latest
The Betrayal of Lampedusa
“At midnight tonight her borders will be opened. Already, for the last few days, they’ve been practically unguarded. And I’m sitting here now, slowly repeating, over and over, these melancholy words of an old prince Bibesco, trying to drum them into my head: The fall of Constantinople is a personal misfortune that happened to all of us only last week.” – Jean Raspail, Camp of the Saints, Epilogue (1973).
Within the last 48 hours, the Mediterranean island of Lampedusa, once host to 6000 Italians, has been overrun by upwards of 18,000 African migrants, the vast majority of whom are military-age men. Some of them have been shipped to Germany, but they continue to vastly outnumber the native population.
Since their arrival, the migrants have taken to fighting amongst themselves, struggling over the island’s waning and already limited resources, with local officials struggling to maintain control. As every astute observer of politics and history will know, violence within the in-group is typically remedied by violence against an out-group, making the possibility of further and more severe chaos, far from a hamstrung hypothetical, a very real threat at this time.
In no uncertain terms, Lampedusa is experiencing an invasion, one which has been instigated without any formal declaration of war between nations yet will afflict the island in much the same way.
Given the nature of this event, I am reminded of Jean Raspail’s The Camp of The Saints, the final words of which provide the opening to this article. The author grimaces as the last outpost of European civilisation, Switzerland, is forced to capitulate to the ‘rules-based international order’, having been outcast as a rogue state for closing its borders amid a continent-wide migrant invasion.
Lampedusa is symbolic of the transformation which has occurred in towns and cities across all of Europe. From England to Italy, from Spain to Poland, from France to Germany, from Sweden to Greece, mass immigration from Africa and the Middle East, as well as Eastern Europe to a lesser and more regionalised extent, has radically transformed the essence of many European settlements, altering them in such a way not seen since Antiquity.
In England, in this year alone, we’ve become well-acquainted with the dire consequences of mass immigration. From rising tensions between the Blacks and South Asians in Peckham to ethnoreligious violence between Indians and Pakistanis in Leicester, divisions which the established order has tried to dilute by promoting anti-white rhetoric in the name of intersectional social justice.
Amid this litany of troubling events, it is easy to forget our European friends face many of the same problems, and that such problems are not an idiosyncratic quirk of the British state.
Unfortunately, similar to such cases, many will not feel sympathy for the people of Lampedusa. Some of native descent in Europe will remark on the inevitability of this ordeal, as if it was apolitical in nature or without a realistic alternative. Erstwhile, some of foreign descent will wryly remark that such an invasion is deserved; if not ‘deserved’, then a change for the better, and if not a change for the better, then negligible happenstance unworthy of press coverage.
Our leaders have known about Lampedusa’s troubles for no less than 20 years. However, instead of preventing such activity, they have spent decades trying to transform illegal migration to a standard bureaucratic procedure. If you can’t beat them, join them!
Since the early 2000s, Lampedusa has been a prime transit point for African and Middle Eastern migrants seeking to enter Europe. Migrants have been paying smugglers to ship them to the island, from which they are transported to the Italian mainland for processing.
Not that any of the processing matters of course. Those without the right to stay, even under Europe’s distinctly liberal asylum laws, continue to live on the mainland, as their deportation orders are barely enforced.
When the Italian government struck a deal with the Libyans in 2004, obliging the latter to accept African immigrants deported from Italian territories, the European Parliament condemned the agreement, and the ensuing repatriations, as unconscionable, unworkable, and quite possibly, illegal.
In 2009, roughly 2000 migrants overwhelmed the island’s asylum facilities. Only capable of accommodating 850 people, the migrants started to riot. How dare the people of Lampedusa be so unprepared for their completely unscheduled, unsustainable arrival!
Catching word of the riot, the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) quickly issued a condemnation; not of the traffickers, not of the authorities, or the migrants, but of the Italian people.
In May 2011, roughly 35,000 migrants had landed on the island since the start of the year. By August, the number had increased to roughly 50,000, with most of the arrivals being men in their 20s and 30s. Compared to the recent arrivals, it is clear things have not changed in this respect either.
Following the 2013 Lampedusa Disaster, in which a boat carrying over 500 migrants, mostly from Eritrea and Somalia, sank off the coast, resulting in at least 300 deaths, Pope Francis prayed not for the natives, but those complicit in a criminal operation to illegally enter their home.
In 2015, from January to April, over 1500 migrants died on the route from Libya to Lampedusa, making it the deadliest migrant route in the world, and just as was the case two years prior, efforts went towards making the trafficking network more legal, more safe, and more efficient, rather than ending the practice altogether.
Consequently, boats needn’t travel far off the coast of Africa to be brought to the mainland by the EU or the UN. The prevailing political mentality is that migrant deaths in the Mediterranean are best averted when the EU, the UN, or some other official organisation does the traffickers’ dirty work for them, showing little-to-no consideration for the domestic consequences of their precious so-called ‘humanitarianism’.
In the case of Lampedusa, the idea that an island of one community should become an island of two, lacking a tangible sense of common belonging, situates both groups into a state of war, and such a war is unjust, both in the sense it is unnecessary, and in the course which it is likely to follow, assuming it is not dealt with in a fitting manner.
From the Pelagies to the Aegeans, every island in the Mediterranean is the first in a trail of dominoes, each of increasing size, intersecting at every European capital, with every tremor created from their fall being more forceful than the last.
I do not want what has happened in Lampedusa to happen tomorrow, the day after, next week, next month, next year, or ever after. It is the height of political and moral arrogance to plunge an entire community of people, overnight no less, into such existential uncertainty.
To subject anyone, native or foreigner, to such sordid and egregious indignity is to betray every metric of justice, and anything short of mass deportations, the immediate defunding of complicit NGOs, and the destruction of every treasonous convention and law, will amount to nothing but betrayal, a betrayal of Lampedusa and all the peoples of Europe.
Richard Weaver: A Platonist in the Machine Age
“Modern man is a moral idiot.” – Richard M. Weaver. 1948. Ideas Have Consequences.
The American cultural critic Richard Weaver (1910-1963) is unfortunately an obscure figure. However, I can’t conceive a thinker whose message would be of greater interest or novelty for the contemporary world. Weaver bewails the decadence and hopelessness of the twentieth century as much as Oswald Spengler or Jose Ortega y Gasset. Yet his account of their causes is far more philosophical: his explanation of the “dissolution of the west” is that it has abandoned its classical heritage.
For Weaver was a latter-day High Tory. A Platonist who thought ancient Greek mores were still alive among folk in the rural American south (his first work was on this very topic, see: The Southern Tradition at Bay). Already an oddity in the 1930s, he was the sort of conservative that has barely existed in the mainstream Anglophone world since the nineteenth century.
Weaver’s great work is Ideas Have Consequences, from 1948. It carries a single thesis from beginning to end. Europe’s mental decadence began at the close of the Middle Ages. It was then that the English churchman William of Ockham decided to abandon a doctrine almost universally held before him. A doctrine common to Socrates, Plato, Aristotle, and the Stoics. A doctrine believed by Catholics, Jews, Orthodox, and pagans. This doctrine is realism.
This is my partial review and partial meditation on Weaver. His prose is vast, so I can only chew over a selection of what it covers. I shall focus on three issues which stand out to me: fragmentation, the spoiled child psychology, and what Weaver calls the “great stereopticon”.
Realism is the view that abstract entities exist. For example, if I see the sun, a basketball, and a balloon, and call these all “spheres”, that word “sphere” refers to something separate from my mind. When I say, “All these things are spherical”, that term “spherical” describes a real feature of how the world truly is.
It was the widespread opinion of ancient and medieval people that such concepts as “redness”, “roundness”, “catness” and “humanity” were the basic building blocks of reality. These were the patterns that individual things conformed to, to make them what they are. Each one acts like the blueprint for a building. In the same way a pile of bricks isn’t a dome unless it has roundness, a pile of bones and organs isn’t a dog unless it has “dogness”. That is, unless it conforms to the pattern of an idealised dog.
Realism then allows for nature to have a sort of duty inherent to it. For, if to be a dog is to conform to the pattern of an ideal dog, then this pattern is what dogs should be. A dog that doesn’t eat meat, doesn’t play fetch, and doesn’t wag his tail fails to be a proper dog; and so, we call it a “bad” dog. Likewise, to be human is to embody the ideal pattern of “humanity”. Good people embody it better, and bad people embody it less.
This means morality is a simple movement from how we are to how we ought to be if we fulfilled our ideal. Beings come into the world imperfect. They only arrive at their proper pattern through hard training and discipline. Moral rules like “don’t steal” and “don’t lie” are guides to help us get from one point to the other by telling us what being an ideal human consists of. Just like “eat meat”, “play fetch” and “wag your tail”, are commands telling the dog how to be a proper dog. This understanding is what, for example, informs Stoicism. Marcus Aurelius insists that the good man is virtuous regardless of what others do or say to him. Because his goodness consists of fulfilling an ideal pattern of conduct, which doesn’t change with the words or actions of others.
What if we deny all this though? What if, like William of Ockham, we declare this all superstition, and say general terms only refer to our own thoughts? This would make us nominalists, a word derived from the Latin nomen meaning “name”. We’d be saying abstract terms are mere names in the mind; conventions for grouping things together, which truly have nothing in common. This is where Weaver is true to his name and weaves us the consequences.
First, nature goes from how things should be to how things just are. Without ideals for things to aspire to, it becomes impossible to talk of imperfection. If there’s no ideal dog, for example, then there’s no such thing as a deficient dog. Dogs come in many shapes and sizes, some eat meat and live to fourteen, others never eat, and they die at one. But all are equally natural and morally neutral.
Applied to people, this causes the death of virtue. For, without an ideal human personality type, all our instincts, inclinations and desires also become morally neutral. Nature produces some people with an extreme hunger, and others with almost none. The human mind and body go from something that must be cultivated to meet an ideal, to a machine that runs on automatic. Passions just happen and calling them flawed now seems ridiculous. Weaver writes, “If physical nature is the totality and if man is of nature, it is impossible to think of him as suffering from constitutional evil”.
