage market. After several betrothals were played with, Eleanor was ultimately engaged to Prince Edward, heir to the throne of England. They wed on the 1st November 1254. Eleanor was about thirteen and Edward only a couple of years older.
Edward and Eleanor had a famously loving marriage. They were close from the moment they married, no doubt helped by the fact that they were practically the same age. Edward never strayed from his wife or had any illegitimate children, an extreme rarity for the time. He loved the fact that she joined him on the Crusades. Eleanor’s death would devastate him and it was only by need that he chose to remarry. They were rarely apart.
The pair had sixteen children- eleven daughters and five sons. Only seven of their children lived past infancy- indeed, the future Edward II was their youngest son and child. Eleanor adhered to the parenting styles of the time by sending her children away to be educated and barely seeing them. She did care for their education and arranged her daughters’ marriages.
Pre-Reign and Queenship: Eleanor and Edward initially lived on the continent, but moved back to England in 1255. During the Second Barons’ War, Eleanor joined her husband as he fought in Wales. She once again was at his side when he traveled to fight during the Crusades. At this point, Eleanor had given birth to six of her children. Three more would be born during the Crusades, though only one would live to adulthood.
In 1272, they received word that Edward’s father had died. They nevertheless stayed on the continent until 1274, whereupon they returned to England. The pair were crowned together on the 19th August of that year.
Eleanor was uninvolved in politics due to her husband’s views on the matter, but was seemingly alright to it. She instead focused on culture. Her influence included arts, literature, education, decoration and clothing. Eleanor’s superior education helped her in that respect. In that way, she fulfilled the traditional role of Queen- she was not political and focused on the feminine aspects of a reign.
Whilst she enjoyed a close relationship with her husband, Eleanor was generally very unpopular with the public. Her business dealings, which made her incredibly wealthy in both land and money, were seen as unbecoming for a queen. The large foreign retinue of cousins that came with Eleanor were also disliked, though Eleanor was smart enough not to let the men marry English noblewomen. She also supported her husband’s crusade against the Jewish people.
By the mid to late 1280s, Eleanor was frequently ill. In 1290, it was clear that she was dying. Eleanor used her remaining time to arrange the marriages of her children. In November of that year she was no longer able to travel and was thus given quarters in Nottinghamshire.
On the 28th November 1290, Eleanor Castile died at the age of 48-49. Her husband was by her side. Eleanor is buried in three places- her viscera (internal organs) in Lincoln Cathedral, her heart at Blackfriars Monastery and the rest of her body in Westminster Abbey. Edward would later be buried beside her.
Personality: Eleanor was an intellectual with a passion for the arts and culture, something that is part of her legacy. She was also extremely brave and strong, as evidenced by her joining her husband on the Crusades. Several of her children were born abroad as opposed to the safety of England. Unfortunately, Eleanor had her flaws. Her ruthlessness towards the Jews may not have been the same as her husband’s, but she still seized lands from them. Her general business dealings made her unpopular.
Legacy: Eleanor’s most famous legacy is that of the Eleanor crosses. Her broken-hearted husband built twelve large, intricate crosses to mark the stops taken as her body was taken back to London. Only two remain. Eleanor’s cultural influence was also strong. She is also often remembered for the loving relationship she shared with her husband, a sharp contrast with that of other medieval marriages.
Margaret of France
- Life: c.1279-14th February 1318
- Reigned: 8th September 1299-7th July 1307
- Spouse: Edward I (m.1299)
- Children: Three
- Parents: Philip III of France and Maria of Brabant
- Origin: France
Early Life: Margaret of France was born around 1279 in Paris. Her parents were Philip III of France and Maria of Brabant. She was the youngest child of both parents, with Philip having been married to Isabella of Aragon until her 1271 death. Margaret has a brother, a sister, and five half-brothers, though most did not live past childhood.
Very little is known about her early life, but she was likely well-educated as a princess of France.
Marriage and Children: Margaret’s older sister Blance was initially engaged to Edward’s son, the future Edward II. Upon hearing of Blanche’s apparent beauty, Edward broke off the relationship in hopes of marrying his son’s betrothed. It turned out that Blanche had already been married off. Her half-brother Philip IV had been king since Margaret was six and offered her as Edward’s bride. An angry Edward refused and declared war on France. Eventually, an agreement was made. Margaret’s half-niece Isabella would later marry Edward II as part of the agreement.