Fragmentation results from the loss of an ideal to hold knowledge together. For, where the ideal concept of a thing is lost, there’s no one principle to explain its parts. The blueprint of a house, once in my mind, makes everything about it understandable at a glance. But without the blueprint, the atrium, room, and corridor lose all meaning (imagine explaining what a corridor is to someone without any notion of a house and what it should look like). Since, from the realist perspective, the ideal is what determines knowledge, the long-term consequence cannot be but the elimination of truth.
As Weaver then says, modern man, “Having been told by the relativists that he cannot have truth, (…) now has “facts.”” Gentlemen of the Middle Ages to the eighteenth century, he notes, had a broad humanistic knowledge. They had it because they were schooled in a classical worldview. The gentleman of Ancien Regime Europe sought not pedantic obsession, but to know how ideals relate to each other. So he was like an architect, having the whole plan of the building before him. He could then inform the more expert workmen how best to make this plan a reality.
The gentleman has been gradually replaced by the specialised technocrat as the ruler of western societies. Every field (biology, economics, architecture, etc.) becomes isolated from the rest, and presents itself as the unique solution to all problems. Those who practice them, the technocrats, are each busy making the world in the image of their chosen subjects. The technocrat asks neither why, nor wherefore, but only how. This is, for Weaver, the “substitution of means for ends”. Since, having lost the plan which gives purpose to learning, the tool now becomes the aim. Statecraft becomes a competition between obsessives, who each advance only their own segregated hobbies because they no longer serve human nature.
Modern man is a “spoiled child” according to Weaver. The path to this is indirect, but obvious when seen. Once ideals are denied, everything that seems fixed and permanent becomes liquid. The cosmos is a machine which we can take apart and reassemble to our own fancy. A cat, for example, isn’t a natural type which ought to have four legs, meow, eat meat, etc. It’s a pile of flesh and bones just so arranged into cat-like shape. We can therefore change it as we see fit. And since humans ourselves have no ideal pattern to conform to, what we see fit is anything whatsoever. This is what Francis Bacon, the father of modern science, sets out to do when he says nature should “be put on the rack”, for our benefit.
Our own goodness, in other words, has come apart from any natural limit. This means goodness is now limitless pleasure (pleasure being the only thing remaining when all purpose is removed from nature). So, man becomes a “spoiled child” because he demands the fabric of reality itself be bent to his delight. Science goes from the quest for wisdom to the slave of indulgence. Progress now means destroying whatever stands in the way of comfort and convenience. The masses get used to thinking of nature not as what exists, but as an enemy that must be overcome. Rights without duties are the inevitable result.
Here Weaver, the abstract metaphysician, makes a practical point. The spoiled child endlessly consumes, because he sees no limit to his pleasure, and appetites grow with the feeding. Yet production means enduring discomfort for the sake of an end, and hedonists are averse to this. The hardest worker is the person who believes work improves him; the one who thinks the human ideal is fulfilled by work. But “The more [modern man] is spoiled, the more he resents control, and thus he actually defeats the measures which would make possible a greater consumption”.
Nominalism is the philosophy of consumption, but realism is the philosophy of production. A nominalist culture thus runs the risk of collapse through idleness.
A stereopticon, or stereoscope, is an old-fashioned machine used to look at three-dimensional stereoscopic images; the ancestor of 3D glasses. Weaver likens mass media in nominalist societies to a stereopticon because its aim is to maintain an illusion. For, Weaver thinks, the above modern project of specialisation, hedonism, and progress at all costs is fated to fail. If ideal concepts truly exist outside the mind, then all attempts to ignore them will end badly. They shall re-assert themselves at every attempt to destroy them, and thwart whatever projects are built on their denial.
As the ideal drops out, society fragments into myriad groups with incompatible perspectives. Like the blind men in the Buddhist proverb, each one touches the elephant and calls it a different animal. The biologist, the head of a social club, the accountant, and engineer; each fails to see the higher truth that unites his vision with the rest. Modern states face, then, the problem of getting these specialised obsessives to agree to a common action or set of beliefs. Thus, it presses mass media for this purpose. Radio, cinema, and television spin a narrative where endless consumption makes people happy, and progress is irresistible and unrelenting. Journalists and directors adopt a single “unvarying answer” to the meaning of life: pleasure, aided by technology and consumption.
Weaver believes the effect is to re-create Plato’s cave through media. The prisoners, chained in a cave, are forced to watch the parade before them: vapid film stars, gung-ho newsreels, advertisements for cars and coffee makers. They are spiritually and mentally starved yet believe the cure to their trouble is the shallow, materialistic life portrayed on the cave wall. This is not grand conspiracy according to Weaver. Rather, a society with such bloodless aspirations is forced to use propaganda. The unhappiness it causes would otherwise be too obvious for people to bear: “They [media] are protecting a materialist civilization growing more insecure and panicky as awareness filters through that it is over an abyss.”
Such a propagandised civilisation, our author warns, will suffer cyclic authoritarian spasms. Conditioned to think progress is relentless, modern man “… is being prepared for that disillusionment and resentment which lay behind the mass psychosis of fascism.” Long gone are the gentlemen who could move us from how we are, to how we ought to be, if we fulfilled our ideal. When the stereopticon fails, the public looks to anybody who can impose duties on them. These tend to be thugs fed on the same materialism as everyone else.
In conclusion, Weaver paints a picture of a culture undergoing a long, agonising death, yet clinging to the fantasy of its own life. Societies whose false idols are failing cope like a balding man whose hairs retreat ever more. He compensates with a combover until there’s nothing left to comb. Nominalism creates a contradictory culture. Glorifying pleasure, it expects heroism. Fragmenting the sciences, it expects wisdom. Destroying a common ideal, it expects its citizens to form a common front.
The treatment is polemical, and not a replacement for reading philosophers themselves. As a Platonist, Weaver unnecessarily denigrates Aristotle at times, blaming him for the decline of the medieval worldview. Yet some authors of similar politics to Weaver (like Heinrich Rommen or Edward Feser) would dispute this. He also glosses over Enlightenment projects like those of Rousseau and Kant without much analysis (Charles N. R. McCoy criticises them in much more satisfying detail). But for one wanting an overview of how a single wrong turn can doom a whole culture, Weaver’s clarity is unparalleled. His work is especially good as a locus classicus, with which to compare current trends against. Seldom, in my reading, do I find Weaver has nothing to say on a given topic.
Stop Pigeon Hate
Why is the pigeon so hated? Is it due to his availability as a target? After all, he is a common sight in our towns and cities, so common he can seem like an omnipresent nuisance.
Maybe it’s his appearance? Admittedly, he is less stunning than other birds; his generally grey countenance is far less pleasing than the radiant scheme of a kingfisher or the sparkled wings of a starling.
Perhaps it’s his stature? Small and stout, he’s certainly an easier target than any bird of prey, lacking the brawn of an eagle or the sleekness of a falcon.
Whatever the case, the pigeon does not have a good reputation. Recently, he has faced criticism for a variety of reasons, from trying to liberate mankind from its self-imposed enslavement to mass media, to taking over a house after the landlord made the avoidable mistake of leaving the windows open for four weeks.
In my view, the public’s attitude towards pigeons can be best summarised with a well-known, albeit not entirely original, comment from Ken Livingstone, former Mayor of London: “pigeons are rats with wings.”
Now this is simply not true. Given the opportunity, the pigeon shows himself to be a considerate and upstanding member of our society, which is certainly more than can be said for many of its human participants.
Naturally, some nuance is required. After all, there are many different types of pigeon and there is no strict distinction between a pigeon and a dove, the latter of which has marginally better connotations, such as being a symbol of peace and salvation.
The largest and most common pigeon in the UK is the woodpigeon. Shy and tame, they are mostly grey with white patches on its neck and wings. Although primarily found in rural areas, they can also be found in more urban areas.
Due to their sizeable presence, you’ve definitely heard their call, especially if you live in suburban England. The soundtrack to a gloomy Sunday evening, their gentle cooing stirs a sense of melancholy in the local children, reminding them they have got school tomorrow.
Secondly, there is the collared dove, which gets its name from the black mark which stretches around the back of its neck. Pale brown, with reddish eyes and feet, unless there’s a buffet on offer, they’re almost exclusively seen on their own or in pairs.
Indeed, the collared dove’s unwavering monogamy is arguably more defining than the mark to which it owes its name. Wrapping only half-way around it’s neck, hence it’s comparison to a collar, when united with another collared dove, it becomes a full matrimonial ring. How’s that for nature’s poetry?
Then, there are rock doves. Also known as the feral pigeon, they are ancestors of domesticated pigeon. Coming in a diverse range of colours, from dark blue to black, from pale grey to white, from a rustic brownish orange to a brick-red.
These are the urban sprawl of pigeons. Whilst all creatures are innocent until proven guilty, should you find a stray blob of poop on an inner-city pavement, he’s going to be your prime suspect. When people speak of rats with wings, they think of the cooing greaseball known as the rock dove.
Similar to rock doves, stock doves have darker feathers, especially on their rump and wings, a distinct green neck patch, and a pink chest. Concentrated in the English midlands and southwest, becoming rarer in northern Scotland and Ireland, the UK is home to over half their European population.
However, unlike the rock dove, the stock dove is less likely to be seen in urban and suburban areas, preferring farm life to big city living. This is because he is generally shyer and more averse to humans than his cosmopolitan cousin.
Finally, the turtledove is the runt of the flock, being only slightly bigger than a blackbird. Arriving in the UK in spring and leaving for Africa in winter, its feathers are a distinctive mottled mix of a black and golden brown, with a white-rimmed black tail.
Unlike his relatives, the turtledove is a picky eater, choosing to indulge on cereal grains, oilseed rape, and chickweed. Unfortunately, due to his refined tastes, the turtledove has been in decline since the mid-90s, largely due to a lack of his favourite delicacies.