Despite Edward’s devoted love to his late wife Eleanor, the fact he only had one living son made it essential that he remarry. In the end, Edward and Margaret would enjoy a very happy marriage. Their age gap was at least forty years, but they lived harmoniously. Margaret’s decision to join her husband on the front was reminiscent of Eleanor and thus pleased him greatly. Their relationship was so great that Margaret would refuse to remarry upon his death.
Margaret had two sons within two years of marriage, fulfilling Edward’s hopes of further sons. She would later have a daughter that she named Eleanor after her predecessor.
Queenship: Like Eleanor, Margaret was not involved in politics but was surely a close confidant of her husband. She also bravely joined her husband at the front, something that endeared her greatly to him.
Margaret fulfilled her role as Queen in more ways than just providing sons. A medieval Queen was expected to be a mediator and a calm, feminine influence on her husband. The kind Margaret would intercede on behalf of those who had displeased the king. This most notably extended to her stepson Edward, who often quarreled with his father. Edward was only two years Margaret’s junior and the pair got on extremely well.
After nearly eight years of marriage, Edward I died on the 7th July 1307 aged 68.
Post-Queenship: Margaret remained in England following Edward’s death. Despite her youth (she was 26 when she was widowed), Margaret refused to remarry, saying that ‘when Edward died, all men died for me.’
She remained on good terms with her half-niece Isabella upon the girl’s marriage to Edward II in 1308. Unfortunately, Edward’s association with Piers Gaveston soured their previously excellent relationship. Margaret’s rightful lands were confiscated but she later got them back.
Personality: Margaret was a singularly kind, warm woman who was an excellent queen. She fulfilled her duties through her interceding on behalf of others and mediating between her husband and stepson. Margaret’s kindness went beyond what was expected of the time and thus won her affection. She showed bravery by joining her husband on the front. Despite their large age gap, Margaret was a devoted spouse and remained loyal after her husband’s death. She was kind to her successor Isabella.
Legacy: Margaret is not as remembered as her predecessor Eleanor, probably helped by the fact that she was not the mother of a king. Her granddaughter Joan, however, would marry Edward II’s son and become mother of Richard II, the boy king. Her loyalty to Edward is something some will remember.
Isabella of France
- Life: c.1295-22nd August 1358
- Reigned: 25th February 1308-25th January 1327
- Spouse: Edward II (m.1308)
- Children: Four, including Edward III
- Parents: Philip IV of France and Joan I of Navarre
- Origin: France
Early Life: Isabella of France was born around 1295 in Paris. Her parents were Philip IV of France and Joan I of Navarre. Philip’s half-sister Margaret was Isabella’s predecessor as Queen, and they were both engaged to their respective husbands through the same agreement. Philip himself was a handsome man known to be a very strong and hard king. Joan was a beloved Queen who enjoyed a close relationship with her husband. She died when Isabella was about ten.
As befitting a princess of France, Isabella received a thorough education, probably similar to the one her aunt Margaret received.
Marriage and Children: The agreement that had Edward I and Margaret of France married saw Isabella engaged to Edward’s son. The king attempted to stop the marriage several times, but the issue became moot when he died.
Edward II married Isabella on the 25th January 1308 in a very elaborate ceremony. Unfortunately, it was not a good marriage. The roughly twelve year-old Isabella was immediately sidelined at her own wedding reception when Edward sat with his favourite Piers Gaveston. He went so far as to gift all of Isabella’s jewellery and presents to Gaveston, angering her and the nobles. Their poor relationship will be explored further in the Queenship section, as the repercussions were great.
As Isabella was only around twelve at the wedding, it was a while before the wedding was probably consumated. The pair’s first child, the future Edward III, was born nearly five years after the wedding. Isabella and Edward would have two sons and two daughters.
She was the typical medieval mother in her parenting style. Her machinations alienated her son Edward to the point of him imprisoning her upon reaching his majority. Isabella was close to her daughter Joan in later life.
Queenship: Isabella was immediately ignored by her new husband. This was not helped by her youth and the fact that she was too young to consummate the marriage, but Edward II was not a good husband. Her jewels and gifts had been given to Piers Gaveston. She was denied money and maintenance, forcing her to complain to her father.
Eventually, Isabella found herself allying with Gaveston. Despite her relative youth, Isabella was an intelligent young woman who was attempting to forge her own political path. Unfortunately for her, Gaveston had earned the ire of the powerful nobles and would be executed in 1308. Isabella was pregnant at the time.
Things would only get worse, despite Isabella successfully giving birth to a son. Edward became close to the Despensers, a father and son duo who would soon become his closest allies. Hugh Despenser the Younger was a great favourite of Edward and it’s believed that they had a sexual relationship. Isabella found herself still cast out of Edward’s inner circle. Despite her problems with a lot of the nobility, Isabella supported their efforts to get rid of the Despensers.
With Despenser at his side, Edward became a despot over the next few years. Isabella set up her own household far away but would be punished by having her children taken away and her lands confiscated.
Luckily, Isabella was able to get herself sent to France as a peace envoy. Whilst there, she rallied anti-Edward forces with the help of Roger Mortimer, a leading nobleman. The forces arrived in England and quickly took over. Edward was captured two months later and forced to abdicate. Both Despensers were brutally executed.
Isabella had her son Edward installed and crowned in early 1327. Meanwhile, the former Edward II was shuttled around before being placed in Berkeley Castle. He died on the 21st September of that year. The circumstances of his death are murky. Historians remain divided as to whether he was murdered or died of natural causes, though murder is more likely.
Post-Queenship: With Edward III barely a teenager, he required a regent. Isabella, along with Mortimer, fulfilled that role. She ensured her son listened to her and the boy had limited power. Mortimer was a careless man and was stupid enough to treat Edward badly. Eventually, Edward had enough, especially after his father’s death. The trigger was Mortimer ordering the execution of Edward’s uncle, the Earl of Kent.
Edward took his mother and Mortimer by surprise when he captured them in late 1330. Whilst he placed Isabella in a luxurious house arrest, he had Mortimer executed without trial.
Isabella spent years living very comfortably and was often visited by family and friends. Despite her cold reputation, she was a loving mother to her daughter Joan and doting grandmother.
The ‘She-Wolf’ of France died on the 22nd August 1358 around the age of 62. She is buried at Grey Friars’ Church.
Personality: Isabella was a complicated woman. She showed great intelligence and political acumen, but was also very ruthless and sharp. Whilst many queens were forced to live through their husband’s affairs, none would be quite humiliated as Isabella was. She was called a ‘She-Wolf,’ but we must remember she was a humiliated child bride. Such actions in men would not be treated so poorly. Whilst Isabella was controlling of her son, she did prove to be a loving grandmother.
Legacy: Isabella is remembered as a cold, calculating woman as opposed to the pure and virtuous ladies of her era. She succeeded in giving birth to heirs but did not follow the tradition of ‘feminine’ queenship. The truth is more complicated- Isabella was ruthless and cold, but no more than other historical figures.
Philippa of Hainault
- Life: 24th June 1310/1315-15th August 1369
- Reigned: 24th January 1328-15th August 1369
- Spouse: Edward III (m.1328)
- Children: Thirteen, including Edward the Black Prince
- Parents: William I, Count of Hainaut and Joan of Valois
- Origin: France
Early Life: Philippa of Hainault was born on the 24th June 1310 or 1315 in Valenciennes, modern day France. Her parents were William I, Count of Hainaut and Joan of Valois. She was the third of their eight children. Whilst Philippa did not have the title of princess, Joan of Valois was the granddaughter of a French king and sister of the other.
She was likely well-educated.
Marriage and Children: A betrothal between the future Edward III and Philippa was tentatively discussed as early as 1322. Four years later, Edward’s mother Isabella had them officially engaged in return for William’s help in invading England.
The marriage was a success even before the wedding, as it is said that Philippa cried when Edward left to return home. Their proxy wedding occurred in October 1327 before their official marriage three months later.
Edward and Philippa had a strong, loving relationship that lasted throughout their marriage. This did not stop Edward from straying in his wife’s later years, as he had a young mistress named Alice Perrers, with whom he had three children. It is argued that this only occurred when Philippa’s health was poor and that it was kept from her. This was oddly progressive for the time, as kings didn’t usually hide mistresses. Whilst he did have the affair with one other woman, Edward’s true love was clearly Philippa.
The pair managed to have thirteen children- eight sons and five daughters, eight of whom would live to adulthood. Interestingly, most of their children would marry rich English nobles as opposed to foreign royals. This was most unusual for their eldest son and heir Edward, who married his widowed cousin Joan. Perhaps the happiness between Edward and Philippa allowed them to have their own children be married for love.