Given this, we can see that the pigeon is not merely a rat with wings. All at once, the pigeon is a sensible everyman, a young lover, a boisterous yuppie, a country bumpkin, and a persecuted aristocrat. They are diverse and endearing creatures with varying personalities and habits, reputations and interests, but much of the public want to exterminate him over a few measly droppings.
Every bird defecates, but the pigeon is solely hated for doing so. It’s for this reason I militantly oppose anti-pigeon architecture. Every public building in Britain is glazed with spikes, ruining their appearance in the name of protecting it.
On several occasions, I have sat in York station, waiting for my train home, with a quiet emotional investment in pigeons looking for somewhere to perch, watching them steer clear of the spikes, mentally cursing the communist station master who had them installed.
I’d prefer railway staff clean up bird droppings than behave like members of the Cheka, indulging their pathetic power fantasies by shouting at people for standing less than a country mile behind the yellow line. Mate, mate, mate. Health and Safety, yeah?
Following the riots of Oxford Street, which included looting and violent clashes with the police, one left-wing academic suggested the chaos could’ve been avoided if the rioters had access to public swimming pools.
As most people realised at the time, this suggestion is ridiculous on a number of levels. For one, unlike animals, humans have an innate tendency towards evil. It is easy to imagine machete brawls between illiterate migrants and fake bomb threats by TikTok pranksters overrunning such places.
However, it raises an important, if only loosely related question: why are there so few public birdbaths?
Despite his reputation as a feathered hobo, the pigeon is quite a cleanly creature, taking every chance he gets to fastidiously groom himself.
We have a birdbath in our garden, and we have many regulars, our most well-known being an especially rotund and fluffy woodpigeon, whom my mother affectionately refers to as Fat Wilbur.
I do not see this ‘winged rat’ Livingstone speaks of. Wilbur makes his stop, does what he needs to do, takes in the atmosphere, before moving on his way, not wanting to overstay his welcome. Should other pigeons accompany him, he makes room, as they do for him, and all is well.
The idea that such tranquillity could emerge in a society as presently low trust as ours is simply absurd. Of course, being a pigeon, it’s unlikely he does this for any pretentious, perception-based reason. Indeed, his fixation must be rooted purely in the value of cleanliness itself!
However, contrary to pervasive anti-pigeon sentiment, the pigeon is not only a cleanly creature, but a clever one too.
It can be hard to accept that pigeons, creatures known for flying into windows and pecking at cigarette butts, can distinguish between Picasso and Monet, but they can. In fact, according to the scientific research we have, pigeons are amongst the most intelligent birds in the world, showing a variety of relatively complex cognitive abilities.
Of course, whilst it is undeniable that humans are much smarter than pigeons, we do not use our superior faculties particularly well.
Whilst humanity may be threatened by the whims of idiots or a lack of imagination, hindering our ability to innovate and develop, our kind is similarly threatened by overthinking.
As a result, we deny ourselves the ability to be authentic, we shun risks in the name of avoiding embarrassment and pain when such risks could just as easily bring us laughter and joy. In the words of Paglia: “consciousness has made cowards of us all.”
As such, we should not be surprised when pigeons manage to be funnier than us. Just by being what they are, pigeons are funnier than basically every living comedian. Every wannabe BrewDog-sipping funny man, with his safe-edgy humour and hashed-out irony, fails to be more amusing than a random birb going about its business.
Walking around in circles, sporadically pecking the pavement, stopping occasionally to exhibit his dumbfounded ‘the lights are on, but nobody’s home’ expression, bobbing its head like its listening to a really good song, it is a grave fault in our being that a character as innocently absurd as this is considered less amusing than James Acaster.
Even the mere idea of a pigeon is funnier than most human attempts at humour. Go ahead, in your mind, visualise a pigeon (don’t worry, the cops can’t do anything… yet). You see that? Now that’s comedy. If you deny this, you Just Don’t Get It. Not much I can do about that.
Looking at these odd creatures, has nobody once thought: what are they up to? What’s their game? Why did they peck there and not there? Why did he take flight for seemingly no reason? Is there some secret pigeon meeting he needs to get to? What’s his schedule? Does he have time for an interview?
Yet, despite his apparent gormlessness, it is clear pigeons are far more sensitive than the average human.
If you’ve ever commuted anywhere via public transport, you’re no doubt familiar with the hectic nature of it all. From the loud noises to the chaotic stampedes, from the excruciating delays to the dodginess of certain folk, commuting isn’t exactly what most people would call an enjoyable experience.
Of course, whilst we might find certain aspects of commuting more annoying than others, we all agree on one thing: the worst part of commuting is other people.
Compare this to the pigeon, who shows consideration for personal space, does not play loud music, doesn’t try to con you out of your money, and generally minds its own business, preferring to get out of your way, rather than get into it.
If what Sartre says is true, that hell is other people, perhaps heaven is to be in the company of animals. More to the point, who is better company on a long commute than a pigeon?
Undoubtedly, the pigeon is not a faultless creature, and the shortcomings of us and other beings cannot excuse or undo this fact. That said, any fault which can be found with the pigeon can easily be remedied by human custodianship. We must spare him from the misguided disdain of busy adults and the clumsy tyranny of misbehaved children.
Pigeons are not flying rats, nor are they government spies. They are our friends and we should treat them as such. Stop Pigeon Hate!
Digital Censorship Is Now the Perfect Crime
The combination of free speech and the internet should provide an unprecedented democratising effect on public discourse. After all, anyone with a decent idea can now reach out to millions of people worldwide, regardless of their wealth, respectability or social status. The potential for innovation is endless.
And yet, looking at the world today you would be hard-pressed to find a clear exemplar of this democratising effect. It appears that new technology has also created new forms of censorship. Control of public speech is now so subtle-fingered that it’s often hard to recognise as censorship or even detect when it’s happening at all.
To understand this new phenomenon, it’s worth taking some time to consider how social-media algorithms work and why they’ve become so important to our society.
Ideas spread through social networks and the fastest social networks are those found online, managed by large corporate platforms like Facebook, WeChat, Twitter and YouTube. These sites all curate what’s seen by the user into a ‘feed’. In order to create the feed, posts are ranked automatically based on numerous statistical parameters: the number of views, likes, comments and shares; the ratio of these quantities to each other; the upload date; the topics and tags assigned to the post; and so on. Network spread is accelerated by the number of followers of the poster and of the commenters and sharers. So far, this is common knowledge – but the algorithm doesn’t stop there.
It’s a trivial piece of programming to scan each post for keywords and assign a score to the post according to its content. Some words are coded as ‘negative’ or ‘positive’, or linked to different emotions like anger, outrage, joy, pride and so on. Based on this score, you can assign a different behaviour to how the social network treats the post. The post might be ‘throttled’ and shown to a disproportionately small number of accounts or it might be ‘boosted’ and shown to a large audience.
Instead of emotions, algorithms can also score posts on their political alignment with a range of contemporary pieties, such as racial or social justice, lockdown advocacy, or climate change. Individual accounts could then be given scores based on the type of posts they make, ensuring that the most egregious or inflammatory posters are quietly and gently smothered into irrelevance. Everything is automatic. No humans are involved. You, the poster, would have no idea whether censorship was happening or not.
The mechanism described above need not be the exact approach used by Twitter, Facebook or any other site. Consider it an illustrative example of how an engineer like myself could easily build multilayered and highly sensitive speech control into the networks of public discourse, to run a controlled speech environment that seems ostensibly like free speech.
Ultimately, all meaningful public discourse is now finely manipulated by the hidden algorithms of these social-media corporations. This is a reality of life in the 2020s. And with private companies manipulating public speech in these arbitrary and unaccountable ways, governments around the world are eager to get a slice of the pie.
Bearing the new algorithms in mind, consider how a government might suppress an idea that’s hostile to its interests. In the 1500s, the king’s men would march off to all the troublesome printing presses and intimidate the publishers with threats of vandalism, imprisonment or execution. It is against these weapons that the great Enlightenment arguments for free speech were constructed. Indeed, smashing up publishers was a risky move, creating martyrs and stirring opposition to absolute rule among the educated classes.
But in the 2020s, no such kerfuffle is necessary. State censorship has become astonishingly easy. The government need merely express its views to the management of a social-media company via their private channels, and every post sharing a particular idea will be throttled, demoted or blacklisted. Even if you can post the idea, the prominence of its spread has been hamstrung. It is thus the perfect crime, costing governments nothing, creating no martyrs and leaving opponents and their followers with paranoid doubts as to whether they were suppressed in the first place.
Different governments achieve this in different ways. The US is a world leader in invisible censorship, helped by the fact that almost all major social networks are Silicon Valley entities (enjoying close ties to the US intelligence apparatus). The most visible incidences of US censorship on social media concerned sensitive information about the Biden family during the 2020 US Elections, and the control of narratives surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown measures.
Across the pond, the EU has passed into law a Digital Services Act (DSA), which came into effect last month (25th August 2023). The law empowers a large taskforce on disinformation, answerable directly to the European Commission, to immerse itself in public discourse control and censorship on all major social networks. Twitter is required to meet regularly with this taskforce and answer to demands of the Commission regarding ‘misinformation control’ or face fines and other sanctions from the EU.
Critics of the EU will note that the EU parliament is again sidelined by this troubling new institution. And like the GDPR regulation of 2016, this is liable to become a global standard in the relationship between state institutions and the internet.
What terrible danger demands such a robust approach to information control, you might ask? The usual suspects appear in a list of disinformation trends compiled by the EU-funded fact-checking hub, EDMO:
- ‘nativist narratives’ and opposition to migration;
- ‘gender and sexuality narratives’ that cover trans issues;
- the ‘anti-woke movement’ that ‘mocks social-justice campaigns’;
- ‘environment narratives’ that criticise climate-change policies.
Each of these problem issues is subjective and political in nature. It appears that the EU is concerned with changing the views and opinions of its 450 million subjects to match the ‘social justice’ ideology of their leadership – which is precisely the opposite of democratic governance.