Queenship: Philippa may have been Queen in name, but her mother-in-law Isabella was Queen in every other way. Isabella did not like relinquishing her title and thus prevented Philippa’s coronation. It was not until Philippa was pregnant that she was crowned. Luckily for Philippa, she bore a healthy son and unrelated events saw Mortimer executed and Isabella imprisoned.
Throughout her time as Queen, Philippa proved to be enormously popular and beloved. She was not necessarily political in the way Isabella was, but she used her influence when necessary. Edward trusted her to act as regent when he was away and she proved herself more than capable.
It was Philippa’s kindness and charity that made her loved. The most famous of these cases was that of the Burghers of Calais. Angered by the holdout of the city, Edward swore he’d spare the citizens if six of the leaders (burghers) made themselves known and surrendered to him. Before he could presumably have them executed, a barefoot and pregnant Philippa fell to her knees before him. She begged him to spare them, saying that their unborn child would be punished if they did not. Edward was supposedly so moved by this that he agreed to let them live.
Her charity extended to those at home. Philippa also bravely encouraged troops fighting the Scottish invaders, something sorely needed as Edward was out of the country.
In her later years, Philippa fell ill. Those years saw Edward turn to Alice Perrers and father three children with her. Philippa finally passed on the 15th August 1369, somewhere in her mid-fifties. Edward was with her at her deathbed. She asked Edward to ensure that all of her debts and obligations were fairly paid.
Edward spent £3K on her tomb. Her death also saw a massive decline in his popularity. He was vilified for cheating on his loving wife with a younger woman- something extraordinary in a time where it was expected that kings would stray. Alice Perrers would become a huge villain in England. Perrers was accused of taking advantage of an old, grieving king by accepting extravagant gifts. Her interference in politics was not welcomed.
Upon his death, Edward was buried with his beloved Philippa.
Personality: Philippa is one of the most revered consorts in English history. Her kindness, warmth and generous nature made her beloved throughout her country. She was a very successful Queen- she completed the role of feminine mediator and provided her husband with many children. Even without that, her good heart kept her through. The fact that Edward was castigated for taking a mistress shows how loved she was.
Legacy: Philippa is not often remembered. She did not leave a lasting legacy through arts or culture, despite leaving a mark on the textile industry. Her eldest son did not become king, but her grandson would be. Philippa’s sons Edmund and John of Gaunt would become a direct monarchical ancestor.
Anne of Bohemia
- Life: 11th May 1366-7th June 1394
- Reigned: 20th June 1382-7th June 1394
- Spouse: Richard II (m.1382)
- Children: None
- Parents: Richard IV, Holy Roman Emperor and Elizabeth of Pomerania
- Origin: Czech Republic/Czechia
Early Life: Anne of Bohemian was born on the 11th May 1366 in Prague, modern day Czechia. Her parents were Richard IV, Holy Roman Empire and Elizabeth of Pomerania. Elizabeth was Richard’s fourth and final wife. Anne had three brothers, one sister, three half-brothers and three half-sisters. Richard was the most powerful king of the age and was also extremely popular.
She was likely well-educated.
Marriage and Children: The marriage between Anne and Richard II was an odd one. Despite Anne being the daughter of an extremely powerful monarch, she did not have a large dowry or other assets. The main reason was due to a problem with the Church and two rival popes. Richard and the Holy Roman Emperor both opposed France’s choice.
Richard and Anne were both fifteen when they married on the 20th January 1382. Despite Anne’s unpopularity and lack of wealth (Richard having to pay Anne’s brother for marriage), the two became devoted to one another. Richard never strayed and always defended Anne.
No children were born of the union. Anne was blamed by society, as women were at the time, but Richard never cast doubt towards her.
Queenship: Anne was known as ‘Good Queen Anne,’ which shows that she overcame early unpopularity. She would often intercede on behalf of others, as Philippa of Hainault had. This constant kindness made her beloved by the English people, and eventually the court. It was her sweetness that won the nobles over.
After a happy twelve years of marriage, Anne died aged 28 on the 7th June 1394. Edward was bereft. He ordered the palace that she died in to be torn down. Edward also refused to enter any building besides a church where he’d been with Anne. After his own 1400 death, Edward was buried with a tomb he’d already prepared beside Anne’s.
Personality: Anne was reportedly a sweet and kind woman. She cared greatly for her subjects and was merciful to a fault. It was her good nature that pushed away early criticisms directed towards her.
Legacy: Anne is not often remembered. She, and indeed Richard himself, has no children together, so she did not see any direct descendants claim the throne. Anne did bring new fashions over, such as new shoes.
In Conversation with Curtis Yarvin III (Political Testosterone and BBC Pidgin)
Curtis Yarvin, known by his pen name ‘Mencius Moldbug’, is one of the most prominent social critics and reactionary writers of the contemporary era. Yarvin’s blogs, ‘Gray Mirror’ and ‘Imperial Melodies’, can be found on Substack.
Yarvin’s words are in light.
Are you familiar with my favourite institution of journalism? As you know, Orwell worked at the BBC, a great service. I used to listen to BBC short wave as a kid in Cyprus. It used to go ‘beep, beep, beep, beep’, you know, but there’s another part of the BBC that most people don’t know.
Oh!
It’s BBC Pidgin.
Yes! I knew you were going to say that.
[*Laughing*]
You know how many people’s minds you can blow when you show them BBC Pidgin?
Oh my God, oh my God, it’s like the sophisticated version of Rick Rolling.
Oh, it’s so good.
You send them to a story, I’ve been sending people to the BBC Pidgin story about FTX, right?
It is impossible, this is the thing, it’s impossible to read it without sounding like you’re doing something incredibly transgressive.
No, no, no [*Reading from an article on BBC Pidgin], “Dis na as rumours say di FTX and oda firms wey im own bin dey shake financially cause pleti pipo to start to try to dey comot dia money from di platform wey dem dey take buy and sell digital tokens. As mata come tie am rope for neck, Oga Bankman-Friend bin try to organise bailout but e no work.” [*Laughing*] and um…
Oh my God. I’m going to have to type out that transcription.
Yeah, yeah, yeah, yeah, I would start with a Google and get it right, like the poem. You know, you don’t wanna [*inaudible*] oh my God. Yeah, but in any case, like, it’s, it’s, you know, the easiest way to explain, like, how like, Mary Tudor, you know, would look at England today, would be like…she’d have the same response to everything that we have to BBC Pidgin. And, and, right –
Even the Victorians, even the Victorians.
Even the Victorians.
It’s like, you know, Blockbuster still exists but its last outlet is in some pointless town in Wisconsin or something.
Yeah, yeah, yeah.
That is basically the United Kingdom today. It’s uh…
Yeah, but it doesn’t have to be. Knowing that decline is just a consequence of a form of government should be this endlessly exciting, invigorating, hope, where like, absolutely no hope seems to exist. The fact that no hope seems to exist means that sort of all of these bullshit paths toward hope like Brexit have been exhausted and no energy should be diverted into them, which is good, because they’re traps, and like, the energy of a complete collapse is not really the energy of a collapse, it’s the energy of a reinvention. It’s like, you know, this amazing, joyous, recreation of the modern world, kind of shaking off its 20th Century birth pangs. It’ll be incredible. And it’ll be incredibly wonderful and exciting and glorious and certainly not violent in any particular way because…
Because it doesn’t need to be.
It doesn’t need to be. You know, and, and, and, Sir Arthur Scargill is no longer in the building, let alone like, you know, the workers of London will rise up and there will be a new Peterloo. So, you know, like the clack of history turns, and it turns for them as well as for us.
There’s not enough testosterone for anything like that anyway.
There’s not enough testosterone and actually, you know, literally, there’s not enough testosterone as well as figuratively in many ways, and so you’ll just see these old regimes just crumble like East Germany. And it’s like…people will be like “Why didn’t that happen earlier? Because it could have happened earlier, but it didn’t”.
And, yeah, so, you know, the extent to which the problem of like, spreading this picture, and especially spreading this picture in a way which doesn’t scare anyone, you know, because there’s nothing scary about it. Like, you know, and there’s absolutely nothing scary about it and this is the job of we, the dark elves, on both sides of the Atlantic.
It’s been a huge pleasure. I’m getting a little bit tired.
Curtis, thank you very much for your time.
It has been a great pleasure talking to you and thank you for listening.
In Conversation with Curtis Yarvin II (American Gorbachev and The Duke of Croydon)
Curtis Yarvin, known by his pen name ‘Mencius Moldbug’, is one of the most prominent social critics and reactionary writers of the contemporary era. Yarvin’s blogs, ‘Gray Mirror’ and ‘Imperial Melodies’, can be found on Substack.
Yarvin’s words are in light.