The arguments of classical liberal thinkers are outdated when it comes to combating this new form of censorship. It is true that whenever an idea is silenced, the community is made poorer by not having heard its voice – but can that argument be made with the same vehemence when the idea is merely muffled or massaged into a lower engagement ratio by a tangled web of hidden algorithms? Is there an essential ethical difference between government interference with public discourse through social-media algorithms and the interference of an agenda-driven Californian software engineer who happens to work at one of these companies? Most media outlets don’t even describe this process as censorship, after all: it’s just ‘content moderation’.
Proponents of subtle censorship will point to the numerous social goods that might conceivably come from light-fingered thought control on social media. These include the suppression of enemy state propaganda, the neutralisation of dangerous conspiracy theories, and the management of violent sectarian ideology that could cause social harm or terrorism. But aside from the foiling of vague and nebulous threats, whose impact can never be reliably predicted, it is hard to see what conceivable gain comes from surrendering our right of free public discourse to unelected state organs like the European Commission taskforce.
The danger we face is that our present situation could rapidly evolve towards the total engineering of public discourse on social media. Western governments have shown an alarming desire to create populations that are docile, disorganised and progressive-thinking, rather than trusting the democratic process to produce good ideas through argumentation and open debate. Subtle censorship on social media has the potential to nudge us into a dystopia, where people are only permitted to organise around an elite-approved set of curated ideas.
Soundbites Over Sound Ideas
‘It’s a no to NOS.
We will ban nitrous oxide, also called laughing gas, putting an end to the littering of empty canisters and intimidation in local parks.’
This tweet by Downing Street earlier this year tells you everything you need to know about its policies. In an attempt to curb antisocial behaviour and littering, the government wants to ban nitrous oxide, more commonly known as laughing gas.
Seriously.
Ok, is it the worst policy in the world? No. It’s probably one that most people would agree with. The problem is that the government has said that banning it would end the issues described. It’s a plaster on a stab wound.
That’s what the government likes to do. It likes to offer pretty promises that won’t do anything to curb real issues.
Anti-Social Behaviour
Anti-social behaviour is evident in our communities. The elderly may grumble about how ‘kids in my day had more respect’ and to give them credit, they’ve got a point.
Society has a lot to say as to why this is. One reason given is the destruction of the nuclear family, especially fatherlessness. Studies have shown that children who grow up in single-parent families, particularly those without a father present, are more at risk of becoming criminals. Others point to a lack of discipline in the home and school. Scottish teaching unions warn that teachers are at risk of dismissal and unfair treatment when disciplining children.
Banning nitrous oxide will not solve the problem of anti-social behaviour. They will still drink and smoke weed and cause chaos. They will continue because they know that they can get away with it. The government and other authority groups are yet to actually come up with a solution to these problems. If they continue to allow criminals to get away with things, then they will.
Labour often blame the Conservatives for this. The usual line is that the Tories have slashed funding for youth and community centres, which encourages crime and anti-social behaviour. This is an argument many refute. Many live in areas with parks and swimming pools and leisure centres. These are free and accessible activities. Bored kids don’t go out and rob. These are kids with no discipline or regard for other people. It’s easy to find something to do these days. Instead, lack of discipline and glamourising such a lifestyle fuels this epidemic.
Obesity
The Welsh government has unveiled plans to restrict 2-for-1 deals, multibuys and other deals on ‘unhealthy’ foods. They have argued that it will help decrease obesity and diabetes.
The English government did a similar thing in 2022, banning sweets and junk foods from being displayed near tills.
The logic behind them is as follows: it will stop people impulsively buying junk food and will prevent kids from begging their parents for treats at the till. Suddenly, obesity and diabetes will drop.
Sure.
Obesity is more than just junk food. Firstly, perhaps the government should acknowledge that a lot of parents and people in general have a thing called self-control. They can easily avoid sweets or just tell their children ‘no.’ Sure, some may fall into it, but many can resist temptation.
Secondly, people will also still go down the sweet aisle. They will still get treats, even if they’re a little further down.
Thirdly, the government can bog off controlling lives.
In a cost of living crisis, one would think making things more expensive is just a bad idea. If the government was to actually tackle costs, then maybe healthier food would be easier to buy and make. They cannot get rid of convenience, but it would be nice if prices were better. With more and more people feeling the squeeze, the idea of affordable good food is a tempting one indeed.
One must also factor in things like exercise. Eating alone does not solve health problems. Once again, our elders will complain that kids don’t go outside because they’re glued to a screen. I don’t like to give it to them, but again, how often do you see a toddler being pacified by a tablet?
Both indoor and outdoor sports are easily available. It does not even have to be organised- anyone can have a kickabout in the park. Perhaps we could encourage more PE and sports at school. It’s not just kids either- we should all move about a little more.
Heat
Once again, the government wants to ban something. This time, it’s oil boilers that are on the chopping block. The plans would see those not connected to the gas grid be forced to find a new source of heat.
Having new boilers and heat sources installed is not cheap- it can cost up to tens of thousands to replace. That is money not many people have. Add that to high heat and energy bills, mix in the cost of living crisis, and you have a terrible policy.
The plan is a clear attempt to win over environmentalists. Politically, it’s extremely stupid. Most hardcore environmentalists won’t vote Tory anyway. Secondly, rural areas are usually Conservative. Annoying your voters is not a great idea, especially when you’re lagging in the polls.
It’s a policy that is not only politically useless, but it’s actively hurting people’s finances. Once again, the government claims to know best. It’s a pretty soundbite policy, but not a solution.
Once the government decides to find actual solutions- or even just stick their noses out- things could actually improve a bit. Instead, they just focus on nice graphics and soundbites sent out by their press officers. It’s idealism and stupidity in equal measure.
Political spin seems to be the in thing. They tell us what they think we’d like to hear as opposed to using their limitless powers to help. If they are going to get involved in our lives, then let it be for the better.
Soundbites don’t work and the second the government realises that, then progress can be made.
Kino
Against the Traditionalists
A Premise:
Deep, and yet deeper down, below the marsh slime and the swamp rot, even underneath poppy roots and the granite rows, Old England’s Foundations lie. While thinned and turned soils are cold and damp, the fiery Mantle warms and pulses, twisting round and circling on itself; the Core sees into itself and ponders on its shadows; to reach out into the cold and dark, hope perchance to find new wheels to turn, or perhaps not. Content, in the underworld, dreaming of the pictures of its marble face, Old England’s Foundations are buried the deepest, overwritten by thin and beaten sheets of plaster and tissue paper.
Yet, this is a fantasy: circumstantial myths of Old England, and its Foundations. Those marshes were sealed, and the swamps became roads, and the shapes and the names of the trees do not matter anymore. Accumulated plays turned in on themselves and became a meaningless fresco; the hand-me-down uniform, hoarded in poverty, with no weavers to craft anew. That Core is no form but a feeling, fleeting and shallow, giving only the image of warmth. Gawp at the statues and the towers and the gold on the wall. They were never yours.
Intermission, The Alchemists’ Folly:
Higher, and yet higher so, far reaching beyond the sea and above the clouds, up and up Nature’s Ladder, climbs a Champion. For all its power and glory. He soon received the ravenous attention of The Crow, the most cunning of all the birds. It said: “I have seen many climb, and their plans dissolved away, but wear my feather, and sing my song, and Nature’s sure to play”. The Crow put a feather on The Champion’s shoulder, and The Champion cawed until he had near reached the clouds. He looked down to measure his climb, and one cheek was slashed by The Crow’s feather; he saw many other smaller birds with more beautiful sounds and colours than The Crow, hiding fearfully away in their nests.
Higher and higher, between the feathers and the stars, up The Ladder, climbed The Champion. The clouds from below were sunlit pillars in the sky yet seemed smoke and fog inside. At once, the guiding stars were blotted out, and The Champion was frozen in the dark. He begged it clear, and The Cloud said: “Truly, Nature loves to hide, and seems at first a chaos sight, but learn its ways, obey and pay, by water’s path will light”. The Champion’s waterskin was plucked by a gale, and The Cloud gave in credit due a magic hailstone, and it magnified the light of the stars. His fingers were cold and heavy, his water was lost, and the constellations seemed more twisted than ever before; but, with the dim path seen by magic divined, The Champion waged on.
An earthquake struck, and The Ladder path fell; weathered wood, by many footsteps heeled, shattered with the turning of a generation. His bearing steers all amiss under the dizzying constellations, for the old way is no more; and The Champion loses their footing, curses the folly, and plummets into brine under the bottommost rungs; championing, no more. The Fool who works with wood and nail, at the bottom of The Ladder, did not build houses that day, for another ladder was built by him; and The Fool then propped it, already to seize the opportunity, to climb the path again. But The Cloud and The Crow remain in their Nature, as they wait between the salt and the stars.
Their Conclusion:
Hailing practice and ritual, making nothing new, and the new, ugly; what comes from a fool’s history? Yesterday’s legislation becomes today’s tradition, and old and common habits are preserved by kitsch committee. To justify what happened, because it happened, accounting to stacked sediments of past scoresheets? If that is good, then good is evil; bored eyes make nothing beautiful around our empty hands, so we make eternities of nothing, and are compassed about by our enduring appetites. With Nature as your sentimental measure, you pay tribute to accidental shadows on the wall. Where is The True, The Good, The Beautiful? God have mercy on your windswept souls.
Featured
To be Anti-Refugee is Un-British
I
Compassion for asylum seekers is a traditional British value – a real British value, not a Quango-invented value like ‘tolerance’ that wouldn’t be out of place in any Western European country.
Britain’s reputation as a friendly haven for the oppressed is wholly based in historical fact – and I don’t mean “we found the skeleton of a 15th century black man in Cornwall, and that’s why unfettered channel boat crossings are a good thing”.