Well, to be honest, I’m an American, and I write for Americans, and, you know, my view is that revolution only comes from the top. The collapse of the Soviet bloc did not start in Poland, it did not start in Czechoslovakia, it did not start in East Germany, although those countries were in a way culturally ahead of the Soviet Union, but the collapse had to come from the top down. And, so, you know, realistically, I think was that means is that if you saw a dissolution of the American Empire – you’d need a president to do it in the United States, you have a similar situation because the executive branch is technically under the command of the president, but in fact the wires have been completely cut – almost completely cut – and so those wires would have to be restored with more conflict but, again, you have the fact that opinion in the security forces is still – except at the very top levels – is still basically patriotic. There still is this patriotic backbone, there’s still soldiers who know how to fight, there’s still, you know, there’s still something there, of course, as you know.
And, then, you know, how does that get from there to England? If you have an American Gorbachev Doctrine, what you’re basically seeing is Washington saying to basically every capital around the world “Hey, guess what? You used to have pretend independence but now you have real independence”.
What real independence – let’s say you’re talking to the government of France. You’re like…
“Hey France, guess what? You have real independence now, we’re selling the American embassy, we’re sending everyone home. They can stay if they want and in future we’re going to follow – actually the text in the original Monroe Doctrine address – in regard to your country, and what that says is that we will take no interest in any conflicts among it, we will buy your wine, we do not care what your form of government is, we will buy your wine nonetheless, whether you’re ruled by, you know, Louis XX or the French Communist Party, or French Hitler, or, you know, we don’t care. We will buy your wine. You’ll watch our movies. Everything will be fine and if there’s some kind of need for international relations – sometimes issues come up – you know, for example, birds, when they migrate, they typically go north, south, north, south, they go up and down. Sometimes there’s a storm, the birds get lost, right? And a bird that should be in the Americas will get blown and it will wind up in France, and someone will catch the bird and they’ll be like [*flawless French accent*] ‘oh, this bird, it does not belong here’, and they’ll put it through some kind of AI recognition programme and they’ll say [*flawless French accent again*] ‘oh, this is the American bird’, and then you have international relations because basically the bird, [*French accent*] ‘the bird, of course, where do we send the bird? How do we feed the bird in the package?’ You know um, these details need to be worked out, OK? And I would suggest that these details could be worked out either by email or maybe on a Zoom. You could Zoom, or you could do it in the metaverse. You could do it in the Metaverse. You could have a really big imposing embassy but in the metaverse. And, and, I think that’s really quite sufficient to deal with problems, like that, of the bird.”
Let’s say you say that to France, and you’re like…
“Hey France, you want your colonies back? You want Algeria back? It’s up to you. You want to take all the Algerians into France, up to you. You want to send all the Algerians back to Algeria? Up to you. You want to reconquer, you know, French West Africa? Up to you. You want to reconquer Mexico? Restore the dynasty of Maximilian. Up to you, because, you know, that’s not the United States, uh, and we have adopted the position that we’re going to respect classic international law and we’re abandoning the global Monroe Doctrine, we’re even abandoning the local Monroe Doctrine. Hey, Brazilian army, you want to rebuild your country? You want to get rid of the favelas? You want to, you know, go full dictator and send the Communists home? Not a problem. Hey, Brazilian Communists gangs, you want to seize the country and like, re-enact, you know, the Jacobins in Paris? Not our business.”
You know, and, and, and –
Fire up the helicopters! Sharpen the guillotines!
Yeah, right, right, and what you’d see in a country like Mexico, you’d see an almost instantaneous reassertion of order as the army realised it could just get rid of the drug gangs and govern the country. Bang. Nothing to stop them, no reason to stop. Bang, they do it, the place is cleaned up and Mexico City is as safe as Tokyo. I exaggerate slightly. I exaggerate slightly at four in the morning at the worst districts you might still want to be a little bit careful. You might see a little bit of trash somewhere occasionally. Someone might have thrown an orange. You know, should you eat off the street, I would probably not advise eating off the street. But, you know, yeah, you could restore the Porfiriato, you know, in Mexico. You could basically roll back all of these revolutions.
You know, England seeing that, basically realising that all around the world, every country in the world, was getting fixed up by kings…
You know, in Africa, Paul Kagame got like special dispensation to be a king. The like, international community felt so guilty about having, you know, abetted the genocide that they’re like “OK, you know, normally we’re against strongmen. We don’t have strongmen, your country needs to be run by weak men. No strongmen. No, you can’t have one strongman, you’ve got to have a lot of weak men. Your country is going to be a filthy, corrupt, vile, disgusting mess. Um, that’s just how it is, it’s called ‘freedom’. Freedom is very important and don’t worry, we’ll send lots of aid money and lots of aidocrats. Of course there are far more aidocrats than there ever were imperialists. We’ll send all these people, you know, to help you out, but you’re country has to be a mess. Rwanda…OK, fine, you can govern yourselves, you can have a big man. You can have a king in all but name. You can have Paul Kagame, and you can have streets…OK, I wouldn’t eat off the streets in Kigali either, but I would walk through any part of Kigali at four in the morning. [*Chuckles*] And you’re just like this one exception to the global extended super Monroe Doctrine”.
And, like, the worst Goddamn country in Africa, at a certain point, cleans itself up, and becomes the Japan of Africa. And, it’s just like so…so obvious when you think about it.
At that point a royal restoration in the UK would be like peer pressure. Like Charles, Charles and Prince William, OK, they’re fashion followers. Guess what? Fashion changes, they’re going to follow a new fashion. They’re gonna be like “Wow! Louis XX has sure made Paris nice again. Wow! I can actually take the RER, you know, from the airport without putting my life at risk. Uh, wow, could we try something like that? You know, in the UK? And boy, sure we could, uh, wow, you know, all I know how to do is hand out the Big Issue and look imposing in the tabloids. I’d better hire a capable CEO to run…how about Demis Hassabis, OK?”
And call him the Duke of wherever the fuck he wants.
Yeah, yeah, yeah, yeah, “We’ll make Demis Hassabis the, you know, the Duke of Croydon or whatever and…” [*laughing*]
[*Laughing*] Croydon.
“And he’ll be the Strafford, you know, um, um, to my Charles I”.
Um, you know, Demis Hassabis will be like “OK, we’re going to take Strafford’s policy of ‘Thorough’ – what would a policy of ‘Thorough’ mean today? Dissolve parliament, of course, and govern by a decree, or executive order, or royal prerogative, or whatever you call it then, and um, you know, I am, you know, a weak womanish man, and so Demis Hassabis will be my, you know, Lord Cecil, and he’ll make a new England”.
I’m just randomly choosing a British CEO. I guess Hassabis is not an English name, but it’s fine, he’s a foreigner, you know, is he some kind of Cypriot or something?
It doesn’t matter at this point, does it?
It doesn’t matter, it doesn’t matter. Absolutely. After Rishi Sunak it does not matter, right?
In Conversation with Curtis Yarvin (The Return of Don Quixote and Anglo-Meiji Restoration)
Curtis Yarvin, known by his pen name ‘Mencius Moldbug’, is one of the most prominent social critics and reactionary writers of the contemporary era. Yarvin’s blogs, ‘Gray Mirror’ and ‘Imperial Melodies’, can be found on Substack.
Yarvin’s words are in light.
There’s a little-known Chesterton work called The Return of Don Quixote. Don’t know it at all?
I don’t. I mean, I’m familiar with the original Don Quixote by Cervantes.
Yeah, yeah, yeah, The Return of Don Quixote, and it’s about the victory of a joyous reactionary movement, written as an Edwardian novel, set in the future. It’s very interesting and it sort of catches the sort of joyousness right, which is an absolutely essential part of, like, any kind of restoration of this type.
And yet, you know, kind of Russian Hide And Seek, which is of course a much later work, is more…black-pilled, you might say, and perhaps a little more convincing. And I would say, sort of read them both. You’ll get kind of some of both of these ideas, but just breaking out of this incredible, I mean, it’s like, when you look in the rear-view mirror at Brexit. It’s like 0.1% of a British Meiji, right? And it’s a completely failed venture, and a completely failed thing, you know, I was reading Richard North’s blog EU Referendum, back in the earlier ‘00s, you know, I think he was associated to some extent with, like, early UKIP, and, um you know, the idea of having a referendum on Britain leaving the EU in 2005, let alone that referendum winning, it seemed like such, what we call here, a stretch goal.
It seemed so unimaginable and it happens. This incredible revolution happens and of course it happens and it doesn’t amount to shit. It just has no momentum. As soon as it wins it begins to lose. And, actually, the main effect of Brexit was to destroy the Brexit movement.
Pretty much.