Now to be clear: a refugee is not a migrant. Most channel crossers are economic migrants looking for wealth, which I am not here to defend nor discourage. When this article says “refugee”, I am referring to those fleeing war or persecution, such as Ukrainian civilians, Iranian political opposition, or Uyghur Muslims from China. And while I do not advocate handing out visas to all 21 million stateless refugees in the world today, it is my opinion that we should take in many more than we currently do – regardless of any policy towards other forms of migration – and make the United Kingdom the best and most welcoming place in the world to be a refugee. Not just for altruistic reasons either – we can greatly benefit from this arrangement.
From 1828 to 1905, at the height of her imperial power, the number of immigration restrictions the British Isles had was zero. The borders were completely flung open, allowing anyone who was downtrodden, oppressed, or impoverished the chance to live a life of freedom and security behind the protection of the Royal Navy.
This was a point of pride to the Victorians – the Times newspaper wrote in 1858;
“Every civilised people on the face of the earth must be fully aware that this country is the asylum of nations. We are a nation of refugees. There is nothing on which we are prouder and more resolute.
All Europe knows and respects the asylum of these isles.”
The first wave of refugees from the continent – since the Huguenots – were the French clergy and nobility fleeing the Reign of Terror. Around 4,000 arrived in 1792, settling mostly in Soho and other affluent areas of London. They were forced to undertake manual labour for the first time in their lives, working as tailors or publishers. Due to a lack of Catholic churches in London at the time, Anglican churches such as Saint Pancras welcomed their brothers in Christ and offered church facilities for Catholic masses and burials. No fewer than eight former French bishops are interred at the church.
The Duchess of Gontaut wrote of her arrival to England;
“Arriving at Harwich…made my heart beat faster in the hope of a better future. It was a happy premonition because from that moment we experienced the good and loyal hospitality of the English.”
Successful integration of refugees is surprisingly easy – give them the chance to work, and access to resources. Economic deprivation is the number one predictor for whether or not an ethnically diverse neighbourhood is socially coherent, but current policies make this nearly impossible; Refugees in Britain must wait 12 months after arrival before they have the right to employment.
Labour is the world’s most valuable commodity—yet for 12 months, a refugee is forced to relax in a four-star hotel and eat free chef-prepared meals, all paid for by taxpayers. The faster a refugee can obtain a job, the faster they can be turfed out of hotels and become productive members of society.
II
The Victorians were so committed to the policy of free asylum that they were even willing to create diplomatic scuffles to uphold it.
In the mid-century came the socialists. Marx, Engels, Kropotkin and co. all escaped harassment from tyrannical European governments by making the free and prosperous shores of Britain as their home.
In 1858, a collection of these continental anarchists based in a London lodging house plotted a failed assassination of Napoleon III. One man who stood trial for this conspiracy was French exile Simon François Bernard. The French government demanded he be punished – but the British press were steadfast in their opposition to a conviction. Partly because it would undermine the policy of open borders (some things never change), but also because anything that frustrated our eternal rivals was surely a good thing.
While I don’t suggest we invite any Islamic terrorist groups to set up an embassy in Fitzrovia, we can learn from this example to forge our modern-day policy on political refugees.
I and many readers of The Mallard yearn for a restoration of Britain’s prestige on the world stage, a way for our now Empireless nation to regain that global reach. So what could be more of a leverage over our enemies than aiding those who are consistently a thorn in their side?
Several Hong Kong dissidents such as Nathan Law have already fled here and continue to campaign for a free Hong Kong from the safety of the UK. We could extend this to other Chinese, Iranian, or Russian political dissidents, and be the first port of call for Governments-In-Exile. Provided that they do not actively harm British or Western interests, we can only gain geopolitically by being the prime destination for exiled activists the world over.
III
The open borders policy came to an end at the start of the 20th century. The last wave of refugees were impoverished Poles and Jews escaping persecution from the Russian Empire. One such refugee named Israel Lipski was hanged in 1887 for the murder of a woman in Whitechapel, and the story gave rise to the notion of “pauper aliens” committing crimes, stealing jobs, and pushing up rents.
The Conservative government of the day proposed the first restrictions on immigration in 1902. But they weren’t completely without opposition – it was none other than Winston Churchill who said these new rules were;
“a loathsome system of police interference and arbitrary power that would harass the simple immigrant, the political refugee, the helpless and the poor…This country has so greatly gained from the old, tolerant, and generous practice of free entry and asylum. This law is expected to appeal to insular prejudice against foreigners and racial prejudice against Jews.”
And Churchill was right. Even today (despite eye-catching headlines) the effect refugees have on the crime rate is low. During the 2015 European migrant crisis, Germany took in over 1.4 million refugees – yet by 2019, their crime levels had fallen to the lowest in thirty years.
And if a refugee does commit a crime, surely the only person who should be punished is the guilty refugee – not the thousands of other innocent, law-abiding evacuees with whom they arrived alongside.
Nonetheless, the Aliens Act introduced the first restrictions in 1906; immigrants were required to prove they could support themselves financially, not be “liable to become a charge upon the public rates” (i.e. disabled), and have a clean criminal record.
IV
But this was not the end for Britain’s role as an international safe haven for the oppressed. During the Great War, almost 250,000 Belgian refugees were given shelter on these isles, all housed and fed for the duration of the war despite the hardships and food shortages suffered by the nation. The generosity displayed by the British is illustrated in the 1916 Fredo Franzoni painting “Landing of the Belgium Refugees”, showing dozens of boats carrying huddled masses landing in Kent. They are being welcomed by a large crowd led by the mayor of Folkestone. To the side, a nurse stands ready to tend to the sick, while two children bear welcoming gifts. A British ensign flies prominently from one of the ships.
Many of the Belgians were housed by individuals volunteering a spare room. Others were housed in purpose-built villages ran by the Belgian government-in-exile, where inhabitants used Belgian currency and spoke Flemish. Despite some local objections to these ethnic enclaves, within a year of the war being over, 90% of refugees had returned to Belgium. Their only lasting impact being a few memorial plaques, and Agatha Christie’s Hercule Poirot – who was based on a Belgian that Christie had housed during the war.
If we could do it in 1914 during total war, we can certainly do it today.
Granted, the cultural differences between a Brit and Belgian are smaller than a Brit and a Syrian, or an Iranian, or a Venezuelan. But those of you who are worried about the social and ethnic composition of Britain needn’t worry about refugees – like the Belgians, the average refugee spends less than ten years in exile before returning to their native country, and only the most protracted conflicts such as in Afghanistan or Vietnam produce refugees who stay longer than 20 years. Those who choose to stay permanently are clearly integrated Anglophiles who prefer British society over the land most of their compatriots have since returned to.
Overall, while you and I may disagree on general high or low skill migration into Britain, it’s quite clear that compassion for asylum seekers is a long-forgotten tradition that we should reclaim. We can learn from the 19th century to build an asylum system that is both economically and geopolitically a benefit to us – as well as, of course, being the moral thing to do.
It’s Over/We’re Back or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Rollercoaster (Magazine Excerpt)
In short, the year started badly but was peppered with good moments. By mid-2022 it was going excellently, and I thought I was finally past the worst of what this year could throw at me. My hubris was rewarded with some of the worst few months of my life so far. I know that, in the grand scheme of things, I should be thankful for all that I have, and I certainly recognise that I have it much better than most people. It helps to remember that, but it doesn’t change how I felt and acted at the time.
I suppose that that is the nature of life and hindsight. At the time, these moments seemed to mean everything. They either crush your soul and spirit or bring you to the highest heights. I think that this sentiment is expressed quite well in the ‘it’s over/we’re back’ memes that have propagated themselves across my twitter timeline for the past few years. We outright refuse to recognise our own mundane victories and losses, and instead focus on the peaks and troughs – this is natural of course, we would go completely insane otherwise.
I don’t think it is bad to allow these experiences to hit you. Part of the human experience is to be hit by these ups and downs. It is the dwelling on these events that becomes a problem. Holding on to fading hurt and fleeting success instead of moving on in some sort of twisted nostalgia for our best and worst moments can lead us down a very dark and dangerous road. It makes us forget who we are and who we can be. Our lessons learnt, we should embrace the change and simply move on. It is in these moments that we grow and mature as people, and become a better version of ourselves.
For me personally, this year has been an absolute rollercoaster of highs and lows, and that has been very hard to deal with. Things seem to be better now, however, and I am filled with enthusiasm for what the new year can bring me. I think that 2023 will be an amazing time for personal growth and development. I still have a lot of weight to lose, but I am steadfast in my determination to see it through this year. Coming to terms with my situation and state of mind will not be easy, but life is not supposed to be easy. Nothing worth doing is easy.

This is an excerpt from “Provenance”. To continue reading, visit The Mallard’s Shopify.
Predictions for 2023 (Magazine Excerpt)
The 2022 midterms should have been a bloodbath. It should have been a huge sweep for the Republicans, relegating the Democrats to the depths of minority rule. Instead, the Republicans managed to win the House only respectably, whilst the Dems kept the house. It’s widely believed that better candidates could have kept the house.
Good candidates do exist. Ron DeSantis managed to make gains in Florida. Glenn Youngkin flipped Virginia. Brian Kemp safely won re-election in Georgia. Unfortunately, there were also many poor candidates. A competent Republican could have beaten John Fetterman in Pennsylvania. Somebody else could have beaten Katie Hobbs.
The same is true for Presidential elections. The Republicans have only won one election in the 21st century outright, with both the Electoral College and popular vote – George W. Bush in 2004. 2000 and 2016 both saw Electoral College wins but popular vote losses. Whilst external events came into play, it’s not a great look.
That being said, it almost seems that the Republicans like losing. They’re not making any real attempt at winning. Whilst they might choose decent candidates, there’s a high chance they won’t.

This is an excerpt from “Provenance”. To continue reading, visit The Mallard’s Shopify.
Avatar: The Way of Water Review (Magazine Excerpt)
It has been almost 12 years since the release of one of the highest grossing films of all time – that being 2009’s Avatar, James Cameron’s sci-fi epic.