You can’t help but feel that when you do something and people put that much effort and that much hope into something, and in retrospect you can look at it and just say “Well duh, obviously that was gonna…there was no way that could have worked in any way, shape, or form and done anything useful or relevant, or whatever,” and, the, you know…the definition of insanity is making the same mistake twice, and, right, and here, is just the form of government that has been how England rose to greatness and has been governed for pretty much all of the last two millennia, you know, before the invitation to William, right? You know, I guess, you know, William, it’s hard to know to what extent William of Orange was really interested in British domestic affairs. I don’t know how great it was.
Queen Anne was certainly pretty feeble and um, you did know that the um, the king has the right to veto legislation in parliament, right?
Yes.
And do you know who the last person, the last king, who actually used that power was?
It’s not going to be James I is it? Someone distant. Charles I?
Here’s a hint. It wasn’t a king at all.
Really? OK, so was it Queen Anne then? Was it in fact Queen Anne?
It was in fact Queen Anne. Uh, she did it once, and I forget over what. Probably some completely symbolic bullshit.
I see. They went “No, no, this is no good, we’ll get this Dutch fellow”.
Yeah, yeah, it was sort of their ‘lordships die in the dark’ moment. I think, like you know, the People’s Budget of 1911 or whatever. Yeah, Queen Anne was like the legitimate daughter of James II, right? And there was some hope that – and she was basically a Jacobite heir – it’s sort of like this woman Georgia Meloni who gets elected in Italy spouting all this rhetoric and then she’s like “We must fight for the Ukraine, the cause of Ukraine is the cause of all of us”, right?
You know, when I was in Portugal, I was in a small town in this summer and, you know, all of the…you would swear the whole population of Setúbal, Portugal, had come out and, like, popular enthusiasm for the cause of the Ukraine was everywhere, spontaneous graffiti, right, you know, and it’s like, these expressions of popular enthusiasm, like ‘workers of the world, unite’ in Czechoslovakia in 1976. You know, the greengrocer does not really care about workers of the world and I’m pretty sure that if you’re a bus driver in Setúbal, Portugal, your interest in the Dnieper isn’t really – excuse me, Dnipro – is fairly limited, and the uh, just, I mean, it’s increasingly comical, and so, the idea of just like, this whole structure collapsing in one boom is so much more realistic than the idea of Brexit. It’s so much more realistic. People think it’s unrealistic, no, it may be unrealistic, but it is vastly more realistic than Brexit.
I read your piece about a Meiji Restoration. I was sat in the middle of a bunch of naval officers and I was thinking “You know what? Rishi Sunak’s not very popular, neither is Keir Starmer, nobody likes parliament, what would actually happen right now if King Charles did in fact just go ‘guys’…”
Martial law.
Yeah exactly. What would actually happen? And you know, there’s been this sort of endless slew of headline after headline after headline of “Oh, this thing isn’t working, we’ll get the army in to drive trucks” and “Oh, this isn’t working, we’ll get the navy in to sort out this hospital”, and you just sort of look at this thing and think “Why is it that the last sort of functional bit of our government is essentially military?” And “Why is it that…” what would actually happen if…would anyone stop it? Would anyone in the military?
Yeah, yeah, yeah.
I was in Dartmouth. I was at BRNC when the Queen died.
Oh wow.
It’s full of these young, early twenties cadets, who are going through…you know, I was there the day…so I think I was one of the last people to officially join the Queen’s navy and one of the first to join the King’s, and you know, everybody, the whole, the whole college just stopped. I went out onto the Parade Ground at about 5pm in the early evening and every church bell in Dartmouth was ringing across the valley. And yes, there’s a huge amount of symbolic nothingness to it –
But that symbolism can be converted back into reality.
Right!
And everyone would be stunned at how easy it was, and how obvious it was.
I don’t think anyone would say no.
Well, would Sir Arthur Scargill bring the unions into the street? Would like, you know, would the SpADs like set up barricades outside of Nelson’s Column? What?
Right, right. I don’t see it.
I don’t see it. And so you can have your New Jerusalem in England’s green and pleasant land. You just have to realise that the chains that are bonding you are made of paper.
But that’s the question. The new Prince of Wales hands out copies of the Big Issue –
[*Laughs*]
And I just don’t see the king going along with this, so what do we do? Do we have some kind of new Cromwellian parliamentary lie where oh no, no, the king is held captive by these malignants and bad ideas, what is it? What on Earth are we doing?
Yeah, yeah, well, you know, um, maybe we, you know, uh, I don’t know, if Prince William did enough acid, maybe?