There has been a running meme for the last couple years that despite the first Avatar film’s wild success in the box office, it isn’t a memorable film. The characters aren’t memorable, the storyline is a copy and paste of 1990’s Dances With Wolves, and that its success hinged on the technological breakthroughs in CGI and 3D film that were a staple feature of the film.
In retrospect, the running joke isn’t far from the truth. Avatar is a film that hasn’t held up for casual viewers on its own merits, but rather through nostalgia of a time that has long passed – a time before the insanity of the last 10 years in the social and political scene, where most people were more concerned about the film’s core messages; that being a deeply environmentalist film, a critique on colonialism, and the insatiable appetite of human discovery wreaking havoc on innocent and more noble creatures.
While there are aspects of the original film I enjoy, such as the detailed world-building that Cameron is known for, and the cutting edge visual effects, it still failed to resonate with me the way it has with many other viewers.
The preaching was exhausting when I watched it the first time in 2009, and it is still exhausting today. I get it. Humans are bad, save the trees, the military industrial complex is so evil, etc, etc.While the second installment Avatar: The Way of Water certainly delves a little deeper into the lore and ups the stakes for the protagonists, it still carries the same bare-bones environmentalist sermon that has become all too exhausting in this day and age, especially when we have Extinction Rebellion and Just Stop Oil cronies ruining fine art and causing general inconvenience to all those around them in our current reality.

This is an excerpt from “Provenance”. To continue reading, visit The Mallard’s Shopify.
Politics is About Winning
In the aftermath of the 2020 Presidential Election, Joe Biden proclaimed victory with a vomit-inducing call for unity. “They are not our enemies. They’re Americans. This is the time to heal in America”. Such pleas are suspect when you’ve spent the last four years treating the other camp as enemies; deplorable Neo-Nazi maggots that need removing from society, etc. “Coming together as Americans” would be easier to do if a common American identity still existed; a concept that politicians like Biden have always felt uncomfortable talking about. Trump’s allegations of election fraud have caused outrage, but why should they? Given that his opponents have convinced themselves he’s a tyrant comparable to Hitler or Mussolini, why wouldn’t they do everything they could to remove him from office? Democracy cannot sustain itself if it allows forces perceived to be anti-democratic to gain power via the democratic process. This is when the most self-righteous defenders of democracy, discover they are not, and cannot be, as “democratic” as they first thought. If the election was rigged, Biden becomes President, and he is seen as legitimate, then I must give him props. A masterclass in the art of winning.
Nevertheless, anyone with even a slither of intelligence can see this farce; rhetoric espousing the need for unity is not only disingenuous, little more than an implicit demand that your opponents should start agreeing with you, but also contrary to the notion of democracy. Democratic politics is irremovably state of conflict. At first, this seems a rather peculiar claim to make. Democracy can be divisive perhaps, but not a state of conflict. Conflict is a word we associate with war and terrorism; it is what democracy theoretically seeks to avoid, making it hard to imagine how these words can be synonymous. Nevertheless, it is reasonable to conclude that, as Carl Schmitt said: “the specific political distinction which political actions and motives can be reduced is that between friend and enemy”. The formulation of political motives cannot be removed from the formulation of political friends and enemies. Politics is about power, and if power is the ability to actualize one’s desires, then politics is the ability to triumph over the enemy in the pursuit of an end; politics is about winning.
Democratic politics is not an alternative to conflict, rather it is an obfuscation of it. If “war is the continuation of politics by other means”, then surely politics is the continuation of war by other means, or as Mao Zedong put it: “politics is war without bloodshed while war is politics without bloodshed”. Nevertheless, whilst we may concede that democratic politics is innately adversarial, defining it as a “state of conflict” sounds hyperbolic. Democratic politics is closer to contest than conflict. Both are fundamentally adversarial, but the former is chaotic and brutish, whilst the latter implies a sense of fair play, established rules, and marks of mutual respect. So be it, politics is a contest, even if contests are about winning.
Political contestation appears in many forms. Voting, joining a party, leafleting, petitioning, protests, debate, discussion, rhetoric, making your opponent look cringe, careerism, parallel institutions, etc. are all methods of contestation. We would separate these from methods of conflict: terrorism, revolution, civil war, etc. Unsurprisingly, bribery, blackmail, and deception fall in the ambiguous twilight zone. Nevertheless, whilst methods of contestation and methods of conflict are different, they both imply adversity and the attainment of victory. If one’s goal is victory, it shouldn’t come as a shock to suggest that some methods of contestation are more effective than others. After all, victory is achieved through assertion that is skilful and effective, rather than reckless or impotent. The idea that we must choose between meaningless debate and senseless violence is a delusion.
Darren J. Beattie was correct in his analysis as to why conventional conservative rhetoric has been so weak. Mainstream conservatism (see classic liberalism injected with a bit of transmogrified Trotskyism) rhetoric falls flat is because it is inherently pacifistic; it immediately puts conservatives on the defensive. Ascendant left-wing slogans by contrast does not have this problem. Their ideas are not posed for your consideration, they are commands by which you must abide. They are not policies, they are instructions. They are not posed as potential solutions; they are prescribed as the solutions. Sir Scruton also identified this problem, whilst the Left tells us we must march forward into the future, conservatives can only advise us to hesitate. Conventional wisdom has been taking a battering in recent times, but it appears that attack is still the best defence. Power is a vacuum to occupied, not something to be left in awe at. Fill it or your enemies will.
The idea that politics being downstream from Parliament is a disease. In the context of politics, the words “winning”, and “power” will be connotated with becoming an MP and forming governments. As such, it makes this doctrine common-sense to the partisan shill and problematic to the enlightened moralist. This is one of the reasons debating has become so futile; nobody agrees on what anything means. You will find that everyone nods their head at the word “equality” but ask them to clarify what “equality” means and you will find their hands at each other’s throats. Herein lies the fundamental rule: the metapolitical defines the political. As omnipresent as they are, bickering politicians and the parties they comprise are little more than pawns in a game of cosmic chess. What shapes them? Hegemony. Our politicians are shaped by the forces, attitudes, and ideologies that are ascendant. Not popular, but ascendant. Ways of thinking that everyone is expected to subscribe to. The subjects of the Prince can argue amongst themselves as much as they please, so long as they do not anger the Prince. For the Prince is the being around which they orient themselves; the Prince is hegemonic. As Machiavelli notes, it is important that the Prince’s priority that he be feared, rather than loved.
The Centre-Ground is a concept often banded around in politics. In divided times it is portrayed as a place to which we ought to return, an alternative to clustering at the polarising extremes. What is the centre-ground specifically? We are told it is the realm of reason as opposed to the dunes of dogmatism which lie beyond its borders. Much like the holy land, it is something in need of conquering, something to be held on to, and immediately recaptured when lost. Of course, this is all rubbish. It’s the kind of fanciful rhetoric that centrists insist they don’t indulge in. Centrism is a dead meme at best and cringe LARP at worst. Nevertheless, the Centre-Ground is an important concept because dissecting it can help us understand hegemony. Look to any self-identifying centrist individual, and you will find a cosmopolitan corporate-friendly establishment wet-wipe who flaunts their “high-status” opinions like the latest expensive consumer item.
However, it must be noted that hegemony is not static. As Macron has shown in France, secular hegemony cannot sustain itself by being a vacancy of something (in this case: state religion). Rather, it must define itself as something, necessitating exclusion. A secular republic cannot tolerate pockets of Islamism if it wants to remain a secular republic. As such we now find Macron, the establishment liberal technocrat, espousing rhetoric expected of Marine Le Pen. The rules are clear: hegemony is not only necessary, it needs to be asserted or it will be lost. Hegemony, even if cannot become a totality, is obligated to move in the direction of becoming one. The irony of secularism is that, despite its portrayal as a liberating nothingness, it is no different than religions in a theocracy; it must do more than exist, it must reign like Jupiter.
Hegemony is an organic manifestation. It is subject to ascent, apotheosis, and decline. It is not immune to contest, corruption, and death. As with hegemony on the international stage, when it is decline it becomes assertive and militant to sustain itself when it is challenged by a potential alternative. This is perhaps why the rise of right-wing populism across the West has coincided with more combatant and coercive forms of egalitarianism. Politics is a contest for power, and like all contests requires a winner and a loser. Contests end in the following ways: victory, stalemate, or defeat. Defeat and stalemate, obvious differences aside, do not depose hegemony. Only by winning can the groundwork for a new order commence. The Thucydidean Trap is escaped only though victory.
Moldbug quipped: “if you can explain to me how democracy can be a good thing and politics a bad thing then… you must know something I don’t”. The effect of a politicised populous has on the social fabric is entropic. Given the array of frontiers that a liberal democracy opens for contestation, it eventually finds it necessary level of cohesion there are subjects and values which become incontestable. When everything is up for contestation, there is chaos. To avoid chaos, somethings must be made incontestable; the things to we can say we all agree upon, that which we have in common. The paradox being that what should be considered incontestable is a highly contested matter; that the apolitical is not immune to politicisation.
Marcus Rashford’s campaign to extend and expand the serving of school meals is a good recent example of how the idea of humanity is made distinct from political matters. The government’s decision was not a political one, it was display of “a lack of humanity”. What is one man’s idea of humanity is another man’s political matter. Under such circumstances, how does one engage in rational discourse? Short answer is that they don’t. What appears in the place of rational discourse? Nothing pretty. Of course, the thought of people violently clashing on the streets of London like political street-gangs in Weimar Germany over whether to tweak a school-meal policy is absurd, although it does make for some bitter squabbles. Besides, such a concept may not be so absurd if the subject matter was substituted for something for fundamental. For instance, are we comfortable to put something as fundamental as the basic essence of our civilization to a vote? Is this really something we can afford to disagree about? Life is defined by degrees of difference; some differences are trivial whilst others more severe, some differences may not actually exist, whilst others are real and downright fundamental. It is when those trivial differences exhaust themselves, in the process of becoming fundamental, is an impasse reached and conflict burdens.
When hegemony is truly challenged, a political disagreement mutates into a Manichean struggle between lightness and darkness, between the “human” and the “inhumane”. This is perhaps why the term “Taking the Red Pill”, the breaking of an illusion as seen in The Matrix, has become so prominent in dissident right circles; it implies that the sanctity of the Cathedral has become contestable. The idea of neutrality is important as it implies a lack of contestation, and therefore it is fair to say neutrality is a product of hegemony. To “win” at politics is not to win an election or win a debate, it is to achieve hegemony; it is to turn something from contestable to something incontestable, it is making whatever opinion you may hold, benchmark of neutrality; neutrality defined in your own terms.
Is losing a contradiction of the idea politics is about winning? No, of course not. Losing implies the existence of winning, and to point out someone’s loss is to concede that it was their intent to win, because it was necessary. You may win the war, but if you aren’t flying your colours by the end of it then it has all been for nothing. Nobody goes into politics to lose; what matters is that people don’t want to. Politics is a realm of contestation. If you have political desires but do not actively contest on behalf of them, then you are destined for disappointment and failure. If you don’t have political desires to contest on behalf of, you shouldn’t be in politics. The former is unaware of the nature of politics, whilst the latter reduces it to a conduit from which to extract things that, albeit are useful for achieving political end goals, are themselves not political (e.g. money, wealth, prestige); politics turns from something to be a part of to something be in. It is better to lose fighting for your ideals, than winning on the behalf of someone else.
The contradictory nature of politics is that it is both viewed as a private matter, something personal, and yet it is something which inherently concerns matters beyond just the self. The word politics comes from politiká: “the affairs of the cities”. The foundation of the City of Rome is encapsulated in story Romulus’ murder of his brother Remus, a story that summarises the ruthless nature of politics. However, as Machiavelli wrote of Romulus’ actions in The Discourses: “the end is good, it will always excuse the means; since it is he who does violence with intent to injure, not he who does it with the design to secure tranquillity, who merits blame. Such a person ought however to be so prudent and moderate as to avoid transmitting the absolute authority he acquires, as an inheritance to another; for as men are, by nature, more prone to evil than to good, a successor may turn to ambitious ends the power which his predecessor has used to promote worthy ends”.
Fukuyama, Huntington and The New World Order
In the aftermath of the Cold War, a 45-year ideological struggle between the two major superpowers, the USA and USSR, several political scholars have offered forecasts concerning the future of conflict and the geopolitical climate post-1991. Two men rose to dominate the debate, one encapsulating a liberal perspective and the other a realist one – and in the decades since, their ideas have come to form the foundations of modern international relations theory.
The first was the political scientist and economist Francis Fukuyama. A Cornell and Harvard alumnus, Fukuyama proposed his thesis in an essay titled ‘The End of History’ (1989), and later expanded on it in his book The End of History and the Last Man (1992). Essentially, he posits that with the collapse of the Soviet Union came the resolution of the battle of ideas, with liberal democracy and free trade having emerged as the unchallengeable winners.
Society, according to Fukuyama, had reached the end of its ideological evolution – global politics has, since the fall of the USSR, been witnessing ‘the universalisation of Western liberal democracy as the final form of human government’. Indeed, we’ve certainly seen a massive increase in liberal democracies over the past few decades, jumping from 35 in 1974, to 120 in 2013 (or 60% of states). Additionally, the broad adoption of free trade and capitalism can be seen as delivering benefits to the global economy, which had quadrupled since the late 1990s.
Even communist states, Fukuyama said, would adopt some elements of capitalism in order to be prosperous in a globalised world economy. For example, the late 1970s saw reformists (such as Chen Yun) dominating the Chinese Communist Party and, under Deng Xiaoping’s leadership, the socialist market economy was introduced in 1978. This opened up the country to foreign investment, allowed private individuals to establish their own businesses, and privatised agriculture – these monumental reforms have resulted in spectacular economic growth, with many forecasters predicting that China will overtake the US as the world’s largest economy by around 2028. We’ve seen further evidence of this turn away from communism in favour of capitalism and freedom: upon its founding, the Russian Federation explicitly rejected the ideology, and many former Eastern Bloc states have enthusiastically adopted liberal democracy, with many also having since joined the European Union.
Regarding the example of China, however, the suppression of freedoms and rights has also been a staple of the CCP’s rule, especially under the current leadership of Xi Jinping. This links to a broader and fairly major critique of Fukuyama’s thesis: the growth of authoritarianism across the globe. With Law and Justice in Poland, Jair Bolsonaro in Brazil, and Rodrigo Duterte in the Philippines (not to mention various military coups, including Turkey in 2016), liberal democracy is undeniably under threat, and clearly not the globally agreed-upon best system of government (this is particularly concerning as it applies to two major powers, China and Russia). Furthermore, 9/11 and the 7/7 bombings serve as pretty hallowing examples of an ideological clash between Western liberalism and Islamic fundamentalism – more broadly radical Islamism has emerged as an ideological challenger to both the West and to secular governments in the Middle East and North Africa.
The second was the academic and former political adviser Samuel P. Huntington. A seasoned expert in foreign policy (having served as the White House Coordinator of Security Planning for the National Security Council under Jimmy Carter), Huntington laid out essentially a counter-thesis to Fukuyama’s, which first took the form of a 1993 Foreign Affairs article, and then a book in 1996, The Clash of Civilisations and the Remaking of World Order. Conflicts in the past, Huntington argues, had been motivated by a desire primarily for territorial gain and geopolitical influence (e.g. colonial wars of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries were attempts to expand the economic spheres of influence of Western imperialist powers).
However, in the 21st Century, the primary source of global conflict will be cultural, not political or economic (and will be primarily between Western and non-Western civilisations). Thanks to globalisation and increasing interconnectedness, people will become more aware of their civilisational roots and of their differences with others – they will aim to entrench and protect these differences, rather than seek common ground with other civilisations.
The Clash of Civilisations identified 9 civilisations specifically: Western (USA, Western Europe, Australasia), Orthodox (Russia and the former USSR), Islamic (North Africa and the Middle East), African (Sub-Saharan Africa), Latin American (Central and South America), Sinic (most of China), Hindu (most of India), Japanese (Japan), and Buddhist (Tibert, Southeast Asia and Mongolia).
Huntington also highlighted the possible revival of religion, Islam in particular, as a major potential issue: it would come to represent a challenge to Western hegemony in terms of a rejection of Western values and institutions. His Foreign Affairs article featured the line ‘Islam has bloody borders’, suggesting that the Islamic civilisation tends to become violently embroiled in conflict with periphery civilisations – Huntington cites the conflicts in Sudan and Iraq as major examples.
It is clear, although still a touchy subject for politicians and policymakers, that Radical Islam poses a serious threat to the safety and stability of the Western world. Aside from aforementioned terror attacks, the rise of extremist fundamentalist groups such as the Taliban in Afghanistan and al-Shabaab in Somalia represents a larger opposition to Western values. However, Huntington’s failure to consider the deep divisions within the Islamic world (especially between Sunnis and Shias) is a major criticism of his argument. Additionally, many of the civilisations he identified show little interest in a clash with the West, mainly as it wouldn’t be in their economic interest to do so (such as India, Japan and Latin America, who are all very interdependent on Western powers).
The Clash of Civilisations thesis does, however, offer a number of steps that the West could take to prevent a potential clash. It should pursue greater political, economic and military integration, so their differences will be more difficult to exploit. Just last year we saw a clear example of this, in the form of AUKUS, the security pact between Australia, the UK and the US.
NATO and European Union membership should be expanded, with the aim of including former Soviet satellite states, to ensure they stay out of the Orthodox sphere of influence. Fortunately for the West, 2004 alone saw NATO admit Romania, Bulgaria, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Slovakia and Slovenia, followed in 2009 by Albania and Croatia. The military advancement of Islamic nations should be restrained, to ensure they don’t pose a serious threat to the West’s safety – a clear example of this is the 2015 Iran Nuclear Deal, reducing the nation’s stockpile of uranium to ensure it couldn’t become an anti-Western nuclear power.
Finally, the West must come to recognise that intervention in the affairs of other civilisations is ‘the single most dangerous source of instability and conflict in a multi-civilisational world’. This is a message that Western politicians have certainly not heeded, especially in regards to the Islamic world – troops were sent into Darfur in 2003, Afghanistan in 2001, Iraq in 2003 and Libya in 2011.
In his 2014 book Political Order and Political Decay: From the Industrial Revolution to the Globalization of Democracy, Fukuyama argues that his ‘End of History’ thesis remains ‘essentially correct’, despite himself recognising the current ‘decay’ of liberal democracy around the world. Both scholars’ predictions have, at periods of time in the post-Cold War era, looked very strong and, at other times, laughably incorrect and misguided. Both Fukuyama and Huntington still offer valuable insights into global dynamics between cultures, as well as the future of global tensions and conflict. However, both theses are undercut by the modern global landscape: democracy is currently on the decline, which undercuts Fukuyama, and civilisational identity remains limited, which undercuts Huntington. Regardless of who got it right, both men have undeniably pushed the debate surrounding the international order to new heights, and will no doubt be remembered as intellectual titans in decades to come.
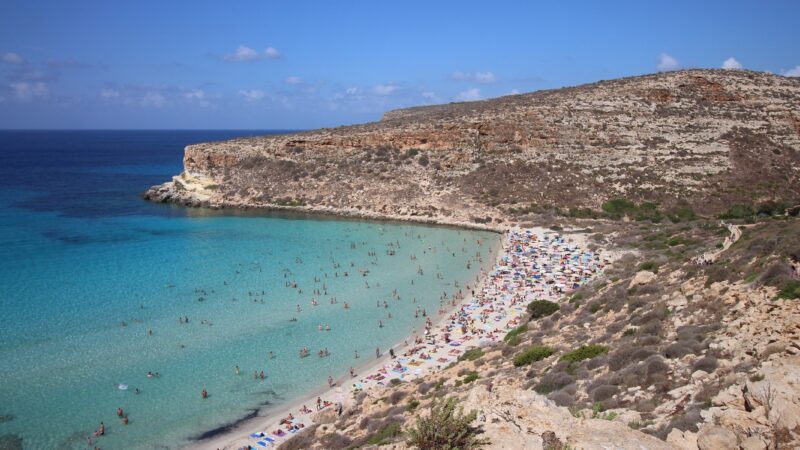
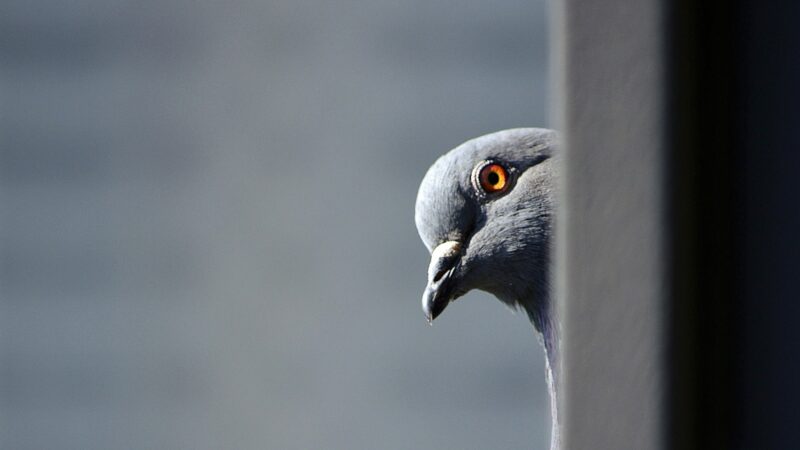













AUKUS and The Path Towards an Anglosphere Bloc
In 2023, the international order seems completely up-ended. Moscow has reverted to imperialism with its invasion of Ukraine, China’s regime is unrelenting in its designs towards Taiwan and Iran is edging closer to acquiring a nuclear weapon. Three decades on since the end of the Cold War and it would seem that Western intentions for a peaceful world now lie in tatters.
Yet we Westerners face our own set of problems. The UK remains more or less directionless on the world stage, its economy and reputation in freefall. On the continent, Hungary and Poland seem determined to stall EU centralisation efforts and the once ironclad relationship between Paris and Berlin appears to be weakening. Meanwhile, the US is mired in a state of total electoral chaos that one would normally associate with a banana republic. Perhaps the next leader of the free world will be running the show from a prison cell. At this point, who really knows?
Recent years have seen the UK, like the US, be radically transformed into a viscerally divided country. Although the polls seemingly indicate a majority now regret Brexit and would seek to reverse it, little thought has been given to how willing the British public would be to adopt the Euro or join Schengen – both of which Brussels would force upon us if we were to rejoin. Yet staunch Brexiteers haven’t exactly had much to offer us either. Since leaving, we’ve just about managed to re-secure the existing trade agreements we already had as an EU member and have joined the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) – which is predicted to grow the UK economy by just 0.08% over the next decade. Evidently, any future success we will enjoy as an isolated, declining power remains very unclear.
What is clear though is that the UK desperately needs bolder vision if it wants to drag itself out of the quagmire it is currently sinking into. It needs a new, invigorating national project that can unite its splintered political factions and galvanise support towards a stronger future. The UK has just exited one of the most successful blocs the world has seen, yet it may have already joined an even greater one – AUKUS.
AUKUS – an acronym of its member countries of Australia, the UK and the US – was formed in 2021 to act as a deterrent to Chinese aggression in the Indo-Pacific. As a military pact, its initial moves have been to assist Australia’s acquisition of nuclear-powered submarines as well as to step up information sharing on AI, quantum and hypersonic technologies.
Although originally hesitant about joining, New Zealand’s government has now expressed interest in becoming AUKUS’s fourth member, with Canada quickly following suit. The addition of these countries makes sense given that both have economic and geopolitical interests in the Pacific and equally view China as a threat. Furthermore, being members of the ‘Five-Eyes’ intelligence pact, neither would seek being shut out of any agreements involving information sharing.
However, their compatibility with AUKUS goes beyond military and security concerns. With a shared democratic ethos and a common system of governance, AUKUS represents not just a strategic pact, but also a values-based alliance uniting all of its members, including potential additions Canada and New Zealand. As such, the potential for AUKUS to welcome even broader collaboration seems apparent already.
Proposals for stronger ties between the five countries are nothing new. By far the most popular concept to be imagined has been ‘CANZUK’. Yet another acronym for its member states, this would involve a hypothetical trade and cooperation bloc comprising all aforementioned countries – with the notable exception of the US. Focusing strictly on expanding economic, security and foreign-policy collaboration, its proponents dismiss the idea of any political union. Crucially, free movement would be implemented, however – just not the kind we associate with Schengen. For it would bar anyone with a criminal record, an infectious disease or those considered to be a national security risk.
Its advocates certainly sell the CANZUK vision well. As they point out, with a population of at least 135 million and a combined GDP of over $6 trillion, CANZUK would be among the top four economic powers in the world. It would comprise an area of 18,187,210 km, making it larger than the Russian Federation. Moreover, with similar levels of development, the potential for the kind of one-sided migration occurring between poorer and affluent member states, as witnessed in the EU, would be minimised. It also helps that free-movement treaties are already in effect between some of these countries – notably the Trans-Tasman Travel Arrangement (TTTA) between Australia and New Zealand.
Yet for all its great potential, proponents have glossed over one major problem – trade. Whilst these countries combined make up a significant chunk of the global economy, commerce among them is minimal. As of last year, the UK was New Zealand’s ninth largest trading partner, Canada’s fifth and Australia’s eighteenth. Similarly, Canada ranks low on trade with Australia and New Zealand and vice versa. However, what they each have in common are strong trade links with the US – ranking anywhere from first to third largest trading partner among them. For this reason alone, an Anglosphere bloc without the US does not make sense economically.
This takes us neatly back to AUKUS – or more precisely, the need for its evolution. Embracing the aforementioned ideals of economic integration, foreign-policy coordination and the establishment of a common travel area would undoubtedly turbocharge AUKUS’s power and completely reshape global politics. The addition of Canada and New Zealand into the mix certainly aids this. AUKUS has already shown it is prepared to respond to a crisis, namely China. The looming threat of a Chinese-dominated century being the driving force behind a gradual transformation of AUKUS into an Anglosphere bloc should not be underestimated. Beijing’s potential to start to outpace the West economically, technologically and even militarily would naturally bring Australia, the UK, the US, Canada and New Zealand into each other’s arms.
Washington’s involvement would be vital for many reasons, including reducing the group’s dependency on trade with China, something that Australia has already declared it seeks to implement. Yet whilst the need for closer cooperation with a behemoth like the US is clear, it would be naïve to suggest that the US could afford to forgo such an arrangement. Indeed, the US needs the Anglosphere now more than ever. The initial reluctance of NATO members France and Germany to step up their support towards Ukraine and Macron’s comments about the EU distancing itself from American policy on China raises big concerns about Europe’s ability to commit to enforcing global security.
The EU itself is riddled by infighting over immigration, enlargement and the contentious issue of ‘ever-closer union’, casting doubt on its survivability. In short, America cannot rely on Europe in the long-term. The EU’s lethargic reaction to the Ukraine crisis underlines this. With multiple, often clashing, foreign-policy objectives among its member states, the prospect of a united Europe, ready to take on the geopolitical challenges of the 21st century, looks remote. If it took the continent as long as it did to pull together and reinforce its eastern frontier against invasion from its most immediate adversary, Russia, then little hope can be expected from future interventions either.
Contrast this with the response from the UK and the US. Both were quick to provide Ukraine with military support, whilst France and Germany sat back and hoped a diplomatic solution would prevail. For Berlin and Paris, their economic ties with Moscow greatly weakened their resolve for a more direct response, to the ire of the Anglosphere as well as fellow EU member Poland. The US, like the UK, now has to accept that its partners on the European continent do not always share its economic or geopolitical interests, nor are they fully capable of putting theirs aside for a common cause. Again, this further highlights the necessity of AUKUS for the US – and in many ways, it renders its expansion into an official bloc more of an inevitability than a hypothetical concept.
For the UK, the conclusion is self-evident. AUKUS is the only realistic option on the table for a directionless UK left out in the global cold. The alliance will continue to be crucial for the UK given our post-Brexit pivot to the Indo-Pacific. But the UK must push for something much larger than a military pact if it hopes to remain relevant in the 21st century. It must call for AUKUS’s expansion into a fully-fledged trade and cooperation bloc, encompassing the totality of the Anglosphere. There may well be push-back and the notion that this could happen overnight would be folly. Nevertheless, the UK will need to start somewhere if it wishes to shake off the Brexit blues. It must step up and begin to take charge of its destiny.
Dreams of a return to the EU are just that – dreams. The mere political unpalatability of having to surrender our currency and control over our borders makes a return to the EU simply incompatible with most British voters. There would be no chance of a rebate over the UK’s financial contributions either. We would need to be all in, or stay out. Nor should we presume that Brussels will be eager to welcome back a country that so openly defied it, for fear of sparking similar exits. We could expect similar reactions from member states such as France, which twice vetoed the UK’s application to join back in the 1960s, as well as Spain, which would no doubt force us into concessions on Gibraltar. The UK must now accept this new relationship with the continent and simply move on.
AUKUS provides the UK with a chance to reinvent its beleaguered image, both at home and abroad. It paves a way out of the tangled forest of confusion and division over our place in the world and heralds a return to a more optimistic and confident UK. The economic benefits it would bring, combined with the chance to rekindle ties with Australia, Canada and New Zealand, and repair our fractured ‘special relationship’ with the US, make it simply too good an opportunity to pass up.
With the EU, Russia and China now having all put their cards on the table, the need for an official Anglosphere bloc has never been more immediate. All that is missing now is the willpower to make it happen.
Photo Credit.